What resources did the Aral Sea provide? The Aral Sea Basin
Endorheic basin
An endorheic basin is a closed drainage basin that retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. Such a basin may also be referred t…
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. The name tungsten comes from the former Swedish name for the tungstate mineral scheelite, tung sten or "heavy stone". Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively combined …
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek Μόλυβδος molybdos, meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, b…
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists as a highly toxic pale yellow diatomic gas at standard conditions. As the most electronegative element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with almost all other elements, except for helium and …
Antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite. Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by t…
See 7 key topics from this page & related content

What were the benefits of the Aral Sea?
Restoring delta wetlands and lakes Ultimately, the Northern Aral Sea project will benefit about 1 million people living in Kazakhstan's poorest region, helping to improve living conditions and reduce poverty.
Did the Aral Sea provide drinking water?
It was really a large lake containing fresh water. Until the 1960s, the water in the Aral Sea was potable, which means that it was drinkable. Potable water can also be used to water crops. But even freshwater lakes and rivers have a little salt in them.
What impact has the Aral Sea has on the environment?
The shrinking Aral Sea has also had a noticeable affect on the region's climate. The growing season there is now shorter, causing many farmers to switch from cotton to rice, which demands even more diverted water. A secondary effect of the reduction in the Aral Sea's overall size is the rapid exposure of the lake bed.
What are the economic impacts of the Aral Sea?
The large-scale irrigation projects, which took away too much water from the Aral Sea, have affected the local economy. It is estimated that some 40,000-60.000 fishermen have lost their livelihoods. The large fish canning factories along the rivers hardly catch any fish anymore.
What resources did the Aral Sea supply to the local inhabitants?
5: What resources did the Aral Sea supply to the local inhabitants? Resources that the Aral Sea supplied were fish, water, transportation and recreation.
Will Aral Sea ever return?
Is the Aral Sea recovering? Sort of. The Aral Sea as a whole will never completely recover. The shoreline has radically changed, and the South Aral Sea remains almost completely desiccated.
How has the Aral Sea affected farming?
As the water supply to the Aral Sea decreased, the demand for cotton increased, and the Soviet Union responded by pouring more pesticides and fertilizers onto the land.
How has farmers been affected by the shrinking Aral Sea?
How have farmers been affected by the shrinking of the Aral Sea? A shrinking Aral Sea meant increasingly less water for irrigation and increasingly salty soil. Cotton production fell as the land around the sea became less suitable for agriculture.
How does the Aral Sea affect people?
The gradual retreat of the Aral Sea shoreline and the drying up of the Syr Darya's deltaic region exposed toxic fertilizer and salt residues to the winds, devastating local plant and animal life and causing serious health problems among the human population.
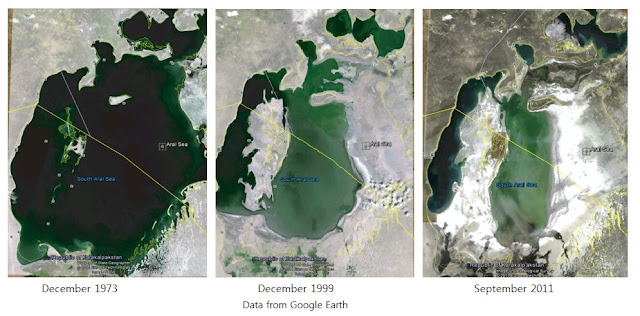
How much has the Aral Sea shrunk?
With no other major source of water, the Aral Sea has been evaporating and shrinking ever since. After 50 years, the lake's area is 25 percent of its original size and it holds just 10 percent of its original volume of water.
What caused the Aral Sea to dry up?
The primary cause behind the shrinking of the Aral Sea is the diversion (for purposes of irrigation) of the main sources of inflowing water, the riverine waters of the Syr Darya (ancient Jaxartes River) in the north and the Amu Darya (ancient Oxus River) in the south, which historically discharged into the Aral Sea.
Is there hope for the Aral Sea?
Some say all hope is lost for the Aral Sea. Once the fourth-largest lake in the world, the Aral Sea has almost disappeared, and it seems nothing can be done to revive its desiccated seabed, restore its natural habitats, and stop the toxic dust storms from decimating communities and livelihoods across the region.
Why was the water supply to the Aral Sea diverted?
Beginning about 1960, the Aral Sea's water level was systematically and drastically reduced, because of the diversion of water from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers for purposes of agricultural irrigation.
What has happened to the water that remains in the Aral Sea?
But more than two decades on, their paths have diverged. Today, the North Aral Sea in Kazakhstan has been revived, with water and economy returning to Aralsk. But the South Aral Sea in Uzbekistan is almost completely desiccated, and its residents are choking on the air.
Can we refill the Aral Sea?
Every river in this vast area drains into dusty deserts, or lakes like the Caspian and Aral Sea. The Aral Sea has been dwindling for decades, but one part of the lake is now growing again.
What would be the best way to replenish the water in the Aral Sea?
What would be the best way to replenish the water in the Aral Sea? Build dams to stop diverting water away from the Aral Sea.
What happened to the Aral Sea?
As the Aral Sea has dried up, fisheries and the communities that depended on them collapsed. The increasingly salty water became polluted with fertilizer and pesticides. The blowing dust from the exposed lakebed, contaminated with agricultural chemicals, became a public health hazard.
When did the South Aral Sea retreat?
Especially large retreats in the eastern lobe of the South Aral Sea appear to have occurred between 2005 and 2009, when drought limited and then cut off the flow of the Amu Darya. Water levels then fluctuated annually between 2009 and 2018 in alternately dry and wet years.
Where did the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers flow?
Before the project, the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers flowed down from the mountains, cut northwest through the Kyzylkum Desert, and finally pooled together in the lowest part of the basin. The lake they made, the Aral Sea, was once the fourth largest in the world.
What was the Soviet Union's water diversion project?
In the 1960s, the Soviet Union undertook a major water diversion project on the arid plains of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. The region’s two major rivers, fed by snowmelt and precipitation in faraway mountains, were used to transform the desert into farms for cotton and other crops.
How much water was diverted from the Aral Sea in the 1960s?
By 1960, the Soviet government had diverted close to 60 cubic kilometers of water from going to the Aral Sea.
What is the climate of the Aral Sea?
The area experiences a desert-continental climate, characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and varying diurnal air temperature. The Aral region receives sparse rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 100 mm. Showers are frequent in autumn and spring. Northwesterly winds are common in winter and autumn, while southwesterly and westerly winds prevail in summer and spring.
What was the main source of water for the Ural Sea?
Until the 1960s, the Ural Sea’s main source of water was rivers Syr Darya and the Amu Darya, accounting for close to four-fifth of its water supply. Rainfall accounted for the rest of the waters. However, when the Soviet government diverted the rivers to irrigate the farms in Ferghana Valley, the water balance was greatly affected due to the high evaporation rate. Evaporation reduced the water level in the lake by the same amount brought in by the rivers. Therefore, the diversion of the rivers caused the sea to shrink slowly over the years. Over the years, the water level has decreased by more than 20 feet. The size of the lake has also declined to less than 10% of the original area.
What is the name of the river that flows into Aral?
During this period, the Amu Darya River, one of Aral’s main inlets, drained into the Caspian Sea. But some geographers, like Nick Middleton, believe the rivers started flowing into Aral in the current geological epoch (Holocene epoch). However, Syr Darya may have started flowing into the lake much earlier.
Where is the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea, also known as Orol Dengizi (Uzbek) or Aral Tengizi (Kazakh) is a saline lake in Central Asia straddling the boundary between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan to the south and north. The lake once covered 68,000 square kilometers between the Kyzylorda and Aktobe regions in Kazakhstan and the Karakalpakstan region of Uzbekistan.
How wide is the Aral Sea?
Before the 1960s, the Aral Sea had a maximum depth of 69 meters (western shores) and a surface area of 68,000 square kilometers. It has a maximum length of 435 kilometers from north to south and was 290 kilometers wide from west to east.
What is the average rainfall in Aral?
The Aral region receives sparse rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 100 mm. Showers are frequent in autumn and spring. Northwesterly winds are common in winter and autumn, while southwesterly and westerly winds prevail in summer and spring.
What were the environmental consequences of the Aral Sea?
Environmental consequences. The rapid shrinkage of the Aral Sea led to numerous environmental problems in the region. By the late 1980s the lake had lost more than half the volume of its pre-1960 water. The salt and mineral content of the lake rose drastically because of that, making the water unfit for drinking purposes and killing off ...
What happened to the fishing industry in the Aral Sea?
The fishing industry along the Aral Sea was thus virtually destroyed. The ports of Aral in the northeast and Mŭynoq in the south were now far from the lake’s shore. A partial depopulation of the areas along the lake’s former shoreline ensued.
What are the health problems in Aral Sea?
As a result, the areas’s inhabitants have suffered health problems at unusually high rates—from throat cancers to anemia and kidney diseases—and infant mortality in the region has been among the highest in the world. Aral Sea: dust storm.
How many islands are there in the Aral Sea?
The Aral Sea derived its name from the Kyrgyz word Aral-denghiz, “Sea of Islands”—an apt designation, as there were more than 1,000 islands of a size of 2.5 acres (1 hectare) or more strewn across its waters. Many of those islands subsequently became joined to the mainland with the shrinking size of the sea.
Where is the Aral Sea?
Area once covered by the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan. The health costs to people living in the area began to emerge soon after water levels had dropped enough to uncover portions of the seabed. Hardest hit were the Karakalpaks, who live in the southern portion of the region.

Overview
Ecology
Despite its former vast size, the Aral Sea had relatively low indigenous biodiversity. However, the Aral Sea basin had an exceptional array of endemic fish subspecies (as well as the three endemic sturgeon species). Most of these still survive in the North Aral Sea, but some, such as the sturgeons, have been decimated or even driven to extinction by the lake's shrinkage. Native fish spe…
Formation
The Amu Darya river flowed into the Caspian Sea via the Uzboy channel until the Holocene. Geographer Nick Middleton believes it did not begin to flow into the Aral Sea until that time.
History
Climate shifts have driven multiple phases of sea-level rise and fall. Inflow rates from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya are affected by glacial melt rates at the rivers' headwaters as well as precipitation within the river basins and cold, dry climates restrict both processes. Geologically driven shifts in the course of the Amu Darya between the Aral Sea and the Sarykamysh basins and anthropoge…
Impact on environment, economy, and public health
The Aral Sea is considered an example of ecosystem collapse. The ecosystems of the Aral Sea and the river deltas feeding into it have been nearly destroyed, largely because of the drastically higher salinity than seawater. The receding sea has left huge plains covered with salt and toxic chemicals from weapons testing, industrial projects, and pesticides and fertilizer runoff. Due to the shrin…
Solution
Many different solutions to the problems have been suggested over the years, varying in feasibility and cost, including:
• Improving the quality of irrigation canals
• Using alternative cotton species that require less water
Institutional bodies
The Interstate Commission for Water Coordination of Central Asia (ICWC) was formed on 18 February 1992 to formally unite Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan in the hopes of solving environmental, as well as socioeconomic problems in the Aral Sea region. The River Basin Organizations (the BVOs) of the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers were institutions called upon by the ICWC to help manage water resources. According to the ICWC, t…
Vozrozhdeniya Island
Vozrozhdeniya (Russian for rebirth) Island is a former island of the Aral Sea or South Aral Sea. Due to the ongoing shrinkage of the Aral, it became first a peninsula in mid-2001 and finally part of the mainland. Other islands like Kokaral and Barsa-Kelmes shared a similar fate. Since the disappearance of the Southeast Aral in 2008, Vozrozhdeniya Island effectively no longer exists as a …