What is increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
What is increased intracranial pressure (ICP)? Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a rise in pressure around your brain. It may be due to an increase in the amount of fluid surrounding your brain.
How do you position a patient with increased ICP?
Body position for the patient with increased ICP. Head positioning for patient with increased ICP. Maintain the patient with increased ICP in the head-up position. What should you try to prevent in a patient with increased ICP?
What does it mean when your ICP is high?
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a rise in pressure around your brain. It may be due to an increase in the amount of fluid surrounding your brain. ... Symptoms of increased ICP in infants include those for adults, as well as some additional signs unique to babies under 12 months old.
Can increased ICP be treated?
Because anxiety can make increased ICP worse by raising your blood pressure, you may receive a sedative as well. Less common treatments for increased ICP include: Can increased ICP be prevented? You can’t prevent increased ICP, but you can prevent head injury. Always wear a helmet when you bike or play contact sports.

How does body position affect ICP?
It has been shown that ICP (i.e., CSF pressure in the ventricles) is reduced when moving from a supine to an upright position, whereas CSF pressure at the lumbar level of the spinal subarachnoid space increases, and it has been hypothesized that there exists a hydrostatic indifference point in the CSF system as well ( ...
Does prone position increase ICP?
Conclusions: The prone position can be used to improve the oxygenation as well as CPP in patients with traumatic brain injury or SAH. However, this method results in raised ICP, and should be used cautiously in patients with reduced intracranial compliance.
Does laying down increase ICP?
Pressures in the skull are higher when patients are lying down than when sitting or standing, and there is strong evidence that this difference between pressures when lying and sitting is higher in patients with a working shunt, and lower in patients without a shunt.
Does sitting increase ICP?
Effect of Position on ICP and PA in Patients Without Shunts Compared to the supine patients, those in the lumbar puncture position had higher ICP (mean difference 3.8 ± 4.2 mm Hg) and those in the sitting and standing positions had lower ICP (mean differences 8.6 ± 4.8 and 9.3 ± 4.6 mm Hg, respectively; Fig. 2).
Which position is used in head injury?
Patient positioning Elevating the head of the bed by 30% while maintaining a neutral spine alignment has been shown to reduce ICP without significantly changing cerebral blood flow. It also aids in promotion of venous drainage.
Is a supine position?
What is the supine position? 'Supine' means lying on the back with the face pointing upward. The supine position is common in certain practices, such as yoga and Pilates. Many people also adopt a supine position for sleeping.
What causes head pressure when lying down?
Causes of Headaches First, when you lie down, blood vessels that run through your head and your neck can become compressed, which temporarily restricts blood flow, causing headaches. Increased blood pressure on arteries from lying down can increase headache pain.
How do you manage raised ICP?
Medical options for treating elevated ICP include head of bed elevation, IV mannitol, hypertonic saline, transient hyperventilation, barbiturates, and, if ICP remains refractory, sedation, endotracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation, and neuromuscular paralysis.
What causes pressure in head when standing up?
The two most common causes of an orthostatic headache are a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and a condition called postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). In rarer cases, a positional headache may also be a result of several other conditions that affect the nervous system, connective tissue, and bones.
When individual is lying on side what will be pressure of CSF?
CSF pressure is usually measured while a person is lying in a horizontal recumbent position. Normal CSF pressure values, in that case, are around 15 cm H2O, and the pressure is the same along the spinal subarachnoid space and inside the cranium [1].
What are the late signs of raised ICP?
Late signs and symptoms include: deterioration of the level of consciousness (LOC) until the patient becomes comatose. decreased respiratory and pulse rates. increased blood pressure and temperature.
What are the late signs of raised ICP?
Changes in blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory pattern are usually late signs of raised ICP in clinical practice. These signs are related to brain stem distortion or ischaemia.
Can you suction a patient with ICP?
Conclusion. Changes in ICP induced by ETS in severe head-injured patients are significant. Suction passes should be limited to two to three per procedure. Repeated suctioning may increase ICP.
What is intracranial tension?
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult.
How is ICP measured?
Intracranial pressure is measured in two ways. One way is to place a small, hollow tube (catheter) into the fluid-filled space in the brain (ventricle). Other times, a small, hollow device (bolt) is placed through the skull into the space just between the skull and the brain.
What does increased ICP mean?
Increased ICP can also mean that your brain tissue itself is swelling, either from injury or from an illness such as epilepsy. Increased ICP can be the result of a brain injury, and it can also cause a brain injury. Increased ICP is a life-threatening condition. A person showing symptoms of increased ICP must get emergency medical help right away.
How to tell if ICP is increased?
nausea. vomiting. increased blood pressure. decreased mental abilities. confusion about time, and then location and people as the pressure worsens. double vision. pupils that don’t respond to changes in light.
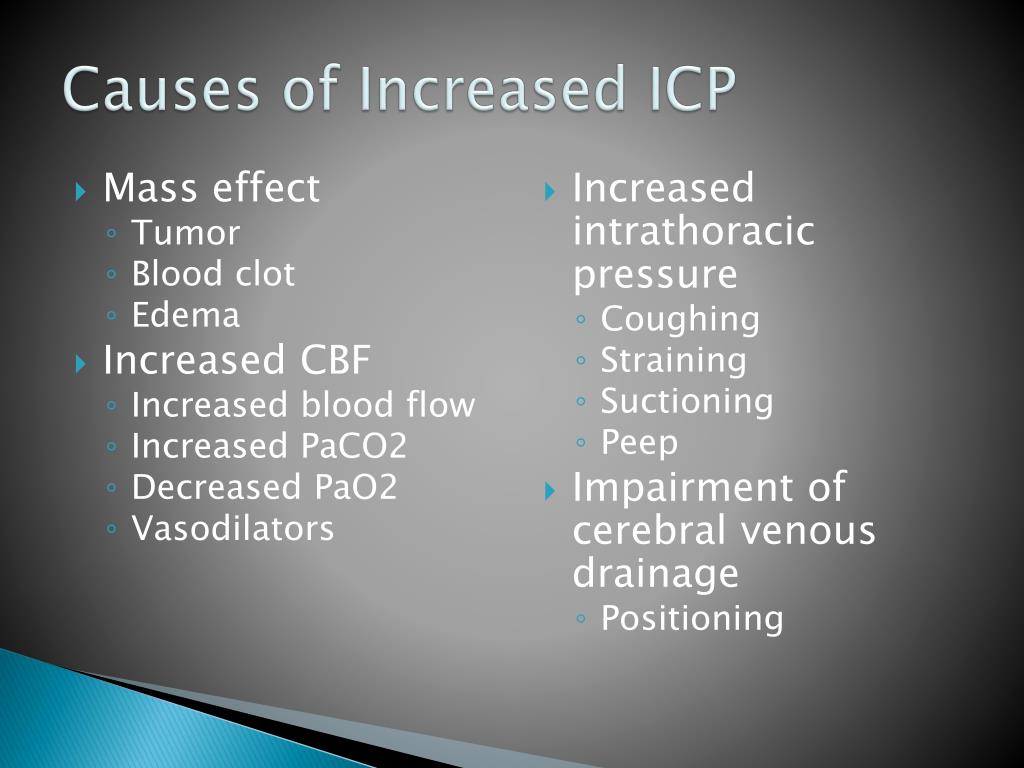
What causes increased ICP?
Other possible causes of increased ICP include: infections. tumors. stroke. aneurysm. epilepsy. seizures. hydrocephalus, which is an accumulation of spinal fluid in the brain cavities. hypertensive brain injury, which is when uncontrolled high blood pressure leads to bleeding in the brain .
How to check cerebrospinal fluid pressure?
They may also measure the pressure of your cerebrospinal fluid using a lumbar puncture, or spinal tap. Images of the brain from a CT or MRI scan may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Why is ICP increased in infants?
Increased ICP in infants can be the result of injury, such as falling off a bed, or it can be a sign of child abuse known as shaken baby syndrome, a condition in which a small child has been roughly handled to the point of brain injury.
What is increased intracranial pressure?
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is a rise in pressure around your brain. It may be due to an increase in the amount of fluid surrounding your brain. For example, there may be an increased amount of the cerebrospinal fluid that naturally cushions your brain or an increase in blood in the brain due to an injury or a ruptured tumor.
Can intracranial pressure cause brain damage?
Delayed treatment or failure to reduce intrac ranial pressure can cause temporary brain damage, permanent brain damage, long-term coma, or even death. The sooner you seek treatment to reduce pressure on your brain, the better the outcome. Last medically reviewed on July 12, 2017.
How to measure ICP?
The use of ultrasound to measure the diameter of the optic nerve sheath has been recently identified as a method to indicate raised ICP. This is usually measured 3 mm behind the globe with 2–3 measurements taken in each eye. The threshold for denoting elevated ICP usually ranges from 0.48 cm to 0.63 cm.
What should be included in an ICP evaluation?
The evaluation of increased ICP should include detailed history taking, physical examination, and ancillary studies.
What is intracranial hypertension?
Intracranial hypertension (IH) is a clinical condition that is associated with an elevation of the pressures within the cranium. The pressure in the cranial vault is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and is normally less than 20 mm Hg.
What causes increased intracranial pressure?
The causes of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) can be divided based on the intracerebral components causing elevated pressures: Increase in brain volume. Generalized swelling of the brain or cerebral edema from a variety of causes such as trauma, ischemia, hyperam monemia, uremic encephalopathy, and hyponatremia.
What is the pressure in the cranial vault?
The pressure in the cranial vault is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and is normally less than 20 mm Hg. The cranium is a rigid structure that contains three main components: brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood. Any increase in the volume of its contents will increase the pressure within the cranial vault.
Is hypertonic saline safe?
Three percent hypertonic saline is also commonly used to decrease cerebral edema and can be administered as a 5 ml/kg bolus or a continuous infusion, monitoring serum sodium levels closely. It is considered relatively safe while serum sodium is < than 160mEq/dl or serum osmolality is less than 340 mOsm. [12]
Does intracranial hypertension increase the risk of death?
Prognosis depends on the underlying etiology and severity of the presentation. Benign intracranial hypertension does not increase the risk of death rate by itself; rather, the death rate is increased by morbid obesity which is a common association with benign intracranial hypertension.
What causes ICP?
Too much cerebrospinal fluid ( the fluid around your brain and spinal cord)
How is ICP treated?
Increased intracranial pressure is an emergency. Treatment might include:
How do you know if you have an ICP?
These are the most common symptoms of an ICP: Headache. Blurred vision. Feeling less alert than usual. Vomiting. Changes in your behavior. Weakness or problems with moving or talking. Lack of energy or sleepiness. The symptoms of ICP may look like other conditions or medical problems.
Is intracranial pressure dangerous?
Key points about increased intracranial pressure (ICP) ICP is a dangerous condition. It is an emergency and requires immediate medical attention. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding in the brain, a tumor, stroke, aneurysm, high blood pressure, brain infection, etc. can cause a headache and other symptoms.
Can ICP be prevented?
You can reduce your risk of certain underlying conditions that may lead to ICP such as high blood pressure, stroke or infection. If you have any of the symptoms, get medical attention immediately.
What level of ICP monitoring is recommended?
ICP monitoring is also recommended (Level III recommendations) in: [8]
What monitors are used for ICP?
Currently, intraventricular monitor with the aid of ventriculostomy or the use of intraparenchymal strain gauge or fiber optic monitors is the recommendation for ICP monitoring. So appropriate monitoring devices should be available. There needs to be utmost care for strict adherence to aseptic conditions during these procedures. There also is paramount importance of implementing algorithmic management guidelines in all patients with invasive ICP monitors for safeguarding all monitor sets.
What is the normal intracranial pressure?
The normal intracranial pressure (ICP) ranges within 7 to 15 mm Hg while in the vertical position, it does not exceed −15 mm Hg. Overnight sleep monitoring is considered the “gold standard” in conscious patients. [1]
Which is more accurate, a strain gauge or fiber optic based system inserted into the ventricles or brain?
Strain gauge or fiber optic based systems inserted into the ventricles or brain parenchymas are more accurate compared to fluid-coupled or pneumatic devices.
Can a slit ventricle complicate ICP?
Difficulties in catheter placement in cases of severe brain edema with slit ventricles can complicate intraventricular monitoring of ICP.
Who should receive a thorough explanation regarding the indication for the procedure and the risks involved before the procedure?
The patient and next of kin/relatives should receive a thorough explanation regarding the indication for the procedure and the risks involved before the procedure, and written consent obtained.
Is ICP reading equivocal?
Complications. An underlying assumption is that an ICP reading at one point is equivocal, and the mirror reflects the global pressure throughout the brain. However, it is confounded by the pressure gradient within the ventricular system as well as the parenchyma brain interface.
