Carnitine: What are the benefits and risks?
- Requirements The liver and kidney usually produce enough carnitine in the human body, so topping up with food or supplements is not necessary. ...
- Food sources Foods that provide carnitine are mainly animal products, dairy, poultry, and meat. ...
- As a therapy Carnitine is said to have many therapeutic properties that may be useful in treating a range of conditions and illnesses. ...
- For athletic performance ...
What forms of L-carnitine are present in the body?
The form present in the body is l -carnitine, which is also the form present in food. Food sources rich in l -carnitine are animal products, particularly beef and pork. Red meats tend to have higher levels of l -carnitine.
What is the role of carnitine in the body?
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, and also participates in removing products of metabolism from cells.
What foods are high in carnitine?
Animal products like meat, fish, poultry, and milk are the best sources. In general, the redder the meat, the higher its carnitine content. Dairy products contain carnitine primarily in the whey fraction [1,3,5]. The carnitine content of several foods is listed in Table 1.
What is the chemical name for carnitine?
Carnitine, derived from an amino acid, is found in nearly all cells of the body. Its name is derived from the Latin carnus or flesh, as the compound was isolated from meat. Carnitine is the generic term for a number of compounds that include L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine, and propionyl-L-carnitine [ 1, 2 ].
See more
Where is carnitine produced?
Mitochondrial oxidation of long-chain fatty acids L-Carnitine is synthesized primarily in the liver but also in the kidneys and then transported to other tissues. It is most concentrated in tissues that use fatty acids as their primary fuel, such as skeletal and cardiac muscle.
How is carnitine formed?
Carnitine, a branched non-essential amino acid, is synthesized from the essential amino acids lysine and methionine.
What products contain carnitine?
Red meat has the highest levels. A 4-ounce beef steak has an estimated 56 mg to 162 mg of carnitine. Carnitine is also found in smaller amounts in chicken, milk and dairy products, fish, beans, and avocado. Vegans tend to get less carnitine from foods, but their bodies usually produce enough anyway.
How do you get carnitine deficiency?
What causes carnitine deficiency? Carnitine deficiency may occur in response to a genetic mutation (gene defect) in the protein responsible for bringing carnitine into the cell (primary carnitine deficiency), or it may occur secondary to other metabolic diseases (secondary carnitine deficiency).
Can carnitine increase anxiety?
Our data suggest that chronic ALCAR administration may produce an inverted U-shaped curve of dose-dependent changes in anxiety-like behaviour.
What does carnitine do in the body?
Carnitine is a substance that helps the body turn fat into energy. Your body makes it in the liver and kidneys and stores it in the skeletal muscles, heart, brain, and sperm. Usually, your body can make all the carnitine it needs.
What food is highest in carnitine?
meatAnimal products like meat, fish, poultry, and milk are the best sources. In general, the redder the meat, the higher its carnitine content. Dairy products contain carnitine primarily in the whey fraction [1,3,5].
Do eggs have carnitine?
The main dietary sources of choline and carnitine are red meat, poultry, fish, dairy products and eggs (yolks).
Is carnitine naturally produced?
The liver and kidney usually produce enough carnitine in the human body, so topping up with food or supplements is not necessary.
What happens if carnitine is low?
Carnitine deficiency may cause muscle necrosis, myoglobinuria, lipid-storage myopathy, hypoglycemia, fatty liver, and hyperammonemia with muscle aches, fatigue, confusion, and cardiomyopathy.
What vegetables or fruits have carnitine?
The main food sources for carnitine are red meat and full-fat dairy products. It is also found in fish, poultry, tempeh, wheat, asparagus, avocados and peanut butter.
Does exercise deplete carnitine?
Indeed, exercise itself leads to l-carnitine depletion in the muscle [29].
Is carnitine an egg?
The main dietary sources of choline and carnitine are red meat, poultry, fish, dairy products and eggs (yolks).
Is carnitine synthesized in the brain?
Although carnitine can be obtained in the diet and synthesized in kidney, liver and brain, it is considered a 'conditionally essential' nutrient for humans under specific circumstances when intracellular levels are low (e.g. premature infants, elderly patients, diabetes and genetic conditions resulting in primary or ...
How does the body make acetyl L carnitine?
Acetyl-carnitine is a substance natural to the body. It is readily formed in cells by the enzymatic addition of an acetyl group to carnitine. Carnitine, also natural to the body, is a modified version of the amino acid lysine.
What is the most common form of carnitine?
L-carnitine is a more common form of carnitine, present in the body and many supplements. Other forms of carnitine include: Acetyl L-carnitine: This form, sometimes known as ALCAR, also plays a role in metabolism.
Where does carnitine come from?
Derived from amino acids, carnitine was first extracted from meat extracts in 1905, leading to its name from Latin, " caro/carnis " or flesh. Some individuals with genetic or medical disorders (such as preterm infants) cannot make enough carnitine, requiring dietary supplementation.
What is the second reaction of acyl-coa?
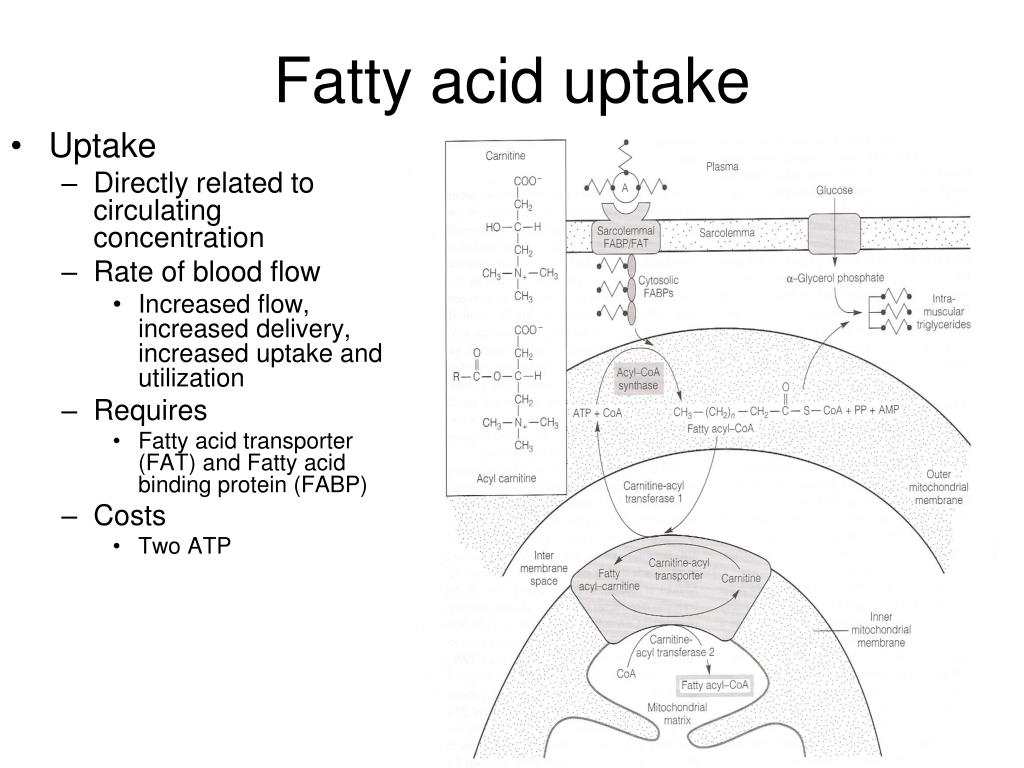
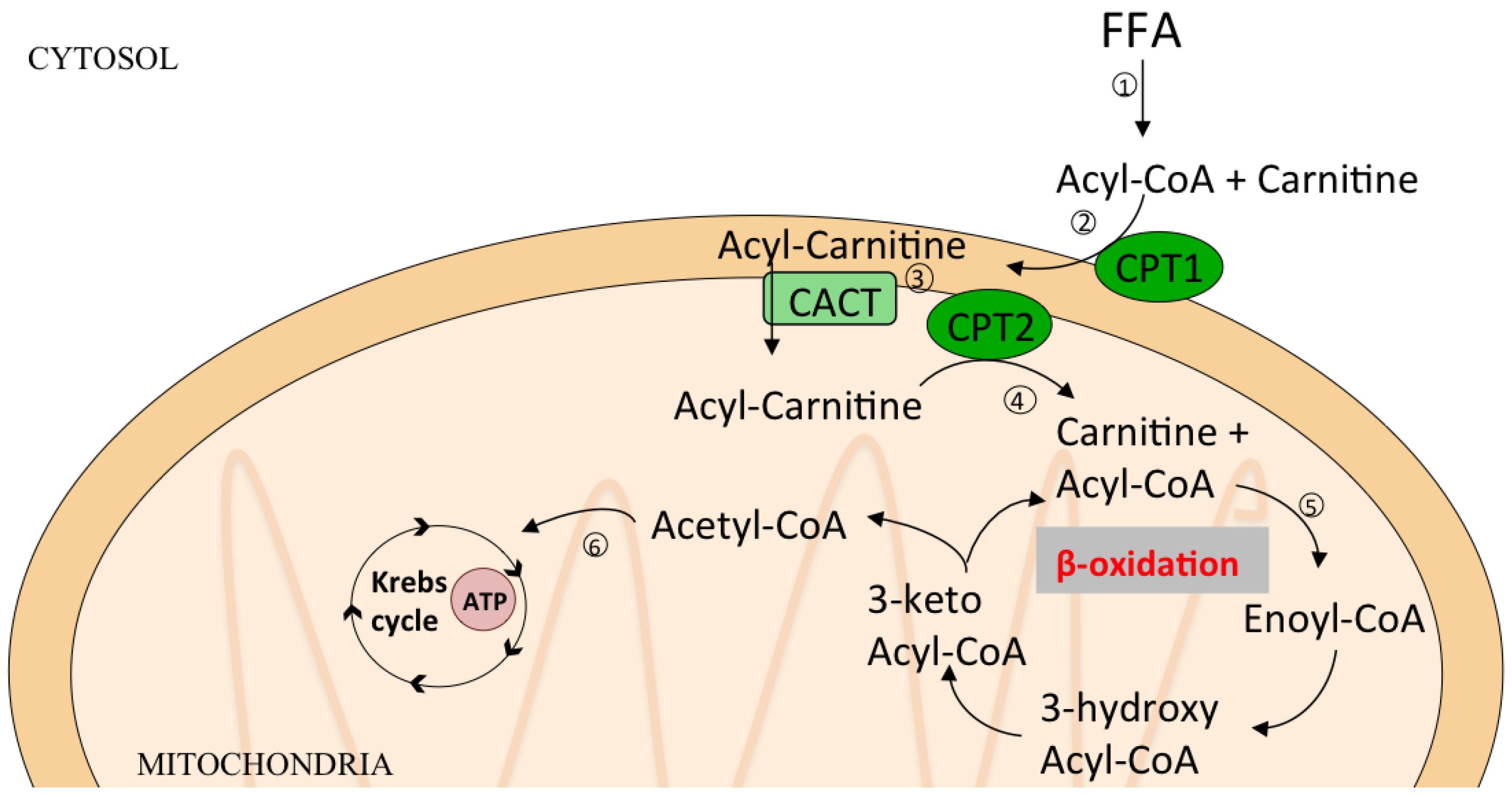
In the second reaction, acyl-CoA is transiently attached to the hydroxyl group of carnitine to form fatty acyl–carnitine. This transesterification is catalyzed by an enzyme found in the outer membrane of the mitochondria known as carnitine acyltransferase 1 (also called carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1, CPT1).
What is the role of carnitine in the body?
In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, and also participates in removing products of metabolism from cells. Given its key metabolic roles, carnitine is concentrated in tissues like skeletal and cardiac muscle that metabolize fatty acids as an energy source. Healthy individuals, including strict vegetarians, synthesize enough L-carnitine in vivo to not require supplementation.
What is the role of the carnitine shuttle in muscle contraction?
During vigorous muscle contraction or during fasting, ATP concentration decreases and AMP concentration increases leading to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK phosphorylates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which normally catalyzes malonyl-CoA synthesis. This phosphorylation inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which in turn lowers the concentration of malonyl-CoA. Lower levels of malonyl-CoA disinhibits carnitine acyltransferase 1, allowing fatty acid import to the mitochondria, ultimately replenishing the supply of ATP.
How do humans synthesize carnitine?
Humans synthesize carnitine from the substrate TML (6- N -trimethyllysine), which is in turn derived from the methylation of the amino acid lysine. TML is then hydroxylated into hydroxytrimethyllysine (HTML) by trimethyllysine dioxygenase (TMLD), requiring the presence of ascorbic acid and iron. HTML is then cleaved by HTML aldolase (a pyridoxal phosphate requiring enzyme), yielding 4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde (TMABA) and glycine. TMABA is then dehydrogenated into gamma-butyrobetaine in an NAD + -dependent reaction, catalyzed by TMABA dehydrogenase. Gamma-butyrobetaine is then hydroxylated by gamma butyrobetaine hydroxylase (a zinc binding enzyme) into l -carnitine, requiring iron in the form of Fe 2+.
How much carnitine does a person produce in a day?
As an example of normal synthesis, a 70 kilograms (150 lb) person would produce 11–34 mg of carnitine per day. Adults eating mixed diets of red meat and other animal products ingest some 60–180 mg of carnitine per day, while vegans consume about 10–12 mg per day.
How does the liver make triglycerides?
The liver starts actively making triglycerides from excess glucose when it is supplied with glucose that cannot be oxidized or stored as glycogen. This increases the concentration of malonyl-CoA, the first intermediate in fatty acid synthesis, leading to the inhibition of carnitine acyltransferase 1, thereby preventing fatty acid entry into the mitochondrial matrix for β oxidation. This inhibition prevents fatty acid breakdown while synthesis occurs.
How much carnitine is in a vegan diet?
Non-animal sources include whole-wheat bread and asparagus. of carnitine per day. A vegan diet normally provides between 10 and 12mg per day. of dietary carnitine into the bloodstream, but only 14 to 18 percent when it is taken as a supplement.
Why is carnitine important?
For athletic performance. Risks. Carnitine is present in almost every cell in the body. It plays a crucial role in energy production, as it is responsible for transporting fatty acids to the mitochondria. Mitochondria exist inside every cell in the body. They produce the energy that cells need to function.
What are the conditions that carnitine is used for?
Health conditions that carnitine may be used to treat include heart failure or heart attack, angina, and diabetic neuropathy.
What is the function of carnitine?
Carnitine has two functions. A part of carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria. They are burned there, or oxidized, to produce energy. Another part transports waste and toxic compounds out of the mitochondria, and this prevents unwanted substances from building up.
Why do people take carnitine?
The University of Maryland Medical Center (UMM) note that people sometimes take carnitine for weight loss, Peyronie disease, kidney disease, and hyperthyroidism, which is an overactive thyroid.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria exist inside every cell in the body. They produce the energy that cells need to function. The body creates carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine. Scientists first isolated it from meat. As a result, takes its name from the Latin word for meat.
Why do some people produce too little carnitine?
There is no recommended daily intake. However, genetic or medical reasons can cause some people produce too little. Primary systemic carnitine deficiency can happen when the protein that is responsible for bringing carnitine into cells undergoes a genetic change. This deficiency causes problems with processing food.
What is the best pork to eat?
On average, cooked pork contains 24 milligrams of L-carnitine in every 3 ounces. Choose low-fat pork that conforms to the same lean meat guidelines as beef. Good choices include tenderloin, sirloin roast, boneless top loin chops or roast, rib chops or center loin chops. Avoid breaded or fried pork in favor of cuts that are roasted, broiled, grilled or braised. Pork is considered a red meat. A diet high in red meat increases your risk of chronic medical conditions like cancer or heart disease, reported a study published in 2012 in the "Archives of Internal Medicine." Eat pork only occasionally and avoid processed pork products like ham or sausage as much as possible.
What is the role of carnitine in energy metabolism?
Kerns studied English literature and neurology at UC Davis. Carnitine aids in energy metabolism and removes toxic compounds from cells. Most healthy people synthesize all the carnitine they need from the amino acids methionine and lysine, but some medical conditions and drugs may lower the concentration in your body.
What fish has the highest carnitine content?
All fish and shellfish contain some carnitine, but cod has the highest concentration of any seafood. A 4-ounce serving supplies between 4 and 7 milligrams. The Monterey Bay Aquarium Seafood Watch suggests choosing handline-caught Atlantic cod from the northeast Arctic or Iceland or Pacific cod captured by trap, handline or bottom longline. Cod of these types are harvested in an environmentally friendly manner and have a low risk of contamination. Pregnant or nursing women and women who plan on becoming pregnant should limit their total seafood consumption to 12 ounces of low-mercury fish, including cod, per week.
How much carnitine is in beef?
Beef is one of the richest natural sources of carnitine, with a 3-ounce serving of steak supplying approximately 81 milligrams of the compound and ground beef containing about 80 milligrams. To limit your intake of fat and cholesterol, choose lean cuts that have 95 milligrams or less of cholesterol, 4.5 grams or less of saturated fat and fewer than 10 grams of total fat in every 3-ounce serving. The Harvard School of Public Health recommends consuming no more than 3 ounces of red meat like beef per week.
How much carnitine is in chicken breast?
Chicken breasts aren't only high in protein, low in fat and cholesterol and a good source of vitamins and minerals, they're high in carnitine, with 3 to 5 milligrams in every 4-ounce serving of cooked meat.
Is pork considered a red meat?
Avoid breaded or fried pork in favor of cuts that are roasted, broiled, grilled or braised. Pork is considered a red meat. A diet high in red meat increases your risk of chronic medical conditions like cancer or heart disease, reported a study published in 2012 in the "Archives of Internal Medicine.".
Is carnitine a good source of carnitine?
Most animal-based foods are good sources of L-carnitine, the biologically active form of carnitine. If you are a vegan or you're concerned about your level of carnitine, talk to your doctor.
What is Carnitine?
Carnitine is classified as an amino acid, although it is not an amino acid in the classic sense. Amino acids are generally used by the body for protein synthesis and/or as a neurotransmitter.
Where does Carnitine come from?
Natural carnitine is found primarily in red meat, so vegetarians may need to supplement to ensure healthy levels in their bodies.
What are the different types of carnitine?
Here are several other types of carnitine: 1 D-carnitine: This inactive form may cause a carnitine deficiency in your body by inhibiting the absorption of other, more useful forms ( 7#N#Trusted Source#N#, 8#N#Trusted Source#N#). 2 Acetyl-L-carnitine: Often called ALCAR, this is possibly the most effective form for your brain. Studies suggest that it may benefit people with neurodegenerative diseases ( 9#N#Trusted Source#N#). 3 Propionyl-L-carnitine: This form is well-suited for circulatory issues, such as peripheral vascular disease and high blood pressure. It may boost production of nitric oxide, which improves blood flow ( 10#N#Trusted Source#N#, 11#N#Trusted Source#N#). 4 L-carnitine L-tartrate: This is commonly added to sports supplements due to its rapid absorption rate. It may aid muscle soreness and recovery in exercise ( 12#N#Trusted Source#N#, 13#N#Trusted Source#N#, 14#N#Trusted Source#N#).
What is the role of L-carnitine in the body?
L-carnitine is a nutrient and dietary supplement. It plays a crucial role in the production of energy by transporting fatty acids into your cells’ mitochondria ( 1. Trusted Source.
How long does it take for L-carnitine to appear?
L-carnitine’s benefits may be indirect and take weeks or months to appear. This differs from supplements like caffeine or creatine, which can directly enhance sports performance. L-carnitine may benefit: Recovery: May improve exercise recovery ( 46.
How much L-carnitine is needed for exercise?
L-carnitine L-tartrate: This form is most effective for exercise performance. Doses vary from 1,000–4,000 mg per day.
What is the mitochondria?
Trusted Source. ). The mitochondria act as engines within your cells, burning these fats to create usable energy. Your body can produce L-carnitine out of the amino acids lysine and methionine. For your body to produce it in sufficient amounts, you also need plenty of vitamin C ( 4. Trusted Source. ).
How much L-carnitine is absorbed?
Interestingly, food sources of L-carnitine have a greater absorption rate than supplements. According to one study, 57–84% of L-carnitine is absorbed when it’s consumed from food, compared to only 14–18% when taken as a supplement ( 61. Trusted Source.
What is L-carnitine?
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative that’s often taken as a supplement.
What is the purpose of L-carnitine?
Carnitine helps the body break down fatty acids and turn them into energy to power the cells. L-carnitine is a conditionally essential nutrient, meaning that the body can generally make enough of it, but, in some cases, a person may have to get the compound from food or oral supplements if they cannot make enough.
How much carnitine is in a day?
Trusted Source. , adults who eat a mixed diet that includes red meat and other animal products get about 60–180 milligrams (mg) of carnitine per day. People who avoid animal products, such as those following a vegan diet, may get roughly 10–12 mg from their diet.
What organs produce L-carnitine?
In the body, the liver and kidneys create L-carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine. The kidneys can also store L-carnitine for later use and eliminate the excess through the urine stream.
What causes L-carnitine deficiency?
Kidney or liver disease. As the kidneys and liver help create and use L-carnitine, disease in these organs or organ failure may lead to L-carnitine deficiency. Doctors may recommend L-carnitine supplementation in these cases to support the function of the kidneys and liver. and prevent deficiency.
What is L-carnitine?
Side effects. How and when to take. Dosage. Summary. L-carnitine, also known as levocarnitine, is a naturally occurring amino acid structure that the body produces. People can also get it from their diet or take it in the form of an oral supplement.
What is the most common form of carnitine?
L-carnitine is a more common form of carnitine, present in the body and many supplements. Other forms of carnitine include: Acetyl L-carnitine: This form, sometimes known as ALCAR, also plays a role in metabolism. It possesses neuroprotective properties that may help protect the nervous system.
What is the main function of L-carnitine?
, helping break down fatty acids for use as energy, keeps the body’s cells powered and working efficiently. L-carnitine also has a secondary function of helping remove some waste products from the cells to prevent them from accumulating and causing problems .
How long does L-carnitine help with metabolic syndrome?
Early research shows that L-carnitine given intravenously (by IV) daily for 7 days increases weight loss and reduces waist circumference in people with metabolic syndrome.
How long does L-carnitin help with liver disease?
Reduced brain function in people with advanced liver disease (hepatic encephalopathy). Early research shows that taking L-carnitine daily for 60-90 days reduces ammonia levels and improves brain function in people with declining brain function related to severe liver disease.
What is the FDA's recommendation for L-carnitine?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved L-carnitine for the treatment and prevention of L-carnitine deficiency in people with serious kidney disease who are undergoing hemodialysis. L-carnitine deficiency. The FDA has approved L-carnitine for treating L-carnitine deficiency caused by certain genetic diseases.
How long does it take for L-carnitine to help with muscle soreness?
Muscle soreness caused by exercise. Early research shows that taking L-carnitine helps to reduce muscle soreness and muscle damage in the first four days after exercise. Fatigue. Early research shows that taking L-carnitine daily for 8 days does not reduce fatigue in healthy people.
What is the chemical that converts fat to energy?
Overview. L-carnitine is a chemical similar to an amino acid that is produced in the body. L-carnitine helps the body turn fat into energy. The body can convert L-carnitine to other chemicals called acetyl-L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine.
What is the purpose of the CONDITIONS OF USE AND IMPORTANT INFORMATION?
CONDITIONS OF USE AND IMPORTANT INFORMATION: This information is meant to supplement, not replace advice from your doctor or healthcare provider and is not meant to cover all possible uses, precautions, interactions or adverse effects. This information may not fit your specific health circumstances.
Can you take L-carnitine with D-carnitine?
It can also cause the urine, breath, and sweat to have a "fishy" odor. Avoid using D-carnitine and DL-carnitine. These forms of carnitine might block the effects of L-carnitine and cause symptoms that resemble L-carnitine deficiency.
What does carnitine do to build muscle?
Often incorrectly labeled as an amino acid, carnitine is often conflated with muscle-building supplements. Carnitine does support muscle building goals, but it in an indirect manner and it starts with the fat burning.
What does carnitine do for hearth health?
Again, we’re headed back to the fat metabolism. The heart prefers fat over carbohydrate for energy. Here’s how Harvard Health explains it: “That’s fine in a healthy heart. But it can be a problem when a narrowed coronary artery limits blood flow to part of the heart because it takes more oxygen to burn fat than it does to burn sugar.”
How does fat transform into energy?
Your body needs nutrients for energy. One of those nutrients is fat. But, fat can’t just transform into energy by wishing it from your digestive tract. It needs to get to the cells — more specifically to the mitochondria — to transform into energy. And the only way it can get there is if carnitine carries it and drops it off. In its simplest explanation, that’s what carnitine does: It transports fats into the mitochondria where they burn for fuel. This process supports your body in numerous important ways, including body composition, athletic performance, and heart and brain health.
What does carnitine do to the body?
This is literally what carnitine does. It transports fats to be burned in the fat furnace that is the mitochondria. Just to be clear, this does not mean that it takes visceral fat and torches it. Having optimal carnitine levels ensures that you are getting the most energy out of the fats you eat, and that your body is equipped to use stored fat for fuel, if necessary.
Why is it important to have more energy in the brain?
More energy for brain cells is more important than just being alert and focused. Cells need energy to survive. When a cell runs out of energy, it dies. And brain cells don’t resurrect themselves often. This compound also helps the brain use alternative energy sources. The brain prefers glucose for fuel, but when glucose levels are lower (like between meals) Acetyl L-Carnitine helps the brain draw energy from fats and ketones.1
Why is carnitine used in weight loss?
Because of the likelihood that many people with excess body fat do not have sufficient amounts of carnitine to accommodate the consumption of dietary fats, carnitine is often used as a supplement to support weight loss efforts.
What are the essential nutrients for carnitine production?
Among these critical nutrients are the amino acids lysine and methionine; iron; and the vitamins B3, B6, and C. If you don’t have adequate intake of these nutrients — above the recommended daily allowance that only provides enough to avoid the problems associated with deficiency — you’re not going to have enough of the raw materials necessary to produce carnitine.
Who is at risk for carnitine deficiency?
The primary condition is passed down from parents to children. A child needs to get an abnormal copy of the gene from both parents.
How is carnitine deficiency diagnosed?
The condition may be diagnosed by a neurologist or geneticist. An infant may be diagnosed through standard newborn screening tests.
What are possible complications of carnitine deficiency?
Heart weakness is a serious possible complication. A weakened heart may not be able to pump blood as well. This can lead to symptoms such as swelling and shortness of breath. Untreated heart weakness may lead to death early in life. Fortunately, heart problems respond very well to treatment with L-carnitine. Your healthcare provider may want to continue to monitor your heart for signs of weakness. Heart problems may be the first symptom of carnitine deficiency.
What causes carnitine to decrease?
The primary condition is caused by an abnormal gene. A variety of health conditions can cause the secondary condition. These decrease the amount of carnitine in the body. They may do this by increasing the amount sent out in urine. Or, they may cause the body to absorb less from food.
What causes low carnitine levels in muscle?
There are 2 types of carnitine deficiency: Primary carnitine deficiency. This is a rare condition caused by an abnormal gene. The gene causes a problem with a substance that carries carnitine inside cells from the blood. In some cases, the condition only leads to low carnitine levels in muscle.
How long does it take for carnitine deficiency to show?
Children with primary carnitine deficiency tend to show symptoms within the first few years of life. But in some cases, symptoms may start as an adult. Symptoms can happen a bit differently in each person. You may have no symptoms, or your symptoms may be mild to severe.
Why is carnitine important?
It plays an important role in getting fatty acids into cells to use for energy. Carnitine is especially important for certain cells, such as muscle cells. With carnitine deficiency, cells that rely on fatty acids for energy may start to work poorly.
