
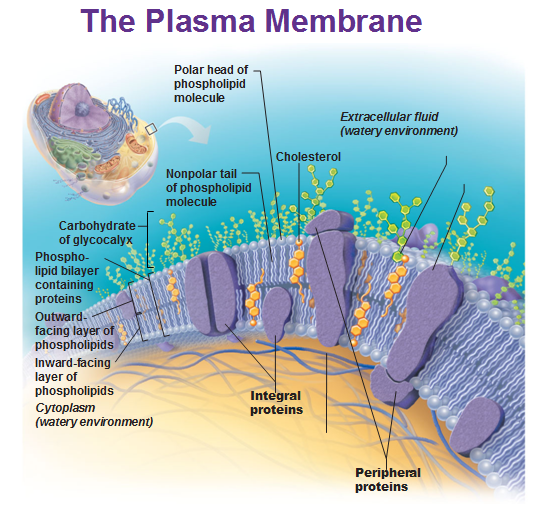
The structure of the plasma membrane
| Gene | Description | Average nTPM |
| AP2M1 | Adaptor related protein complex 2 subuni ... | 471 |
| MSN | Moesin | 380 |
| GNB2 | G protein subunit beta 2 | 264 |
| CD9 | CD9 molecule | 248 |
What are proteins embedded in the plasma membrane called?
What proteins are embedded in the plasma membrane? Integral membrane proteins, also called intrinsic proteins, have one or more segments that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Most integral proteins contain residues with hydrophobic side chains that interact with fatty acyl groups of the membrane phospholipids, thus anchoring the protein to the membrane.
What are the 6 types of membrane proteins?
- Some of the most important types of
- membrane proteins are as follows:
- 1. Peripheral (Extrinsic) Proteins 2. ...
- (Intrinsic) Proteins 3. Asymmetric
- Distribution of Membrane Proteins 4.
- Mobility of Membrane Proteins 5.
- Enzymatic Properties of Membrane Proteins
- 6. ...
- Peripheral or extrinsic membrane proteins
- membrane and are more readily removed
Does plasma membrane produce proteins?
Proteins make up the second major component of plasma membranes. Integral proteins are, as their name suggests, integrated completely into the membrane structure. In fact, their hydrophobic membrane-spanning regions interact with the hydrophobic region of the the phospholipid bilayer.
What are 3 types of plasma proteins?
Types of Plasma Proteins. The three major fractions of plasma proteins are known as Albumin, globulin, and Fibrinogen. On a finer resolution by electrophoresis, these fractions are separated as follows. Albumin – 55.2%. α1-Globulin – 5.3% (α1-Antitrypsin, TBG, Transcortin, etc) α2-Globulin – 8.6% (Haptoglobulin, ceruloplasmin, α2 ...
What are the 3 proteins in the cell membrane?
Based on their structure, there are main three types of membrane proteins: the first one is integral membrane protein that is permanently anchored or part of the membrane, the second type is peripheral membrane protein that is only temporarily attached to the lipid bilayer or to other integral proteins, and the third ...
What are the 4 types of membrane proteins?
Integral proteins come in different types, such as monotopic, bitopic, polytopic, lipid-anchored proteins, or transmembrane proteins. Monotopic integral proteins are only attached to one of the cell's two leaflets. Bitopic integral proteins are transmembrane proteins that can span lipid bilayers once.
Where are proteins found in the plasma membrane?
The overall surfaces of membrane proteins are mosaics, with patches of hydrophobic amino acids where the proteins contact lipids in the membrane bilayer and patches of hydrophilic amino acids on the surfaces that extend into the water-based cytoplasm.
Why are there proteins in the plasma membrane?
While membrane lipids form the basic structure of the lipid bilayer, the active functions of the membrane are dependent on the proteins. Cell adhesion, energy transduction, signaling, cell recognition and transport are just some of the important biological processes carried out by membrane proteins.
What are the 6 membrane proteins?
6 Important Types of Membrane Proteins (With Diagram)Peripheral (Extrinsic) Proteins:Integral (Intrinsic) Proteins:Integral Proteins That Span the Membrane:Asymmetric Distribution of Membrane Proteins:Mobility of Membrane Proteins:Enzymatic Properties of Membrane Proteins:Ectoenzymes and Endoenzymes:More items...
What are some examples of membrane proteins?
Examples of membrane proteins include ion channels, receptor proteins, and proteins that allow cells to connect to each other.
What is plasma membrane made up of?
With few exceptions, cellular membranes — including plasma membranes and internal membranes — are made of glycerophospholipids, molecules composed of glycerol, a phosphate group, and two fatty acid chains. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule that functions as the backbone of these membrane lipids.
What are the protein and lipid constituents of plasma membrane?
The model describes plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components which includes proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids, and carbohydrates; it imparts a fluid character on the membrane. Thickness of the membrane is in the range of 5-10nm.
Where are proteins found in the cell membrane quizlet?
Membrane proteins are important for transporting substances across the cell membrane. Peripheral proteins can be found on either side of the lipid bilayer: inside the cell or outside the cell.
What are the three types of proteins?
Proteins are the basic component of living cells. They are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and one or more chains of amino acids. The three structures of proteins are fibrous, globular and membrane, which can also be broken down by each protein's function.
What are the two types of membrane proteins?
Membrane ProteinsIntegral proteins are permanently attached to the membrane and are typically transmembrane (they span across the bilayer)Peripheral proteins are temporarily attached by non-covalent interactions and associate with one surface of the membrane.
What is a Type 2 membrane protein?
2. Type II membrane protein: This single-pass transmem- brane protein has an extracellular (or luminal) C-terminus and cytoplasmic N-terminus for a cell (or organelle) membrane (Fig. 1b). 3. Multipass transmembrane proteins: In type I and II membrane proteins, the polypeptide crosses the lipid bilayer only once (Fig.
What type of membrane proteins are water filled?
Some intergral membrane proteins use β-barrels to cross the membrane. These structures are typically large and form water filled channels. Extrinsic or peripheral membrane proteins associate loosely with the hydrophilic surfaces of the lipid bilayer or intrinsic membrane proteins. They form weak hydrophobic, electrostatic or non-covalent bonds, ...
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
What types of proteins are found in the plasma membrane? While membrane lipids form the basic structure of the lipid bilayer, the active functions of the membrane are dependent on the proteins. Cell adhesion, energy transduction, signaling, cell recognition and transport are just some of the important biological processes carried out by membrane ...
How do proteins associate with the membrane?
Proteins can associate with the membrane in one of three ways. Intrinsic or integral membrane proteins embed in the hydrophobic region of the lipid bilayer. Experimentally, these proteins can only be isolated by physically disrupting the membrane with detergent or other non-polar solvent.
Do mono save proteins span the membrane?
Mono Save topic proteins insert in one leaflet but do not span the membrane. Transmembrane proteins are the classic examples of intrinsic membrane proteins. These span the membrane, typically in an α-helix conformation and can span the membrane multiple times.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoprotein, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning there's a fat and a protein.
What is the membrane of a cell called?
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) =. The plasma membrane , also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface.
Which membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell?
The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The plasma membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes within the cell.
What are the proteins that make up the membrane?
Proteins. Proteins are wedged between the lipids that make up the membrane, and these transmembrane proteins allow molecules that couldn’t enter the cell otherwise to pass through by forming channels, pores or gates. In this way, the cell controls the flow of these molecules as they enter and exit.
What molecules can pass through plasma membrane?
Water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide can easily travel through the membrane. Generally, ions (e.g. sodium, potassium) and polar molecules cannot pass through the membrane; they must go through specific channels or pores in the membrane instead of freely diffusing through. This way, the membrane can control the rate at which certain molecules can enter and exit the cell.
What is the fluid membrane model?
Fluid Mosaic Model – a model that describes the composition of the plasma membrane and how phospholipids , proteins, and carbohydrates freely move within it.
What is the cell wall?
Cell wall – A structure that surrounds the plasma membrane of plant and fungus cells and provides additional support to those cells. Phospholipid – a molecule that forms the characteristic double layer of the plasma membrane. Semi-permeable – allowing only certain molecules to pass through due to the chemical properties of the membrane.
Why is the cell membrane important?
The cell membrane plays an important role in both of these processes. The shape of the membrane itself changes to allow molecules to enter or exit the cell. It also forms vacuoles, small bubbles of membrane that can transport many molecules at once, in order to transport materials to different places in the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
It is also simply called the cell membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment.
What is the physical barrier that surrounds all cells?
A Physical Barrier. The plasma membrane surrounds all cells and physically separates the cytoplasm, which is the material that makes up the cell, from the extracellular fluid outside the cell. This protects all the components of the cell from the outside environment and allows separate activities to occur inside and outside the cell.
What are membrane proteins?
It is the proteins, therefore, that give each type of membrane in the cell its characteristic functional properties .
How many domains are there in the plasma membrane?
When a sperm cell is examined by immunofluorescence microscopy with a variety of antibodies, each of which reacts with a specific cell-surface molecule, the plasma membrane is found to consist of at least three distinct domains (Figure 10-42).
What are the two ways membrane proteins associate with lipid bilayers?
Various ways in which membrane proteins associate with the lipid bilayer. Most trans-membrane proteins are thought to extend across the bilayer as (1) a single α helix, (2) as multiple α helices, or (3) as a rolled-up β sheet (a (more...)
What are the most useful molecules for membrane biochemists?
The most useful of these for the membrane biochemist are detergents, which are small amphipathicmolecules that tend to form micelles in water (Figure 10-23). When mixed with membranes, the hydrophobic ends of detergents bind to the hydrophobic regions of the membrane proteins, thereby displacing the lipid molecules.
What is the anchor for the protein core?
But for some proteoglycans, the protein core either extends across the lipid bilayeror is attached to the bilayer by a glycosylphosphotidylinositol (GPI) anchor. The term cell coator glycocalyxis often used to describe the carbohydrate-rich zone on the cell surface.
What is the cell coat made of?
The cell coat is made up of the oligosaccharide side chains of glycolipids and integral membrane glycoproteins and the polysaccharide chains on integral membrane proteoglycans. In addition, adsorbed glycoproteins (more...)
How much of the membrane is protein?
In the myelin membrane, which serves mainly as electrical insulation for nerve cell axons, less than 25% of the membrane mass is protein.
What are the components of the plasma membrane?
Lipid components of the plasma membrane. The outer leaflet consists predominantly of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and glycolipids, whereas the inner leaflet contains phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylinositol.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Why are phospholipids impermeable?
Because the interior of the phospholipid bilayeris occupied by hydrophobicfatty acid chains, the membrane is impermeable to water-soluble molecules, including ions and most biological molecules. Second, bilayers of the naturally occurring phospholipids are viscous fluids, not solids.
How are integral membrane proteins released?
In contrast to the peripheral membrane proteins, integral membrane proteinscan be released only by treatments that disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. Portions of these integral membrane proteins are inserted into the lipid bilayer, so they can be dissociated only by reagents that disrupt hydrophobicinteractions.
What is the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane?
Fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. Integral membrane proteins are inserted into the lipid bilayer, whereas peripheral proteins are bound to the membrane indirectly by protein-protein interactions. Most integral membrane proteins are transmembrane (more...)
How many transmembrane proteins are in the reaction center?
The reaction center consists of three transmembrane proteins, designated L (red), M (yellow), and H (green). The L and M subunits each have five transmembrane α helices, whereas the H subunit has only (more...) Although most transmembrane proteinsspan the membrane by α-helical regions, this is not always the case.
Which cell membrane is the most thoroughly studied?
The Phospholipid Bilayer. The plasma membraneis the most thoroughly studied of all cell membranes, and it is largely through investigations of the plasma membrane that our current concepts of membrane structure have evolved. The plasma membranes of mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) have been particularly useful as a model for studies ...
What are the proteins that are associated with the cell membrane?
First, all peripheral proteins are associated with the cell membrane. The amino acid sequences of these proteins are unique in that they draw the proteins to the membrane, and they tend to congregate on the surface of the membrane. This allows them to be in the right place to carry out their designated action.
What are the proteins that transfer electrons?
Many peripheral proteins are also involved in transferring small molecules or electrons. These proteins, due to their affinity to the cell membrane, allow the reactions to stay in a tight space, and be highly coordinated. Many of the proteins found within the electron transport chain are peripheral proteins.
Why are peripheral proteins not hydrophobic?
Second, peripheral proteins do not have a hydrophobic region of amino acids. This, and the polarity of other amino acid groups , keeps the peripheral proteins on the surface of the cell membrane. This is due to the amphipathic nature of phosphoglycerides. This means that the blue “ head ” region is polar and hydrophilic.
What are orange proteins attached to?
In the image, the orange peripheral proteins are seen attached to either the phosphoglyceride lipid molecules which make up the lipid bilayer, or to integral proteins. A protein without these areas of amino acids would not be attracted to the membrane. It would be distributed evenly throughout the cytoplasm, and would not be a peripheral protein.
What is the ability to attach to the membrane but not be locked to it?
The ability to attach to the membrane but not be locked to it allows peripheral proteins to work on the surface of the cell membrane. Peripheral proteins can be activated or disabled through a number of different pathways. Many peripheral proteins are also a part of many complex biochemical pathways. They can be involved in moving substances within ...
What happens if defensins are not attracted to the lipid bilayer?
Defensins proteins must interact with the lipid bilayer to produce a result. If they were not attracted to it, they would not function efficiently. Instead, they would drift around aimlessly. While they do need to find the surface of the membrane, they do not need to integrate within it to destroy it. 2.
Why are proteins considered peripheral proteins?
Peripheral proteins with simple enzyme functions are often peripheral proteins because the molecules they make are needed within or close to the cell membrane. For instance, several enzymes which control the synthesis and destruction of the cell membrane itself are peripheral proteins.
