
The AED is designed to shock VF or VT (ventricular tachycardia Fast heart beat rhythm of the ventricles.Ventricular Tachycardia
Full Answer
What are the shockable rhythms an AED recognizes?
The AED recognized the Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (MVT) as shockable rhythm above a value ranging from 140 to 230 beats per minute (BPM). For Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (PVT) not all AEDs
What are the two rhythms an AED will only shock?
The two heart rhythms the AED looks for are ventricular fibrillation (chaotic, quivering of the heart, also called v-fib) and ventricular tachycardia (life-threatening rapid heartbeat, also called v-tach). If the AED identifies one of these two rhythms, it will instruct the rescuer a shock is advised and charge the AED.
Does an AED restore rhythm to the heart?
An AED is a type of computerized defibrillator that automatically analyzes the heart rhythm in people who are experiencing cardiac arrest. When appropriate, it delivers an electrical shock to the heart to restore its normal rhythm. The conversion of a ventricular arrhythmia to its normal rhythm by an electrical shock is called defibrillation.
How does an AED affect the rhythm of the heart?
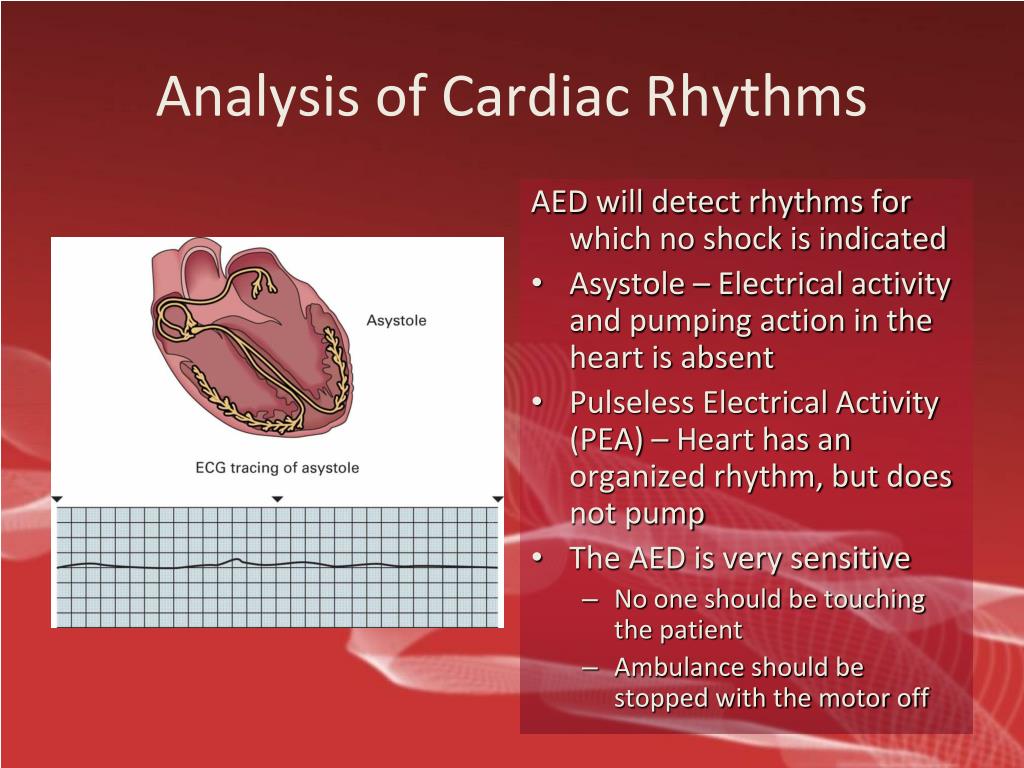
Every two minutes, the AED will continue to look for a shockable rhythm and provide a shock if the rhythm changes to a shockable one. Asystole, also referred to as cardiac flatline, is the total cessation of electrical activity in the heart. This condition may occur after a prolonged period of v-fib or because the heart muscle has actually died.
How many joules does an AED shock?
When a shockable rythm is detected, the AED’s battery charges its capacitors in preparation to shock anywhere from 150 to 360 Joules.
What is an AED pad?
Many people know what an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is, but not necessarily how it works. When AED pads are attached to a person’s chest, the AED immediately analyzes whether that person’s heart is in a cardiac arrhythmia. The main two arrhythmias that will prompt an AED to shock are Ventricular Tachycardia (V-Tach) ...
What is the power of one joule?
To give you an idea of this power, one joule is approximately the energy released when an apple hits the ground from a one meter drop. This shock depolarizes the heart muscle and eliminates the fatal arrythmia by completely stopping the heart altogether.
How many chest pads are used for AED?
Automated External Defibrillators are becoming more common in public places and even at home. An AED is applied to the casualty using two chest pads. These pads are placed as shown in the diagram. The chest pads allow the machine to deliver an electrical shock through the heart muscle.
What is an AED?
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a device used to deliver an electrical shock to a casualty in cardiac arrest.
How does a defibrillator work?
Defibrillation works by stopping chaotic electrical activity in the heart. The most common abnormal rhythm which causes cardiac arrest is known as Ventricular Fibrillation (VF). An electrical shock can stop VF and allow the heart to restore its natural rhythm. There are many causes of Ventricular Fibrillation.
What do a heart monitors do?
They also act as ‘sensors’ and allow the machine to record and interpret the electrical activity of the heart.
Who is John Furst?
JOHN FURST is an experienced emergency medical technician and qualified first aid and CPR instructor. John is passionate about first aid and believes everyone should have the skills and confidence to take action in an emergency situation.
Do you have to be logged in to post a comment?
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest and Ventricular Fibrillation
When SCA occurs, the victim’s heart goes into a pattern known as ventricular fibrillation. This means that the brain is still sending electrical impulses to the heart muscle, but the ventricles quiver in a sort of uncoordinated twitching instead of beating normally.
A Normal Rhythm Has Been Restored
Ideally, the AED won’t advise a shock because the heart has resumed a normal pattern with chest compressions and rescue breaths and/or with the delivery of the first shock. An AED will never shock a person with a normal heart rhythm.
AED No Shock Advised – Remember to Stay Calm
The important thing is to keep calm and listen carefully to the instructions provided. Automated external defibrillators are designed to analyze the heart pattern of cardiac arrest victims and deliver a shock if appropriate.
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is a poorly perfusing rhythm; patients may present with or without a pulse. Most patients with this rhythm are unconscious and pulseless and defibrillation is needed to “reset” the heart so that the primary pacemaker (usually the Sinoatrial Node) can take over.
What is the purpose of defibrillation in cardiac life support?
Much of Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) is about determining the right medication to use at the appropriate time and deciding when to defibrillate. Along with high-quality CPR, emergency medicines and defibrillation are the only two interventions that are likely to restart the arrested heart. Defibrillation a powerful tool in the hands of the ACLS practitioner and it is important to know when to use defibrillation to reset the abnormal rhythm. Determining the underlying cause of an arrest is the most important goal in ACLS, and defibrillation can reset and restart the heart, buying the practitioner time to explore and treat the Hs and Ts accordingly.
What does V-FIB look like?
In this case, the heart quivers ineffectively and no blood is pumped out of the heart. On the monitor, v-fib will look like a frenetically disorganized wavy line. Ventricular fibrillation may be fine or coarse; coarse ventricular fibrillation is more likely to convert after defibrillation than fine v-fib.
What are the two rhythms that are not amenable to shock?
surgical evaluation. Rhythms that are not amenable to shock include pulseless electrical activity (PEA) and asystole. In these cases, identifying primary causation, performing good CPR, and administering epinephrine are the only tools you have to resuscitate the patient.
Is ventricular fibrillation fine or coarse?
Ventricular fibrillation may be fine or coarse; coarse ventricular fibrillation is more likely to convert after defibrillation than fine v-fib. Fine v-fib is sometimes mistaken for asystole. As the treatments for asystole and ventricular fibrillation are different, it is important to differentiate between the two.
