
Does facilitated diffusion always requires a carrier protein?
Unlike diffusion, facilitated diffusion relies on the use of protein carriers to cause the movement of molecules from one gradient to another. Another difference is that facilitated diffusion requires the input of energy. Saturation can occur in facilitated diffusion but not in simple diffusion.
What are three facts about Facilitated diffusion?
Uptake of Nutrients
- Passive Diffusion. Passive or simple diffusion allows for the passage across the cell membrane of simple molecules and gases, such as CO2, O2, and H2O.
- Facilitated Diffusion. ...
- Active Transport. ...
- Primary active transport. ...
- Secondary active transport. ...
- Group Translocation. ...
What biomolecule is responsible for facilitated diffusion?
Carrier proteins involved in facilitated diffusion often have two conformations. The binding of a molecule on one side of the membrane induces a change in the three-dimensional structure of the protein, which allows the passage of the molecule through to the other side.
What are the main characteristics of facilitated diffusion?
What are the Characteristics of Facilitated Diffusion
- Occurs due to the random motion of molecules (Brownian motion)
- Requires a biological membrane for transport
- Requires a carrier protein, thus also known as carrier-mediated diffusion

What is used in facilitated diffusion?
Transmembrane proteins are the proteins present in the cell membrane that facilitate the movement of certain molecules across the membrane. There are certain channel proteins and carrier proteins that accelerate the transport process. Channel Proteins: These help in the entry and exit of substances in the cell.
How do proteins behave in facilitated diffusion?
1:282:52Facilitated Diffusion Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe protein acts like a tunnel that allows the substance. Through this is called facilitatedMoreThe protein acts like a tunnel that allows the substance. Through this is called facilitated diffusion because the protein helps diffusion to happen.
What are the 3 types of transport proteins?
A transport protein completely spans the membrane, and allows certain molecules or ions to diffuse across the membrane. Channel proteins, gated channel proteins, and carrier proteins are three types of transport proteins that are involved in facilitated diffusion.
Does facilitated diffusion require protein?
Facilitated diffusion requires membrane proteins to transport biological molecules. Simple diffusion is one that occurs unassisted by membrane proteins. Since membrane proteins are needed for transport in facilitated diffusion, the effect of temperature is often more pronounced than in simple diffusion.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The electric charge and pH helps in the diffusion across the membrane.
Why is facilitated diffusion important?
Importance of Facilitated Diffusion. Not every molecule can cross the cell membranes. The molecules should be small and non-polar to traverse the membrane. For eg., glucose is a large molecule that cannot diffuse across the cell membrane. Ions like sodium, potassium, and calcium are charged and are repelled by the cell membrane.
What are the proteins that facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane?
Transmembrane proteins are the proteins present in the cell membrane that facilitate the movement of certain molecules across the membrane. There are certain channel proteins and carrier proteins that accelerate the transport process. Channel Proteins: These help in the entry and exit of substances in the cell.
What are the factors that affect facilitated diffusion?
The main factors affecting the process of facilitated diffusion are: Temperature- As the temperature increases, the movement of the molecules increases due to an increase in energy. Concentration- The movement of the molecules takes place from ...
What is the role of the electric charge and pH in the diffusion of water molecules?
In living systems, the lipid based membrane creates compartments which allow the transport of a selective concentration of water-soluble substances. The ions, small molecules, proteins, and other solutes have different concentration across the membranes.
Which proteins are polar and too large to cross the cell membrane?
Amino acids and nucleic acids are polar and too large to cross the cell membrane. Also, the water movement across the membrane in bulk is difficult at times. To facilitate these transfer of substances across the membrane, certain integral membrane proteins or the transmembrane proteins are required.
Which type of protein regulates the entry and exit of substances?
The gated channel proteins are either closed or open and regulate the entry and exit of substances. Carrier Proteins: These are present on the cell membrane. They carry the molecules, change the confirmation of the molecules and release the molecules to the other side.
What do channel proteins do in facilitated diffusion?
Channel proteins assist or ease the transport of water molecules, some small ions and polar ions through the plasma membrane. Here channel proteins facilitated diffusion is discussed.
What happens in facilitated diffusion channel proteins?
The channel proteins ease way for the transportation of large molecules, ions, polar bodies across the cell membrane.
How does facilitated diffusion channel proteins?
In facilitated diffusion the molecules flow freely through plasma membrane With help of proteins which are present in the membrane.
Is channel protein diffusion active or passive?
Channel protein diffusion is always a passive diffusion as in this process energy is not required.
Facilitated diffusion high to low channel proteins?
Facilitated diffusion is always a high concentration gradient to low concentration gradient.
Does facilitated diffusion require a protein channel?
In facilitated diffusion for the transport of molecules, ions, amino acids there is a need of protein channel.
Example of facilitated diffusion with a channel protein?
The glucose molecule transportation is the best example in facilitated diffusion by a channel protein.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is somewhat specific to chemicals that are able to bind to a carrier protein. Absorption of nutrients such as glucose and amino acids across the epithelial membrane of the GI tract occurs by facilitated diffusion.
What is facilitated transport? What are some examples?
The classic example of facilitated diffusion is glucose transport across the membranes of cells such as erythrocytes, muscle, and adipocytes. The carriers that mediate this transport have been cloned and sequenced and fall into a group of proteins that have 12 membrane-spanning segments called glucose transporter (GLUT). Urea is transported across the membranes of many cells by a facilitated transporter called UT.
How are nucleosides transported?
Nucleoside analogs are transported across the plasma membrane either via facilitated diffusion (e.g. AZT) (7) or by membrane nucleoside transporters (e. g. ddC) (8). In contrast, cellular uptake of nucleoside phosphonates is slower and less efficient due to the negative charge of the phosphonate moiety.
What is the term for the uptake of substances into cells by incorporation in vesicles?
Schematic representation of uniporter (left), symporter (middle), and antiporter (right) membrane transport. Endocytosis is a phenomenon that describes the uptake of substances into cells by incorporation in vesicles. This can be divided into phagocytosis (for solid particles) and pinocytosis (for liquid particles).
What is the process of absorbing nutrients?
Absorption of nutrients such as glucose and amino acids across the epithelial membrane of the gastrointestinal tract occurs by facilitated diffusion.
Is membrane transport spontaneous?
However, net membrane transport of a solute against a concentration gradient is not spontaneous.
Why is facilitated diffusion important?
Why is facilitated diffusion necessary? Facilitated diffusion is necessary to move molecules from one side of the membrane to the other without using energy. Facilitated diffusion is especially important for large and charged molecules. These molecules cannot move through the plasma membrane freely by simple diffusion. The plasma membrane is made of hydrophobic phospholipids that are tightly packed together and prevent the movement of large molecules and charged molecules. Thus, facilitated diffusion is essential for moving these essential large or charged molecules.
What is the difference between facilitated diffusion and simple diffusion?
The difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion is the method by which molecules diffuse. In simple diffusion, molecules diffuse across the cell membrane without any help. However, in facilitated diffusion , a protein in the membrane is involved.
What is the plasma membrane made of?
The plasma membrane is made of hydrophobic phospholipids that are tightly packed together and prevent the movement of large molecules and charged molecules. Thus, facilitated diffusion is essential for moving these essential large or charged molecules. paywall_facilitated-diffusion-definition-process-examples. 4:46.
What are voltage gated sodium channels?
Voltage Gated Sodium Channels. There are two types of facilitated diffusion, channels and carrier proteins. The GLUT4 protein is an example of a carrier protein that specifically binds to one substance to be transported. Channel proteins on the other hand allow for the free flow of materials through the protein.
What is the process of moving molecules from high to low concentration across a membrane?
Facilitated diffusion is the process of moving molecules from high to low concentration across a membrane by using a protein channel in the membrane. Facilitated diffusion does not use energy but relies on a protein to facilitate movement.
Why does diffusion occur without energy?
Facilitated diffusion occurs without additional energy input because it moves molecules down their concentration gradient from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What are the different types of passive transport?
Passive transport is any type of movement across the membrane that does not use energy. Passive transport includes the following types of transport: 1 Simple diffusion - Molecules move from high to low concentration directly across the membrane. 2 Facilitated diffusion - Molecules move from high to low concentration across the membrane through a channel protein. 3 Osmosis - The movement of water from an area of low solute to an area of high solute
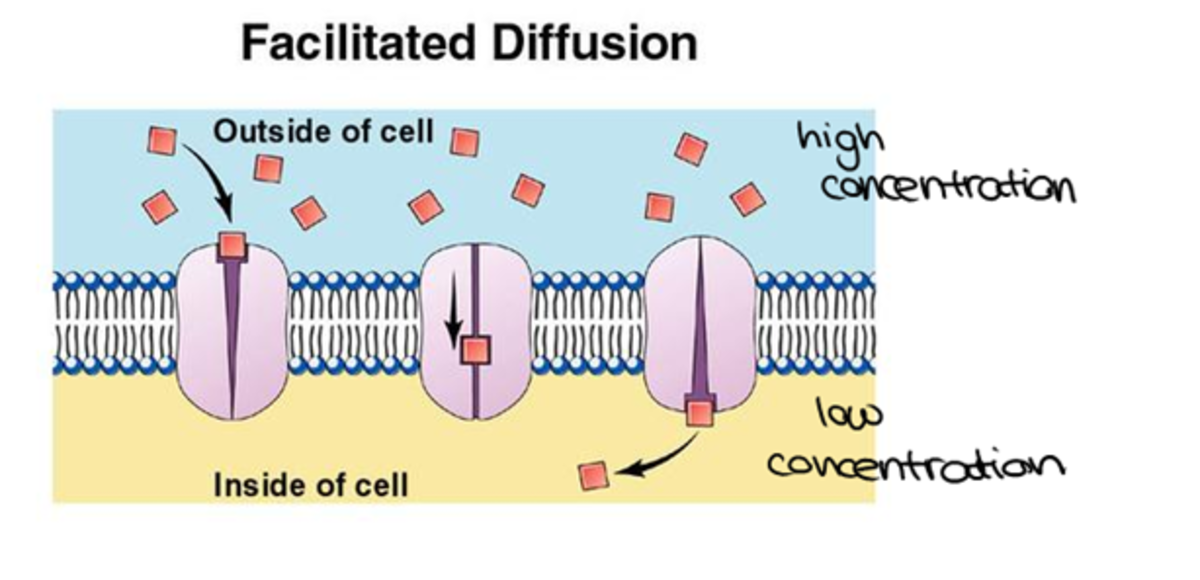
Facilitated Diffusion Definition
Factors Affecting Diffusion
- The driving force behind diffusion of fluids is simply the probability behind Brownian motion. All molecules have some degree of erratic, random movement, largely dependent on temperature. As temperature increases, the energy of these molecules increases. When a substance is highly concentrated in a certain region, molecular movement, especially at the periphery, will lead to th…
Facilitated Diffusion Across Membranes
- Diffusion is ubiquitous across the biosphere. It is seen in the movement of air and water, and is a necessary force driving global weather patterns. Within living systems, the presence of lipid-based membranes creates compartments that allow the selective concentration of water-soluble substances. For instance, mitochondrial membranes can create 2 distinct regions within the org…
Examples of Facilitated Diffusion
- A number of important molecules undergo facilitated diffusion to move between cells and subcellular organelles.
Related Biology Terms
- Brownian Motion– Random fluctuations in the velocity of particles in a fluid medium usually arising from intermolecular collisions.
- Hypoglycemia– Condition characterized by low blood glucose levels.
- Integral Membrane Protein– Proteins that are structurally and functionally an integral part of a biological membrane. Can traverse the entire width of the membrane or be attached through …
- Brownian Motion– Random fluctuations in the velocity of particles in a fluid medium usually arising from intermolecular collisions.
- Hypoglycemia– Condition characterized by low blood glucose levels.
- Integral Membrane Protein– Proteins that are structurally and functionally an integral part of a biological membrane. Can traverse the entire width of the membrane or be attached through a small li...
- Partial Pressure– Hypothetical measure of the concentration of one gas in a mixture of gases.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these statements about facilitated diffusion of molecules is true? A. Does not directly involve ATP B. Needs the presence of another molecule C. Necessary for the diffusion of polar molecules across a membrane D.All of the above 2. Which of these factors affects the rate of diffusion? A. Temperature B. Viscosity of medium C. Size of particles D.All of the above 3. Whic…
Facilitated Diffusion Definition
Principle
Channel Proteins and Carrier Proteins
Factors Affecting Facilitated Diffusion
Examples of Facilitated Diffusion
- 1. Glucose and amino acid Transport 1. The transport of glucose and amino acid from the bloodstream into the cell is an example of facilitated diffusion. 2. In the small intestine, these molecules are taken in via active transport and then are released into the bloodstream. 3. Because glucose and amino acid are larger molecules, they require carrie...
Applications/Importance of Facilitated Diffusion
References
Internet Sources
What Is Facilitated diffusion?
Factors Affecting Facilitated Diffusion
Importance of Facilitated Diffusion
Transmembrane Proteins
- Transmembrane proteins are the proteins present in the cell membrane that facilitate the movement of certain molecules across the membrane. There are certain channel proteins and carrier proteins that accelerate the transport process. 1. Channel Proteins: These help in the entry and exit of substances in the cell. There are two types of channel pro...