What does RNP 5 mean?
The RNP types (e.g.: RNP 5, RNP 1, RNP 0.3) specify the navigation performance accuracy of all the user and navigation system combinations within an airspace. RNP types specify the minimum navigation performance accuracy required in an airspace and is used for airspace planners to design the routes.
What is RNP used for?
Required Navigation Performance ( RNP ) is similar to Area Navigation ( RNAV ); but, RNP requires on-board navigation performance monitoring and alerting capability to ensure that the aircraft stays within a specific containment area.
What does RNP10 mean?
An RNP of 10 means that a navigation system must be able to calculate its position to within a circle with a radius of 10 nautical miles. An RNP of 0.3 means the aircraft navigation system must be able to calculate its position to within a circle with a radius of 3/10 of a nautical mile.
What does rnp2 mean?
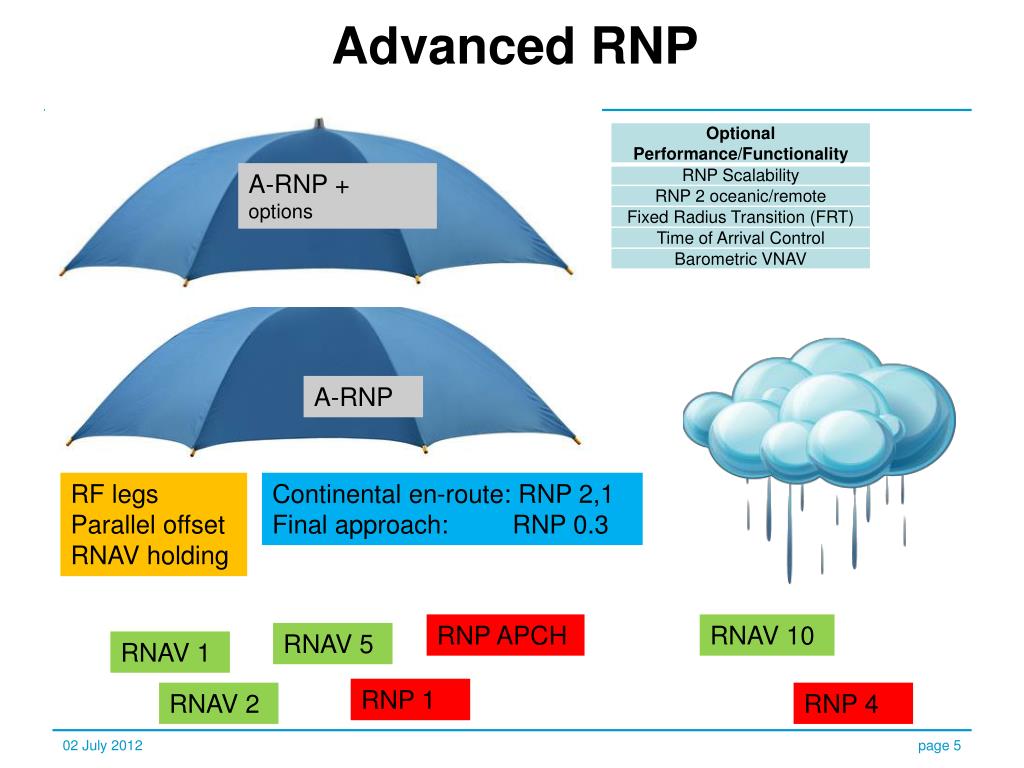
RNP 2 is for en-route oceanic remote and en-route continental navigation applications. RNP 1 is for arrival and initial, intermediate and missed approach as well as departure navigation applications. Advanced RNP is for navigation in all phases of flight.
What causes positive RNP?
A positive result for RNP antibodies is consistent with a connective tissue disease.
What is an RNP blood test?
This test measures the level of Anti-Ribonucleoprotein or RNP antibodies in a blood sample. RNP is a type of autoantibody. In people with autoimmune disorders, these antibodies are produced by the immune system and attack the body's own cells and tissues.
What is advanced RNP?
▪ The Advanced RNP navigation specification permits. the implementation of higher density routes where there is insufficient ground navigation infrastructure for conventional routes. ▪ Advanced RNP is designed for operation on en-route, arrival and departure routes, and approaches.
What does RNAV 5 mean?
b. B-RNAV/RNAV 5 is defined as RNAV that meets a track keeping accuracy equal to or better than +/-5 nautical mile (NM) for 95 percent of the flight time. This value includes signal source error, airborne receiver error, display system error, and flight technical error.
What is the full form of RNP?
RNP stands for “Required Navigational Performance.” It is a metric of system navigational capability.
Where is RNP 10 required?
The areas that require RNP10 include the Central East Pacific (between Hawaii and the US west coast) and Northern Pacific (NOPAC), each utilize 50 nm lateral spacing. RNP10 is also applied in the Southern Pacific (SOPAC) Regions.
Is RNP and RNAV the same?
While both RNAV navigation specifications (NavSpecs) and RNP NavSpecs contain specific performance requirements, RNP is RNAV with the added requirement for onboard performance monitoring and alerting (OBPMA). RNP is also a statement of navigation performance necessary for operation within a defined airspace.
Can you fly RNAV approach without GPS?
Approved RNAV systems using DME/DME/IRU, without GPS/WAAS position input, may only be used as a substitute means of navigation when specifically authorized by a Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM) or other FAA guidance for a specific procedure.
What is difference between RNAV and RNP?
While both RNAV navigation specifications (NavSpecs) and RNP NavSpecs contain specific performance requirements, RNP is RNAV with the added requirement for onboard performance monitoring and alerting (OBPMA). RNP is also a statement of navigation performance necessary for operation within a defined airspace.
Is RNP a GPS approach?
Virtually all GPS approaches require an RNP (Required Navigational Performance) of 0.3, which means an aircraft tracking the final approach course with a centered needle can be expected to be within 0.3 nm of the centerline 95 percent of the time. All IFR-certified GPS units meet 0.3 RNP.
What is the difference between PBN and RNP?
PBN is Performance Based Navigation based on performance requirements of the aircraft on a route or approach or in designated airspace. RNP is required navigation performance which basically means the onboard monitoring and alerting system your aircraft has.
What is RNP made of?
An assembly of molecules containing both protein and RNA. Often used to describe Cas9 protein bound to guide RNA (gRNA), which together form an active enzyme.
What is RNP 4?from quora.com
RNP-4 and RNP-10 are oceanic required navigational performance standards. They are requirements that aircraft must meet to fly in certain oceanic airspace. RNP standards specify how accurately an aircraft must know its position on earth (accuracy), how sure it must be of that position (integrity), as well as as availability, continuity, and functionality standards.
What does ANP mean in a flight?from quora.com
The aircraft's FMC (Flight Management Computer) or GPS, will determine it's ANP (Actual Navigation Performance ) and ANP must be within (smaller than) RNP at least 95% of the time. If unable, the FMC will issue an Advisory or a Caution (if in the approach phase of the flight).
What happens if your aircraft does not meet RNP 4?from quora.com
If your aircraft does not meet RNP-4 standards, you can still be permitted to fly those routes, but controllers will be forced to increase spacing between you and other aircraft.
What is RNAV in aviation?from quora.com
RNAV is short for aRea NAVigation. A type of aircraft own ship navigation, known as Performance Based Navigation (PBN).
What is RNP blood test?
The RNP blood test is used to detect antibodies that are created when the signs or symptoms of connective tissue diseases are present. Called Mixed Connective Tissue Disease [MCTD], it’s actually several diseases that target the tissues which support the different components of the body.
What to do after a positive RNP?
The most important thing you can do after an RNP blood test that is positive is to find a way to reduce stress. The signs and symptoms of the disease are often triggered by stress and relaxation is known to help. Some have found that meditation exercises can be particularly beneficial when managing an outbreak.
Can you get a positive RNP test?
The issue that many people face with a positive RNP test is that there is a lot of conflicting information that can be found online today about what positive results may mean. People can be diagnosed with an RNP test result of 3. It’s also been said that no healthy person can have a high RNP blood test result, yet most providers confirm the first test result with a second result to be certain.
Can you get a false positive on a RNP?
There may also be a false positive result from the RNP blood test for a variety of different reasons. Because of this, it is not uncommon for a medical provider to order a second blood test just to confirm the results from the first one. The issue that many people face with a positive RNP test is that there is a lot of conflicting information ...
Can RNP come back negative?
The RNP blood test results will either come back as positive or negative. The antibodies will either be present or they will not be present. If the results come back as normal, then there is another explanation for the bothersome symptoms that are being experienced.
Who processes RNP applications?
RNP applications are processed by the operator’s local FSDO, but a regional navigation specialist at an FAA NextGen office (AFS-400) conducts a more in-depth review of the submitted documents. The FAA’s review process for RNP and NAT HLA has become more streamlined. But the FAA scrutiny is now more detailed and intensive.
What is the NM for RNP 10?
RNP-10 lateral separation (50 NM) may be applied within the Oakland OCA/FIR between RNP-10 approved aircraft. RNP-10 approval is required for all PACOTS and for all aircraft operating within the CEP at FL290 through FL410. Non-approved aircraft can expect FL280 and below or FL430 and above, traffic permitting.
How much lateral separation is required for RNP-10?
RNP-10 airspace reduces the lateral separation on certain oceanic routes/areas from 90 NM to 50 NM between aircraft, and in some airspace to 30 NM (when RNP-4 and FANS 1/A+ equipped and authorized).
Is RNP 10 authorized in Gulf of Mexico?
In Gulf of Mexico airspace, aircraft not authorized for RNP-10 or RNP-4 operations are required to follow specific procedures for requesting operation in this airspace. See the FAA's AIP ENR 7.4.
What is RNP capability?
RNP capability of the aircraft is a major component in determining the separation criteria to ensure that the overall containment of the operation is met
What is RNAV in RNP?
In the U.S., RNP APCH procedures are titled RNAV (GPS) and offer several lines of minima to accommodate varying levels of aircraft equipage: either lateral navigation (LNAV), LNAV/vertical navigation (LNAV/VNAV), Localizer Performance with Vertical Guidance (LPV), and Localizer Performance (LP). GPS with or without Space-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) (for example, WAAS) can provide the lateral information to support LNAV minima. LNAV/VNAV incorporates LNAV lateral with vertical path guidance for systems and operators capable of either barometric or SBAS vertical. Pilots are required to use SBAS to fly to the LPV or LP minima. RF turn capability is optional in RNP APCH eligibility. This means that your aircraft may be eligible for RNP APCH operations, but you may not fly an RF turn unless RF turns are also specifically listed as a feature of your avionics suite. GBAS Landing System (GLS) procedures are also constructed using RNP APCH NavSpecs and provide precision approach capability. RNP APCH has a lateral accuracy value of 1 in the terminal and missed approach segments and essentially scales to RNP 0.3 (or 40 meters with SBAS) in the final approach. (See Paragraph 5-4-18, RNP AR Instrument Approach Procedures.)
What are PBN requirements?
In the U.S., PBN requirements like Lateral Accuracy Values or NavSpecs applicable to a procedure will be depicted on affected charts and procedures. In the U.S., a specific procedure's Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) requirements will be prominently displayed in separate, standardized notes boxes. For procedures with PBN elements, the "PBN box" will contain the procedure's NavSpec (s); and, if required: specific sensors or infrastructure needed for the navigation solution, any additional or advanced functional requirements, the minimum RNP value, and any amplifying remarks. Items listed in this PBN box are REQUIRED to fly the procedure's PBN elements. For example, an ILS with an RNAV missed approach would require a specific capability to fly the missed approach portion of the procedure. That required capability will be listed in the PBN box. The separate Equipment Requirements box will list ground-based equipment and/or airport specific requirements. On procedures with both PBN elements and ground-based equipment requirements, the PBN requirements box will be listed first (See FIG 5-4-1.)
What is an advanced RNP?
Advanced RNP (A-RNP): Advanced RNP is a NavSpec with a minimum set of mandatory functions enabled in the aircraft's avionics suite. In the U.S., these minimum functions include capability to calculate and perform RF turns, scalable RNP, and parallel offset flight path generation.
What is the lateral accuracy value of RNP 2?
RNP 2 will apply to both domestic and oceanic/remote operations with a lateral accuracy value of 2
Is RNP 1 automatic?
For example, RNP 1 is different from RNAV 1, and an RNP 1 eligibility does NOT mean automatic RNP 2 or RNAV 1 eligibility. As a safeguard, the FAA requires that aircraft navigation databases hold only those procedures that the aircraft maintains eligibility for. If you look for a specific instrument procedure in your aircraft's navigation database ...
Can you fly an RNAV?
Pilots are not authorized to fly a published RNAV or RNP procedure (instrument approach, departure, or arrival procedure) unless it is retrievable by the procedure name from the current aircraft navigation database and conforms to the charted procedure.
What is RNP 5?
Some States have implemented RNP 5 (Europe: BRNAV) for an interim period as a derivative of RNP 4, in order to permit the continued operation of present navigation equipment without modification of existing route structures. 3.
What is RNP in aviation?
The concept of RNP applies to navigation performance and therefore affects both the airspace and the aircraft. The RNP type describes the navigation performance that is expected to be achieved within that airspace for at least 95% of the time by the population of aircraft operating within that airspace.
What is the RNP?
RNP (also called nRNP and U1RNP) is a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein that contains 3 protein autoantigens (called A, C, and 68 kD). Sera that contain RNP antibodies react predominately with the A and 68-kD autoantigens. Antibodies to RNP occur in approximately 50% of patients with lupus erythematosus ...
What is RNP in medical terms?
RNP is 1 of 4 autoantigens commonly referred to as extractable nuclear antigens (ENA). The other ENAs are SS-A/Ro, SS-B/La, and Sm. Each ENA is composed of 1 or more proteins associated with small nuclear RNA species (snRNP) ranging in size from 80 to approximately 350 nucleotides. Antibodies to ENAs are common in patients with connective tissue diseases (systemic rheumatic diseases) including LE, MCTD, Sjogren syndrome, scleroderma (systemic sclerosis), and polymyositis/dermatomyositis.
What is a positive RNP antibody?
Although strongly associated with connective tissue diseases, RNP antibodies are not considered a "marker" for any particular disease except in the following situation: when found in isolation (ie, dsDNA antibodies and Sm antibodies are not detectable), a positive result for RNP antibodies is consistent with the diagnosis of mixed connective tissue disease.
What is RNP in MCTD?
Antibodies to RNP occur in approximately 50% of patients with lupus erythematosus (LE) and in patients with other connective tissue diseases, notably mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD). MCTD is characterized by high levels of RNP antibodies without detectable Sm (Smith) or double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) antibodies.
Can RNP antibodies be tested?
Evaluating patients with signs and symptoms of a connective tissue disease in whom the test for antinuclear antibodies is positive. Testing for RNP antibodies is not useful in patients without demonstrable antinuclear antibodies.
What is RNAV 1?
RNAV 1. Typically RNAV 1 is used for DPs and STARs and appears on the charts. Aircraft must maintain a total system error of not more than 1 NM for 95 percent of the total flight time.
What are the two main categories of PBN?
Within PBN there are two main categories of navigation methods or specifications: area navigation (RNAV) and required navigation performance ( RNP ).
What is PBN in aviation?
PBN also introduces the concept of navigation specifications (NavSpecs) which are a set of aircraft and aircrew requirements needed to support a navigation application within a defined airspace concept.
What is a waypoint in RNAV?
Waypoints may be a simple named point in space or associated with existing navaids, intersections, or fixes . A waypoint is most often used to indicate a change in direction, speed, or altitude along the desired path. RNAV procedures make use of both fly-over and fly-by waypoints. Fly-by waypoints.
Can RNAV be used for navigation?
Unless otherwise specified, a suitable RNAV system cannot be used for navigation on procedures that are identified as not authorized (“NA”) without exception by a NOTAM. For example, an operator may not use a RNAV system to navigate on a procedure affected by an expired or unsatisfactory flight inspection, or a procedure that is based upon a recently decommissioned NAVAID.
Can a pilot substitute for a NAVAID?
Pilots may not substitute for the NAVAID (for example, a VOR or NDB) providing lateral guidance for the final approach segment. This restriction does not refer to instrument approach procedures with “or GPS” in the title when using GPS or WAAS. These allowances do not apply to procedures that are identified as not authorized (NA) without exception by a NOTAM, as other conditions may still exist and result in a procedure not being available. For example, these allowances do not apply to a procedure associated with an expired or unsatisfactory flight inspection, or is based upon a recently decommissioned NAVAID.
Is RNP 1 the same as RNAV 1?
For example, RNP 1 is different from RNAV 1, and an RNP 1 eligibility does NOT mean automatic RNP 2 or RNAV 1 eligibility. As a safeguard, the FAA requires that aircraft navigation databases hold only those procedures that the aircraft maintains eligibility for.
