
What is a substrate in an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
In an enzyme catalyzed reaction, a substrate refers to the chemical compound that is acted upon by the enzyme. Catabolism is the reaction that is being catalyzed in this experiment.
What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction?
The reaction that is been catalysed is the CATABOLISM [BREAKING DOWN] OF HYDROGHE PEROXIDE. The name of the enzyme which catalysed the reaction is CATALASE. The substrate is HYDROGEN PEROXIDE. In an enzyme catalyzed reaction, a substrate refers to the chemical compound that is acted upon by the enzyme.
What is the difference between catalase and catabolism?
In an enzyme catalyzed reaction, a substrate refers to the chemical compound that is acted upon by the enzyme. Catabolism is the reaction that is being catalyzed in this experiment. The enzyme in this experiment is catalase. while the substrate is 3% hydrogen peroxide.
What is meant by a reaction?
A reaction is a procedure that changes over at least one substance (known as reagents, reactants, or substrates) to another kind of substance (the item). Benefit of using an enzyme is that it can be used repeatedly in the same reaction.
What is the function of catalase?
What is substrate in biology?
What is the purpose of enzymes in a reaction?
About this website
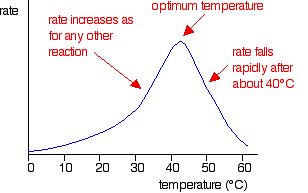
What is the reaction of catalase and hydrogen peroxide?
WHEN catalase is added to hydrogen peroxide, there is an initial rapid evolution of oxygen which lasts for about two minutes, depending on the peroxide concentration. After this, oxygen is given off at a steady rate which slowly decreases in the course of an hour.
Where is the reaction being catalyzed in an enzyme?
The enzyme active siteEnzymes have active sites. The enzyme active site is the location on the enzyme surface where substrates bind, and where the chemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme occurs.
When an enzyme-catalyzed a reaction?
To catalyze a reaction, an enzyme will grab on (bind) to one or more reactant molecules. These molecules are the enzyme's substrates. In some reactions, one substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates come together to create one larger molecule or to swap pieces.
What happens when you mix hydrogen peroxide and potato?
Fresh potato shows an interesting chemical activity. When dipped in a solution of hydrogen peroxide, it triggers bubbling of oxygen. This activity is due to a special protein produced by the potato to protect itself against oxidative stress.
What is an example of a catalyzed reaction?
Another well-known catalyst reaction example involves the platinum metal present in the catalytic converters of cars. This platinum catalyzes the conversion of the toxic gas, carbon monoxide, into carbon dioxide.
What type of reaction is catalyzed?
Catalyzed reactions are typically used to accelerate the rate by which a specific chemistry proceeds. Essentially, the action of the catalyst is to provide an alternative, lower energy pathway for the reaction. For this to occur, the catalytic substance interacts with a reactant and forms an intermediate compound.
What is enzyme catalysis give an example?
Examples are lactase, alcohol dehydrogenase and DNA polymerase.
How is a reaction catalyzed?
A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. Catalysts typically speed up a reaction by reducing the activation energy or changing the reaction mechanism. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions.
What is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction quizlet?
Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy necessary for a reaction to occur. The molecule that an enzyme acts on is called the substrate. In an enzyme-mediated reaction, substrate molecules are changed, and product is formed.
What is the catalyst in potato and hydrogen peroxide experiment?
Catalase, an enzyme found inside a potato, breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. The advantage of this reaction is that you can see the oxygen gas bubbling out as it is formed so you can tell how fast the reaction is happening.
What type of reaction is hydrogen peroxide and potato?
The bubbling reaction you see is the metabolic process of decomposition, described earlier. This reaction is caused by catalase, an enzyme within the potato. You are observing catalase breaking hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water.
What reaction does catalase Catalyse?
catalase, an enzyme that brings about (catalyzes) the reaction by which hydrogen peroxide is decomposed to water and oxygen.
Where is catalysis found?
Catalase is an enzyme in the liver that breaks down harmful hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water.
How is a reaction catalyzed?
A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. Catalysts typically speed up a reaction by reducing the activation energy or changing the reaction mechanism. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions.
How do enzymes catalyze reactions quizlet?
Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy necessary for a reaction to occur. The molecule that an enzyme acts on is called the substrate. In an enzyme-mediated reaction, substrate molecules are changed, and product is formed.
Where are the enzymes catalyzing the reactions of glycolysis found in?
Glycolysis. Glycolytic enzymes are located in the sarcoplasm and are associated with the sarcoplasmic reticulum [10,11]. They convert glucose-6-phosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides (NAD+) to pyruvate and NADH by producing two molecules of ATP.
Biology Enzymes Lab Flashcards | Quizlet
This and salt concentration also affect enzymatic structures. As a result, enzymes denature at extremes of pH and high salt concentrations. In addition, substrates and/or the enzyme's active site groups may become ionized.
Enzyme Catalysis Lab Report - BIOLOGY LAB REPORT Lab 2 ... - StuDocu
Courses. Popular. Community Health Nursing (NU 420) Community Health and Population-Focused Nursing Field Experience (C229) General Biology (BIOS 1010 )
How far away from paper towel should I use IKI spray?
12. Hold the IKI spray bottle 25 – 30 cm away from the paper towel, and mist with the IKI solution.
How long does it take for starch to dry?
3. Set up a positive control for this experiment by spraying a paper towel with the starch solution. Allow the starch to dry for approximately one hour (this time interval may vary by location).
What temperature should water be when using tube 3?
Important Note: The water should be at approximately 85 °C when you place Tube 3 in it. Verify the temperature with the thermometer to ensure the water is not too hot! Temperatures which exceed approximately 85 °C may denature the hydrogen peroxide.
How long to heat water in microwave?
e. If using a microwave, place the microwave-safe bowl in the microwave and heat the water in 30 second increments until the temperature of the water is approximately 100 °C. Use the thermometer provided in your lab kit to verify the water temperature. Wait approximately one minute before proceeding to Step 5.
How to label test tubes?
1. Use a permanent marker to label test tubes 1, 2, and 3. Place them in the test tube rack.
What enzymes digest proteins?
6. Digestive enzym es in the gut include proteases, which digest proteins. Why don’t these enzymes digest the stomach and small intestine, which are partially composed of protein?
Why space positive and negative controls apart?
Note: Be sure to space the positive and negative controls apart from each other to prevent cross-contamination.
What are enzymes made of?
Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering their activation energy therefore increasing the activity rate of the enzyme and more substrates turned into products. The ‘Catalase’ enzyme that was used during this experiment was obtained from peroxisome found in celery which are organelles found in bacteria, plant, and animal cells. It is involved in the breaking down of certain substances and the diminish of reactive oxygen species and that includes hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) which can be a byproduct of the metabolism of oxygen. Hydrogen peroxide is toxic to the cell and so the catalase enzyme is utilised to break down H2O2 to form oxygen molecules and water free of free radicals. As with all
What is the active site of an enzyme?
An Enzyme has an active site that joins together with a substrate to create a product. This is also known as the lock and key hypothesis because the substrate fits into the active site like a key and lock. When this occurs the active site then breaks the substrate into two products, which then repeats constantly. If a high temperature occurs to the active site, which then results in not having an optimum pH level, then it could change the shape of the active site which results in the substrate not fitting. This is called a denatured
How do enzymes increase the rate of biological reactions?
They increase the rate of reactions by reducing the amount of activation energy; hence the barrier to a reaction is lower when an enzyme is being used. Enzymes have an active site to which specific substrate binds. The combination of enzyme and substrate creates a new energy outline with a lower amount of activation energy (Lesson 6.5 A Catalyst and the Rate of Reaction). Once a product has been formed, they leave the active site of the enzyme hence more reactions can occur.
Can enzymes make exergonic reactions?
Enzymes can’t make endergonic reactions exergonic. They can only quicken reactions that will eventually occur, but this enables the cell to have a productive metabolism, routing chemicals through metabolic pathways. Enzymes are very specific for the reactions they catalyze; they make sure the chemical processes go in the cell at any given time. Peroxidase was the enzyme being testing in this experiment. A peroxidase is an enzyme that acts as catalysts, which occurs in biological systems.
What is the function of catalase?
It catalyzes the decay of hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water. It is a significant enzyme shielding the cell from oxidative harm by responsive oxygen species .
What is substrate in biology?
It is a molecule followed by an enzyme. A substrate is stacked into the dynamic site of the enzyme, or the spot that enables weak bonds between the two particles.
What is the purpose of enzymes in a reaction?
They are made up of proteins and act as catalyst inside living cells. They speed up the rate of reaction without being used permanently and without any change in their structure. A reaction is a procedure that changes over at least one substance (known as reagents, reactants, or substrates) to another kind of substance (the item). Benefit of using an enzyme is that it can be used repeatedly in the same reaction.
