
What replaced feudalism in the Renaissance?
May 21, 2020 · What replaced the feudal system? The end of serfdom meant the end of feudalism itself. Europe's manors could no longer function without a labor supply. As feudalism faded, it was gradually replaced by the early capitalist structures of the Renaissance. Land owners now turned to privatized farming for profit. Click to see full answer.
Is feudalism still used today?
Apr 13, 2020 · As feudalism faded, it was gradually replaced by the early capitalist structures of the Renaissance. Land owners now turned to privatized farming for profit. Laborers began demanding - and were given - better wages and additional liberties. Click to see full answer. Likewise, people ask, how did feudalism End in England?
When did the feudal system end?
The Black Death destroyed the manorial system, and the church lost reputation and authority as a result. The medieval social system began to disintegrate. For the next 100 years, fighting forced people to shift their loyalty from feudal lords to the monarch and country; nationalism superseded medieval feudalism.
What is the root word of feudalism?
Apr 10, 2022 · What Replaced The Feudal System? Despite the decline of feudalism, it gradually became a structure of capitalism during the Renaissance. now favor the privatization of farming as a profitable business opportunity. How Did Europe Get Out Of Feudalism? A large number of the feudalistic aspects ceased to exist until about 1500.
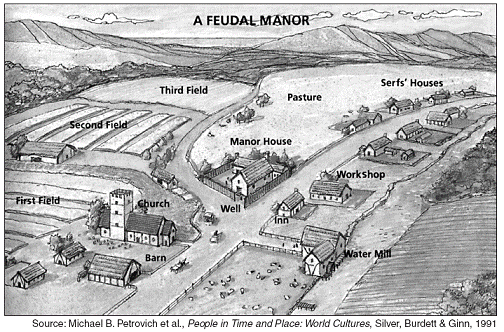
What replaced the feudal system in England?
In the later medieval period, feudalism began to diminish in England with the eventual centralization of government that began around the first quarter of the fourteenth century, and it remained in decline until its eventual abolition in England with the Tenures Abolition Act 1660.
What new government replaced feudalism in Europe?
As a result, absolute monarchy took over Europe as the main power structure. As absolute monarchy spread its dominance those that had ended internal disintegration became great powers. Spain and Portugal were the first among those and were the“superpowers” of the time.
Who replaced the feudal system of economy?
Capitalism replaced the feudal system of economy.Jun 1, 2020
Why did the feudal system in Europe end?
In this lesson you learned about the decline of feudalism in Europe in the 12th to 15th centuries. The major causes of this decline included political changes in England, disease, and wars. Cultural Interaction The culture of feudalism, which centered on noble knights and castles, declined in this period.
What is Japanese feudalism?
Feudalism in medieval Japan (1185-1603 CE) describes the relationship between lords and vassals where land ownership and its use was exchanged for military service and loyalty.Aug 26, 2019
What is feudalism similar to in modern day society?
Both systems are similar in the sense that the lower class always receives the least amount of benefits while the elite (or nobles) receive many benefits and opportunities the lower class are not able to receive (most of the time).
What is feudal system class 10th?
The system consisted of the granting of land for return for military services. In a feudal system, a peasant or worker received a piece of land in return for serving a lord or king, especially during times of war. The peasant now is called as a VASSAL. In the late medieval period, this system became hereditary.
Did India have a feudal system?
Indian feudalism refers to the feudal society that made up India's social structure until the Mughal Dynasty in the 1500s. The Guptas and the Kushans played a major role in the introduction and practice of feudalism in India, and are examples of the decline of an empire caused by feudalism.
Is feudalism still used today?
Answer and Explanation: In large part, feudalism died out by the 20th century. No major countries used the system after the 1920s. In 1956, the United Nations outlawed serfdom, one of the main labor methods of feudalism, because it was too similar to slavery.
What replaced feudalism during the Middle Ages how?
End of the Middle Ages As feudalism faded, it was gradually replaced by the early capitalist structures of the Renaissance. Land owners now turned to privatized farming for profit. Laborers began demanding - and were given - better wages and additional liberties.Jun 26, 2018
How long did feudalism last?
feudalism, also called feudal system or feudality, French féodalité, historiographic construct designating the social, economic, and political conditions in western Europe during the early Middle Ages, the long stretch of time between the 5th and 12th centuries.
What led to the decline of feudalism in England quizlet?
Political changes in England, the bubonic plague, and the Hundred Years' War: Contributed to the decline in the feudal system.
What ended the feudal system?
The Aftereffects of the Hundred Years' War The Hundred Years' War aided in the demise of feudalism by shifting authority away from feudal lords and...
What caused the end of feudalism quizlet?
The fall of the feudal system was aided by political developments in England, the bubonic plague, and the Hundred Years' War. Political development...
How did the Hundred Year War lead to the end of feudalism?
How It Aided in the Abolition of Feudalism Following the Hundred Years' War, the Parliament grew in prominence, while the king's position began to...
How did the Great Schism affect the feudal system?
The Black Death destroyed the manorial system, and the church lost reputation and authority as a result. The medieval social system began to disint...
Why did William the Conqueror create the feudal system?
Feudalism is the name given to the system of administration brought to England by William I following his victory over Harold at the Battle of Hast...
When did feudalism end?
Most of the military aspects of feudalism effectively ended by about 1500 . This was partly since the military shifted from armies consisting of the nobility to professional fighters thus reducing the nobility's claim on power, but also because the Black Death reduced the nobility's hold over the lower classes.
When was feudalism first used?
The adjective feudal was in use by at least 1405, and the noun feudalism, now often employed in a political and propagandistic context, was coined by 1771, paralleling the French féodalité ( feudality ).
What are some examples of feudalism?
For feudalism in other societies, as well as that of the Europeans, see Examples of feudalism. Investiture of a knight (miniature from the statutes of the Order of the Knot, founded in 1352 by Louis I of Naples ). Orava Castle in Slovakia. A Medieval castle is a traditional symbol of a feudal society. Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was ...
Who invented feudalism?
In 1771, in his History of Manchester, John Whitaker first introduced the word "feudalism" and the notion of the feudal pyramid. The term "feudal" or "feodal" is derived from the medieval Latin word feodum.
What is a medieval castle?
A Medieval castle is a traditional symbol of a feudal society. Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, and cultural customs that flourished in Medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships ...
Where did feudalism take place?
Some have taken the feudalism analogy further, seeing feudalism (or traces of it) in places as diverse as China during the Spring and Autumn period (771-476 BCE), ancient Egypt, the Parthian Empire , the Indian subcontinent and the Antebellum and Jim Crow American South.
Who was the most influential historian of the 20th century?
The French historian Marc Bloch, arguably the most influential 20th-century medieval historian, approached feudalism not so much from a legal and military point of view but from a sociological one, presenting in Feudal Society (1939; English 1961) a feudal order not limited solely to the nobility.
How does the feudalism work?
Feudalism is a system of land ownership and duties. With feudalism, all the land in a kingdom was the king’s. However, the king would give some of the land to the lords or nobles who fought for him, called vassals. These gifts of land were called fiefs.
Is feudalism good or bad?
Feudalism provided some unity and security in local areas, but it often did not have the strength to unite larger regions or countries. Small feudal governments could not afford big projects, such as building aqueducts, sewers, or fleets of ships that might benefit society.
What are the effects of feudalism?
The consequence of the feudal system was the creation of very localised groups of communities which owed loyalty to a specific local lord who exercised absolute authority in his domain. As fiefs were often hereditary, a permanent class divide was established between those who had land and those who rented it.
What are causes of feudalism?
As the Vikings invaded western European kingdoms, local nobles took over the duty of raising armies and protecting their property. Power passed from kings to local lords, giving rise to a system known as feudalism.
What replaced the feudal system?
The end of serfdom meant the end of feudalism itself. Europe’s manors could no longer function without a labor supply. As feudalism faded, it was gradually replaced by the early capitalist structures of the Renaissance.
Do any countries still use feudalism?
Feudalism does still exist today in part of the world, but is better known as ‘Neo-feudalism’. An example is in the United States- where the higher class is getting richer, middle class is not going anywhere and there are more poor people now than ever.
Did the feudal system end?
Feudalism was a political, economic and social system that established itself in Western Europe with the Carolingian Empire (IX century) and with the death of Charlemagne. The official abolition of feudalism took place in 1806 by Napoleon Bonaparte, more than three centuries after the end of the Middle Ages.

Overview
Etymology
The root of the term "feudal" originates in the Proto-Indo-European word *péḱu, meaning "cattle", and possesses cognates in many other Indo-European languages: Sanskrit pacu, "cattle"; Latin pecus (cf. pecunia) "cattle", "money"; Old High German fehu, fihu, "cattle", "property", "money"; Old Frisian fia; Old Saxon fehu; Old English feoh, fioh, feo, fee. The term "féodal" was first used in 17th-ce…
Definition
There is no commonly accepted modern definition of feudalism, at least among scholars. The adjective feudal was in use by at least 1405, and the noun feudalism, now often employed in a political and propagandistic context, was coined by 1771, paralleling the French féodalité (feudality).
According to a classic definition by François-Louis Ganshof(1944), feudalism describes a set of …
History
Feudalism, in its various forms, usually emerged as a result of the decentralization of an empire: especially in the Carolingian Empire in 8th century AD, which lacked the bureaucratic infrastructure necessary to support cavalrywithout allocating land to these mounted troops. Mounted soldiers began to secure a system of hereditary rule over their allocated land and their power ov…
Feudal society
The phrase "feudal society" as defined by Marc Bloch offers a wider definition than Ganshof's and includes within the feudal structure not only the warrior aristocracy bound by vassalage, but also the peasantrybound by manorialism, and the estates of the Church. Thus the feudal order embraces society from top to bottom, though the "powerful and well-differentiated social group of the urb…
Historiography
The idea of feudalism was unknown and the system it describes was not conceived of as a formal political system by the people living in the medieval period. This section describes the history of the idea of feudalism, how the concept originated among scholars and thinkers, how it changed over time, and modern debates about its use.
The concept of a feudal state or period, in the sense of either a regime or a period dominated by …
See also
• Bastard feudalism
• Personenverbandsstaat [de]
• Cestui que
• Examples of feudalism
• English feudal barony
Further reading
• Bloch, Marc, Feudal Society. Tr. L.A. Manyon. Two volumes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1961 ISBN 0-226-05979-0
• Ganshof, François Louis (1952). Feudalism. London; New York: Longmans, Green. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
• Guerreau, Alain, L'avenir d'un passé incertain. Paris: Le Seuil, 2001. (Complete history of the meaning of the term.)