
The Calvin cycle consists of:
- Carbon fixation - Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is reacted to produce glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). ...
- Reduction reactions - The enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes reduction of 1,3BPGA by NADPH.
- Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration - At the end of the regeneration, the net gain of the set of reactions is one G3P molecule per 3 carbon dioxide molecules.
What are the reactants and products of the Calvin cycle?
calvin cycle. reactant: carbon dioxide, NADPH, ATP. product: ADP, phospahte, NADP+, glucose. What are the outputs of photosynthesis? In photosynthesis, water, carbon dioxide, and energy in the form of sunlight are inputs, and the outputs are glucose and oxygen.
What event occurs during Calvin cycle reactions?
The light independent process (also called dark reactions or the Calvin-Benson cycle) takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. Carbon dioxide is modified by series of chemical reactions to form carbohydrates. The energy for these reactions comes from ATP and NADPH generated during the light dependent process.
What are the three stages of the Calvin cycle?
What are the steps of the Calvin cycle where ATP is needed quizlet?
- Carbon Fixation – CO2 is broken down to form 3-PGA.
- Reduction – 3-PGA is converted to 3-PGA and reacts with ATP and NADPH.
- Release of on G3P to make carbs.
- Repeat iwth RuBP.
What do light reactions of the Calvin cycle produce?
What are the Similarities Between Light Reaction and Calvin Cycle?
- Both processes produce energy in the form of ATP.
- Also, both are enzyme-mediated.
- Furthermore, both take place in chloroplasts.
- Moreover, both processes take place in autotrophic organisms.
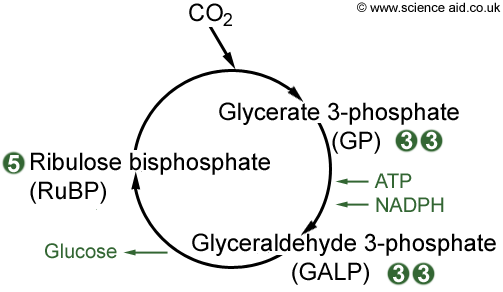
What is the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle. How the products of the light reactions, ATP and NADPH, are used to fix carbon into sugars in the second stage of photosynthesis.
How many turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one G3P molecule that can exit the cycle and go?
Three turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one G3P molecule that can exit the cycle and go towards making glucose. Let’s summarize the quantities of key molecules that enter and exit the Calvin cycle as one net G3P is made. In three turns of the Calvin cycle:
What is the second stage of ATP and NaDPH?
Reduction. In the second stage, ATP and NADPH are used to convert the 3-PGA molecules into molecules of a three-carbon sugar, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ( G3P ). This stage gets its name because NADPH donates electrons to, or reduces, a three-carbon intermediate to make G3P. [Details of this step]
How many molecules are made in a G3P cycle?
In order for one G3P to exit the cycle (and go towards glucose synthesis), three molecules must enter the cycle, providing three new atoms of fixed carbon. When three molecules enter the cycle, six G3P molecules are made.
What is the reaction that makes a six carbon compound?
Carbon fixation. A molecule combines with a five-carbon acceptor molecule, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate ( RuBP ). This step makes a six-carbon compound that splits into two molecules of a three-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase, or rubisco.
How many turns does it take to make a glucose molecule?
A G3P molecule contains three fixed carbon atoms, so it takes two G3Ps to build a six-carbon glucose molecule. It would take six turns of the cycle, or , ATP, and NADPH, to produce one molecule of glucose. [References and attribution]
Why are light independent reactions called light independent reactions?
These reactions are also called the light-independent reactions because they are not directly driven by light. In the Calvin cycle, carbon atoms from are fixed (incorporated into organic molecules) and used to build three-carbon sugars. This process is fueled by, and dependent on, ATP and NADPH from the light reactions.
Which two molecules are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar?from khanacademy.org
This illustration shows that ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar.
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?from sciencedirect.com
Similarly, where does the Calvin cycle occur? Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the inner space of chloroplasts). This illustration shows that ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar.
How many molecules are made in a G3P cycle?from khanacademy.org
In order for one G3P to exit the cycle (and go towards glucose synthesis), three molecules must enter the cycle, providing three new atoms of fixed carbon. When three molecules enter the cycle, six G3P molecules are made.
Why does the cyclic pathway exist?from khanacademy.org
Why does the cyclic pathway exist? At least in some cases, chloroplasts seem to switch from linear to cyclic electron flow when the ratio of NADPH to NADP is too high (when too little NADP is available to accept electrons). In addition, cyclic electron flow may be common in photosynthetic cell types with especially high ATP needs (such as the sugar-synthesizing bundle-sheath cells of plants that carry out photosynthesis). Finally, cyclic electron flow may play a photoprotective role, preventing excess light from damaging photosystem proteins and promoting repair of light-induced damage.
How does light affect photosynthesis?from sciencedirect.com
Light energy is trapped by PSII causing an electron from P680 to be promoted to a higher energy level (an excited state). This excited electron is rapidly transferred to a primary electron-acceptor molecule that is closely associated with P680. If this transfer does not occur immediately, the excited electron falls back to its ground state in P680, giving-off energy (fluorescence) in the process. From the primary electron acceptor, the electron is transferred from one acceptor to another within PSII. In this electron transfer chain, the energy of the excited electron is utilized to move protons (H+) from the stroma to the lumen of the thylakoids. Finally, a mobile electron acceptor carries the electron to PSI where it is transferred to P700. The photochemical reactions can be illustrated in the Photosynthetic Z-scheme ( Fig. 4.5 ).
What is the purpose of NADPH in Calvin cycle?from socratic.org
It provides the energy for the formation of energy rich chemical bonds in glucose. Finally, it changed into ADP. NADPH-It helps the reduction of carbondixide into glucose. Finally, it oxidised into NADP. They produce the ATP and NADPH necessary for the Calvin cycle.
What is the reaction that makes a six carbon compound?from khanacademy.org
Carbon fixation. A molecule combines with a five-carbon acceptor molecule, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate ( RuBP ). This step makes a six-carbon compound that splits into two molecules of a three-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase, or rubisco.
What Two Products Of The Light Reactions Are Used Up In The Calvin Cycle?
What two products of the light reactions are used up in the calvin cycle? NADPH which is an electron carrier and can be reused and ATP or ADP which is an energy molecule that can be rebuilt in another light reaction.
What are the two products of the light reactions used in the Calvin cycle?
How the products of the light reactions ATP and NADPH are used to fix carbon into sugars in the second stage of photosynthesis.
What 2 things does the Calvin cycle use?
The Calvin cycle has two parts. First carbon dioxide is ”fixed”. Then ATP and NADPH from the light reactions provide energy to combine the fixed carbons to make sugar.
What are the two products of light reactions?
The products of the light-dependent reactions ATP and NADPH have lifespans in the range of millionths of seconds whereas the products of the light-independent reactions (carbohydrates and other forms of reduced carbon) can survive for hundreds of millions of years.
What are the reactants and products of light reaction?
The reactants of light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis are H20 (water) ADP and NADP+. The products of light-dependent pathways of photosynthesis are Oxygen ATP and NADPH. The reactants of light-independent reactions are ATP NADPH and Carbon Dioxide.
What products of light reactions of photosynthesis are used in the Calvin cycle?
The net effect of these steps is to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to make sugars in the next stage of photosynthesis the Calvin cycle.
Why does Calvin cycle need products of light?
The Calvin cycle refers to the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis that take place in three key steps. Although the Calvin Cycle is not directly dependent on light it is indirectly dependent on light since the necessary energy carriers (ATP and NADPH) are products of light-dependent reactions.
Where Do Calvin Cycle Reactions Occur?
Unlike the light reactions which take place in the thylakoid membrane the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the inner space of chloroplasts).
Where does the Calvin cycle occur quizlet?
Where does the Calvin Cycle occur? The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma whereas the light reactions occur in the thylakoids.
What reactions occur during the Calvin cycle?
There are three phases to the light-independent reactions collectively called the Calvin cycle: carboxylation reduction reactions and ribulose 1 5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration. Though it is called the “dark reaction” the Calvin cycle does not actually occur in the dark or during night time.
Does the Calvin cycle occur in mitochondria?
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma area in the chloroplasts. The mitochondria is another organelle and the nucleus contains the DNA. The thylakoids are in the chloroplasts and contain the pigment chlorophyll in which the light reactions occur.
What organelle does Calvin cycle occur in?
chloroplasts The two parts of photosynthesis—the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle—have been described as they take place in chloroplasts.
Where does Calvin take place?
The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma of a chloroplast in a plant cell. The stroma is the colorless fluid that surrounds the grana of the chloroplast where the first step of photosynthesis takes place.
Where does the Calvin cycle occur CH 10?
The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma. The light reactions of photosynthesis use _____ and produce _____.

Function of The Calvin Cycle
- The function of the Calvin cycle is to create three-carbon sugars, which can then be used to build other sugars such as glucose, starch, and cellulose that is used by plants as a structural building material. The Calvin cycle takes molecules of carbon straight out of the air and turns them into p…
Calvin Cycle Steps
- Carbon Fixation
In carbon fixation, a CO2 moleculefrom the atmosphere combines with a five-carbon acceptor molecule called ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP). The resulting six-carbon compound is then split into two molecules of the three-carbon compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA). This re… - Reduction
In the second stage of the Calvin cycle, the 3-PGA molecules created through carbon fixation are converted into molecules of a simple sugar – glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate (G3P). This stage uses energy from ATP and NADPH created in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. In this …
Calvin Cycle Products
- Each turn of the Calvin cycle “fixes” one molecule of carbon that can be used to make sugar. It takes three turns of the Calvin cycle to create one molecule of glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate. After six turns of the Calvin cycle, two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate can be combined to make a glucose molecule. Each turn of the Calvin cycle also uses up 3 ATP and 2 NADPH in the …
Related Biology Terms
- Chloroplast – The organellein plant cells where energy from sunlight is turned into ATP and sugar.
- Energy Pyramid – A diagram that illustrates the flow of energy through an ecosystem.
- Photosynthesis– The process by which living things capture energy from sunlight and use it to make fuel and organic materials to build their cells.
Quiz
- 1. Why is the Calvin cycle important to most ecosystems? A. It turns carbon dioxide from the air into carbon that living things can use to make sugars, proteins, nucleotides, and lipids. B. It stores energy from sunlight into the long-term storage form of sugar, which can be used by plants, or eaten by animals to form the basis for the food chain. C. It removes carbon dioxide, which is a gr…