Lidocaine's effects on the central nervous system include inhibiting nicotinic and acetylcholine receptors, inhibiting presynaptic calcium channels in the dorsal root ganglion, inhibiting opioid receptors, inhibiting of neurite growth, inhibiting muscarinic cholinergic receptors, and preventing substance P from binding to natural killer (NK) cell receptors [7,31,32].
What is the mechanism of action of lidocaine?
Lidocaine works by stopping the sodium ions from passing through the voltage-gated channels. So, the signals for pain are stopped even before the signals are formed. Lidocaine binds to the sodium channels. The amide on the lidocaine allows it to act like an amino acid and interact with the active sites in the sodium channel domains.
What is the inhibitory effect of lidocaine on NMDA receptors?
The inhibitory effect of lidocaine on NMDA receptors is consistent with the NMDA receptor-mediated effect on the development of chronic pain [ 41] and is consistent with the temporary relief of such pain provided by lidocaine. [ 42]
What is the role of kinase in the regulation of lidocaine?
Kinase protein signaling pathways are involved in the regulation of glutamate release by lidocaine.
What is the mechanism of action for lidocaine?
Mechanism of Action Lidocaine is 65% protein-bound to albumin and alpha1-acid glycoprotein in the plasma, giving it a medium duration of action compared to other local anesthetic agents. It is less lipid-soluble than other agents, limiting its overall potency.
What is the target for lidocaine?
Although there is evidence that lidocaine can interact with multiple targets, lidocaine's primary clinically relevant target is believed to be voltage-gated sodium channels. Voltage-gated sodium channels play a critical role in the generation and propagation of action potentials in neurons and muscle cells.
How does lidocaine block the sensation of pain?
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic. It prevents pain by blocking the signals at the nerve endings in the skin. This medicine does not cause unconsciousness as general anesthetics do when used for surgery. This medicine is to be given only by or under the direct supervision of your doctor.
Which drug target is inhibited by lidocaine?
Subsequent research confirmed that lidocaine inhibited the activation of NMDA receptors in a concentration-dependent manner with effects in the high micromolar range.
What does lidocaine do to neurons?
In conclusion, lidocaine increases intracellular sodium concentration and promotes excitation in respiratory pacemaker neurons through voltage-dependent sodium channels by altering membrane potential.
How does lidocaine work in the brain?
Lidocaine works by blocking the influx of sodium ions into the membrane surrounding nerves. This prevents the initiation and conduction of impulses along the nerve, which results in an anesthetic effect. Lidocaine belongs to the class of medicines known as class-1b antiarrhythmic drugs.
What are the dangers of lidocaine?
When used sparingly and as directed, topical lidocaine is generally safe. However, misuse, overuse, or overdose can lead to a number of serious health problems and even death. Ingestion of lidocaine can cause numbness of the mouth and throat, which can lead to trouble swallowing and even choking.
How lidocaine prevents the transmission of pain impulses to the brain?
Lidocaine works by temporarily blocking this pathway of pain signals along nerves. It does this by stopping the sodium entering the nerve ending at the site of the pain. This prevents an electrical signal building up and passing along the nerve fibres to the brain.
Does lidocaine block all sodium channels?
Lidocaine blocks voltage-gated sodium channels. Because the majority of these channels are closed until the membrane potential depolarizes, lidocaine has no effect on resting membrane potential --- and therefore lidocaine can't make the resting potential of a damaged cell similar to that of a normal cell.
What drugs does lidocaine interact with?
Lidocaine has mild interactions with at least 28 different drugs....Serious Interactions of lidocaine include:axitinib.bosutinib.cobimetinib.eliglustat.fentanyl.fentanyl intranasal.fentanyl iontophoretic transdermal system.fentanyl transdermal.More items...
Why is lidocaine given during anesthesia?
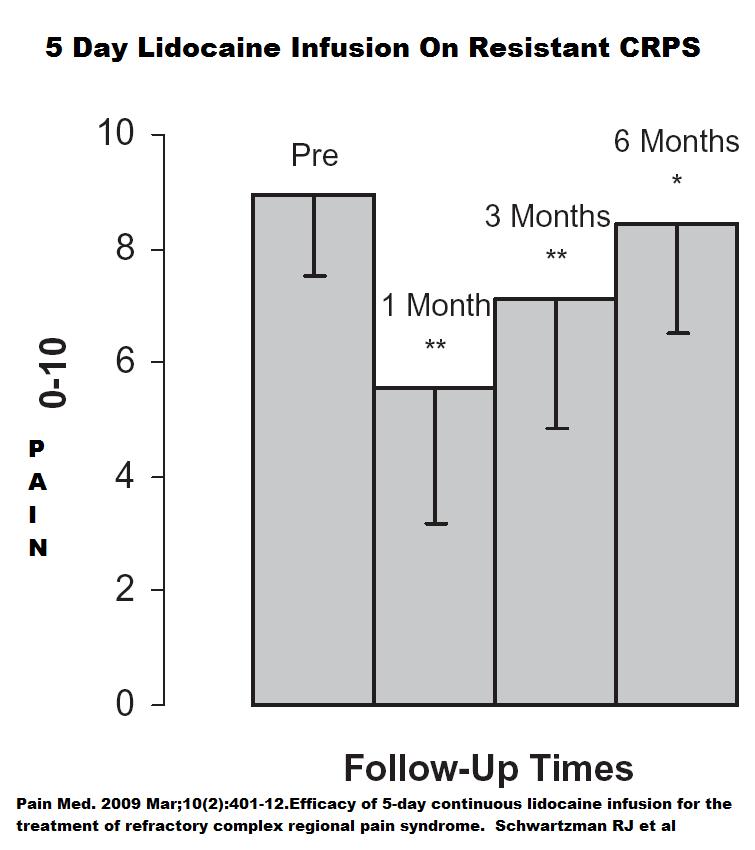
used intravenous lidocaine for the first time as adjuvant during general anesthesia. They showed that lidocaine provides post-operative analgesia with low incidence of post-operative nausea and vomiting [13].
Why is lidocaine the most commonly used anesthetic?
Lignocaine (lidocaine) is the most commonly used anaesthetic in the surgical setting. It is effective, acts rapidly and is relatively free from toxicity and sensitivity. It is available in many different forms, including topical applications (eg, EMLA® Cream and patches) and solutions for injection.
What is 2% lidocaine used for?
Xylocaine (lidocaine HCl) 2% Jelly is indicated for prevention and control of pain in procedures involving the male and female urethra, for topical treatment of painful urethritis, and as an anesthetic lubricant for endotracheal intubation (oral and nasal).
Why is lidocaine used for arrhythmias?
LIDOCAINE (Xylocaine) has become one of the most frequently used drugs in the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias, particularly those associated with acute myocardial infarction. It has been shown to terminate ventricular tachycardia, and it has been given to suppress multiple ventricular extrasystoles.
Why is lidocaine used in induction?
Intravenous lidocaine can prevent systemic hypertension and rise in ICP during laryngoscopy or intubation by suppressing the airway reflexes and providing an adequate depth of anaesthesia (3-6).
How does lidocaine affect action potential?
Lidocaine can therefore block a fraction of the activated sodium channels that do not inactivate during the plateau of the action po- tential, and thereby reduce action potential duration (Colatsky, 1982; Bean et al., 1983).
How does lidocaine affect the cell membrane?
Lidocaine alters signal conduction in neurons by prolonging the inactivation of the fast voltage-gated Na + channels in the neuronal cell membrane responsible for action potential propagation. With sufficient blockage, the voltage-gated sodium channels will not open and an action potential will not be generated. Careful titration allows for a high degree of selectivity in the blockage of sensory neurons, whereas higher concentrations also affect other types of neurons.
How long does lidocaine work?
When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding.
How long does lidocaine stay in your system?
The elimination half-life of lidocaine is biphasic and around 90 min to 120 min in most patients. This may be prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment (average 343 min) or congestive heart failure (average 136 min). Lidocaine is excreted in the urine (90% as metabolites and 10% as unchanged drug).
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat ventricular tachycardia?
Lidocaine. Lidocaine , also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia.
What class is lidocaine?
Lidocaine is also the most important class-1b antiarrhythmic drug; it is used intravenously for the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias (for acute myocardial infarction, digoxin poisoning, cardioversion, or cardiac catheterization) if amiodarone is not available or contraindicated.
What is a numbing agent?
As a local numbing agent, it is used for the treatment of premature ejaculation. An adhesive transdermal patch containing a 5% concentration of lidocaine in a hydrogel bandage, is approved by the US FDA for reducing nerve pain caused by shingles.
When was lidocaine discovered?
Lidocaine was discovered in 1946 and went on sale in 1948. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2018, it was the 233rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
Who administers lidocaine?
Lidocaine will be administered to you by a health professional. Talk to them if you have any concerns.
What is a lidocaine anesthetic?
4. Bottom Line. Lidocaine is used as a local or regional anesthetic to prevent pain signals from being transmitted to the brain during surgical, dental , and other procedures. Lidocaine antiarrhythmic is used in the emergency treatment of certain heart conditions. 5.
What medications interact with lidocaine?
Common medications that may interact with lidocaine include: vasopressor drugs (such as ephedrine or phenylephrine) or ergot-type oxytocic drugs (such as ergometrine) (the combination may cause severe and persistent high blood pressure (hypertension) which may increase the risk of stroke).
What is the class of Lidocaine?
Lidocaine belongs to the class of medicines known as class-1b antiarrhythmic drugs. It may also be called an anesthetic. 2. Upsides.
How long does lidocaine last?
The duration of effect is approximately 60 to 90 minutes. Higher dosages or volumes of lidocaine will result in a shorter time to the onset of anesthesia, a longer duration of effect, a greater degree of muscle relaxation, and an increase in the spread of the anesthesia.
What are the side effects of lidocaine?
If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: Skin redness, itching, a rash, or a feeling of warmth may occur in the region where lidocaine has been administered subcutaneously when used for local anesthesia.
Is lidocaine an antiarrhythmic?
Lidocaine antiarrhythmic may be used in the emergency treatment of cardiac arrest, ventricular arrhythmias, or other severe heart conditions. Systemic lidocaine is administered IV. The IM formulation is no longer commercially available in the United States.
What is a lidocaine?
Lidocaine is an anesthetic of the amide group indicated for production of local or regional anesthesia by infiltration techniques such as percutaneous injection and intravenous regional anesthesia by peripheral nerve block techniques such as brachial plexus and intercostal and by central neural techniques such as lumbar and caudal epidural blocks.
How is lidocaine absorbed?
In general, lidocaine is readily absorbed across mucous membranes and damaged skin but poorly through intact skin. The agent is quickly absorbed from the upper airway, tracheobronchial tree, and alveoli into the bloodstream. And although lidocaine is also well absorbed across the gastrointestinal tract the oral bioavailability is only about 35% as a result of a high degree of first-pass metabolism. After injection into tissues, lidocaine is also rapidly absorbed and the absorption rate is affected by both vascularity and the presence of tissue and fat capable of binding lidocaine in the particular tissues. The concentration of lidocaine in the blood is subsequently affected by a variety of aspects, including its rate of absorption from the site of injection, the rate of tissue distribution, and the rate of metabolism and excretion. Subsequently, the systemic absorption of lidocaine is determined by the site of injection, the dosage given, and its pharmacological profile. The maximum blood concentration occurs following intercostal nerve blockade followed in order of decreasing concentration, the lumbar epidural space, brachial plexus site, and subcutaneous tissue. The total dose injected regardless of the site is the primary determinant of the absorption rate and blood levels achieved. There is a linear relationship between the amount of lidocaine injected and the resultant peak anesthetic blood levels. Nevertheless, it has been observed that lidocaine hydrochloride is completely absorbed following parenteral administration, its rate of absorption depending also on lipid solubility and the presence or absence of a vasoconstrictor agent. Except for intravascular administration, the highest blood levels are obtained following intercostal nerve block and the lowest after subcutaneous administration. Additionally, lidocaine crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
How long does it take for lidocaine to be eliminated?
The elimination half-life of lidocaine hydrochloride following an intravenous bolus injection is typically 1.5 to 2.0 hours. Because of the rapid rate at which lidocaine hydrochloride is metabolized, any condition that affects liver function may alter lidocaine HCl kinetics. The half-life may be prolonged two-fold or more in patients with liver dysfunction.
How long is lidocaine stable?
Commercially available solutions of lidocaine hydrochloride in 5% dextrose usually are stable for 18 months after the date of manufacture. Commercially available solutions of lidocaine hydrochloride in 5% dextrose may be provided in plastic containers.
Where is lidocaine metabolized?
Lidocaine is metabolized predominantly and rapidly by the liver, and metabolites and unchanged drug are excreted by the kidneys. Biotransformation includes oxidative N-dealkylation, ring hydroxylation, cleavage of the amide linkage, and conjugation. N-dealkylation, a major pathway of biotransformation, yields the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide. The pharmacological/toxicological actions of these metabolites are similar to, but less potent than, those of lidocaine HCl. Approximately 90% of lidocaine HCl administered is excreted in the form of various metabolites, and less than 10% is excreted unchanged. The primary metabolite in urine is a conjugate of 4-hydroxy-2,6-dimethylaniline.
What are external analgesics?
External analgesic drug products for over-the-counter human use. Analgesic, anesthetic, and antipruritic active ingredients. The active ingredient of the product consists of any of the following within the specified concentration established for each ingredient: (a) Male genital desensitizers. ... Lidocaine in a metered spray with approximately 10 milligrams per spray.
What is the mean systemic clearance for lidocaine?
The mean systemic clearance observed for intravenously administered lidocaine in a study of 15 adults was approximately 0.64 +/- 0.18 L/min.

Overview
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the ski…
Medical uses
The efficacy profile of lidocaine as a local anaesthetic is characterized by a rapid onset of action and intermediate duration of efficacy. Therefore, lidocaine is suitable for infiltration, block, and surface anaesthesia. Longer-acting substances such as bupivacaine are sometimes given preference for spinal and epidural anaesthesias; lidocaine, though, has the advantage of a rapid onset of action. Adrenaline vasoconstricts arteries, reducing bleeding and also delaying the resor…
Adverse effects
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are rare when lidocaine is used as a local anesthetic and is administered correctly. Most ADRs associated with lidocaine for anesthesia relate to administration technique (resulting in systemic exposure) or pharmacological effects of anesthesia, and allergic reactions only rarely occur. Systemic exposure to excessive quantities of lidocaine mainly result in central nervous system (CNS) and cardiovascular effects – CNS effects …
Pharmacology
Lidocaine alters signal conduction in neurons by prolonging the inactivation of the fast voltage-gated Na channels in the neuronal cell membrane responsible for action potential propagation. With sufficient blockage, the voltage-gated sodium channels will not open and an action potential will not be generated. Careful titration allows for a high degree of selectivity in the blockage of sensory neurons, whereas higher concentrations also affect other types of neurons.
History
Lidocaine, the first amino amide–type local anesthetic, was first synthesized under the name 'xylocaine' by Swedish chemist Nils Löfgren in 1943. His colleague Bengt Lundqvist performed the first injection anesthesia experiments on himself. It was first marketed in 1949.
Society and culture
Lidocaine, usually in the form of its hydrochloride salt, is available in various forms including many topical formulations and solutions for injection or infusion. It is also available as a transdermal patch, which is applied directly to the skin.
• Lidocaine hydrochloride 2% epinephrine 1:80,000 solution for injection in a cartridge
• Lidocaine hydrochloride 1% solution for injection
Veterinary use
It is a component of the veterinary drug Tributame along with embutramide and chloroquine used to carry out euthanasia on horses and dogs.
See also
• Dimethocaine (has some DRI activity)
• Lidocaine/prilocaine
• Procaine
• Mexiletine
How It Works
- Lidocaine may be used as a local anesthetic or in the treatment of arrhythmias.
- Lidocaine works by blocking the influx of sodium ions into the membrane surrounding nerves. This prevents the initiation and conduction of impulses along the nerve, which results in an anesthetic e...
- Lidocaine belongs to the class of medicines known as class-1b antiarrhythmic drugs. It may …
- Lidocaine may be used as a local anesthetic or in the treatment of arrhythmias.
- Lidocaine works by blocking the influx of sodium ions into the membrane surrounding nerves. This prevents the initiation and conduction of impulses along the nerve, which results in an anesthetic e...
- Lidocaine belongs to the class of medicines known as class-1b antiarrhythmic drugs. It may also be called an anesthetic.
Upsides
- Lidocaine prevents the transmission of pain impulses and is used as a local anesthetic to numb specific areas of the body before minor surgical, dental, or other procedures. The effect of lidocaine...
- May be combined with epinephrine which increases the intensity and duration of the anesthetic effect and constricts the blood vessels, reducing bleeding.
- Lidocaine prevents the transmission of pain impulses and is used as a local anesthetic to numb specific areas of the body before minor surgical, dental, or other procedures. The effect of lidocaine...
- May be combined with epinephrine which increases the intensity and duration of the anesthetic effect and constricts the blood vessels, reducing bleeding.
- Lidocaine may also be used to produce regional anesthesia (a loss of sensation in a specific region of the body; for example, an arm or a leg or the entire pelvic region).
- Lidocaine antiarrhythmic may be used in the emergency treatment of cardiac arrest, ventricular arrhythmias, or other severe heart conditions.
Downsides
- If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include: 1. Skin redness, itching, a rash, or a feeling of warmth may occur in the region where lidocaine has been administered subcutaneously when used for local anesthesia. Bruising, bleeding, swelling, and pain at the inje…
Bottom Line
- Lidocaine is used as a local or regional anesthetic to prevent pain signals from being transmitted to the brain during surgical, dental, and other procedures. Lidocaine antiarrhythmic is used in the emergency treatment of certain heart conditions.
Tips
- Lidocaine will be administered to you by a health professional. Talk to them if you have any concerns.
- Tell all your healthcare providers about all your medical conditions, allergies, and all the medicines you use. Also, let them know if you have had recent surgery.
- When used for local or regional anesthesia, a temporary loss of sensation and a restriction i…
- Lidocaine will be administered to you by a health professional. Talk to them if you have any concerns.
- Tell all your healthcare providers about all your medical conditions, allergies, and all the medicines you use. Also, let them know if you have had recent surgery.
- When used for local or regional anesthesia, a temporary loss of sensation and a restriction in the ability to move the affected body area may occur.
Response and Effectiveness
- When administered as a local or regional anesthetic, lidocaine is effective almost immediately. The duration of effect is approximately 60 to 90 minutes.
- Higher dosages or volumes of lidocaine will result in a shorter time to the onset of anesthesia, a longer duration of effect, a greater degree of muscle relaxation, and an increase in the spread of...
- When administered as a local or regional anesthetic, lidocaine is effective almost immediately. The duration of effect is approximately 60 to 90 minutes.
- Higher dosages or volumes of lidocaine will result in a shorter time to the onset of anesthesia, a longer duration of effect, a greater degree of muscle relaxation, and an increase in the spread of...
- The duration of action of lidocaine may be prolonged in people with liver disease.
Interactions
- Medicines that interact with lidocaine may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works for, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with lidocaine. An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of the medications; however, sometimes it does. Speak to your doctor about how drug interactions should be mana…
References
- Lidocaine injections [Package Insert]. Revised 06/2022. McKesson Corporation dba SKY Packaging https://www.drugs.com/pro/lidocaine.html
- Lidocaine antiarrhythmic [Package Insert]. Reviewed 10/2021. ASHP https://www.drugs.com/monograph/lidocaine-systemic.html
Further Information
- Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use lidocaine only for the indication prescribed. Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. Copyright 1996-2022 Drugs.com. Revision date: August 29, 2022. Medical Discl…