Why does the right lung have 3 lobes?
- The lungs are not equal in size. ...
- The left lung is smaller because of the space taken up by the heart .
- Each lung is separated into lobes branching off the main bronchus; the right lung has three lobes, while the left has only two lobes.
What separates the lungs from the chest wall?
Lung–Chest Wall Interactions. The lung and chest wall move together in healthy people. The pleural space that separates the lung and the chest wall is best thought of as a “potential” space because of its small volume. Because the lung and chest wall move together, changes in their respective volumes are the same.
How many segments does the lung have?
The lung segments extend to the peripheries with the bronchus as the base. There are ten segments in the right lung (upper lobe, three; middle lobe, two; lower lobe, five) and eight segments in the left lung (upper lobe, four; lower lobe, four).
What are lungs separated by?
The right lung has three lobes and is slightly larger than the left lung, which has two lobes. The lungs are separated by the mediastinum. This area contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, and many lymph nodes. The lungs are covered by a protective membrane known as the pleura and are separated from the abdominal cavity by the muscular diaphragm.
See more
What separates the lungs from the?
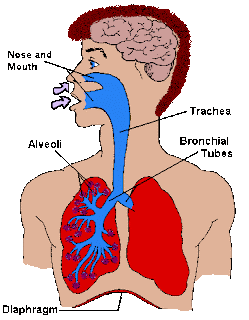
The diaphragm is a thin dome-shaped muscle which separates the thoracic cavity (lungs and heart) from the abdominal cavity (intestines, stomach, liver, etc.). It is involved in respiration, drawing downward in the chest on inhalation, and pushing upward in exhalation.
What separates each lobe of the lungs?
Each lung is divided into lobes by fissures. Both lungs have oblique fissure and the right is further divided by a transverse fissure. The oblique fissure in the left lung separates the superior and the inferior lobe. The oblique and horizontal fissure divides the lungs into superior, middle and inferior lobes.
What separates the lungs from each other and from the mediastinum?
The visceral pleura covers the lung and separates the lobes from one another. The pleural space is a potential space that may compress the lungs or heart with fluid, tumor, or infection. The right and left pleural spaces are separated from one another by the mediastinum.
Is the membrane that separates the lungs?
Pleura. Pleurae are serous membranes that separate the lungs and the wall of the thoracic cavity. The visceral pleura covers the surface of the lungs, and the parietal pleura covers the inside of the thorax, mediastinum, and diaphragm.
Why are the lungs separated into lobes?
These anatomical partitions help prevent mechanical damage or infectious agents from affecting nearby the lobes. oblique fissure separates the two lobes of the left lung.
What are the 3 borders of the lung?
The three borders include the anterior, posterior, and inferior borders. The anterior border of the lung corresponds to the pleural reflection, and it creates a cardiac notch in the left lung.
What does the mediastinum separates?
The mediastinum completely separates the right and left pleural cavities. As in humans and other mammals the esophagus lies dorsal (posterior) to the trachea and its bifurcation and to the pericardium and ventral (anterior) to the thoracic (descending) aorta (Figure 4.8D.).
How is the lung attached to the chest wall?
The pleura includes two thin layers of tissue that protect and cushion the lungs. The inner layer (visceral pleura) wraps around the lungs and is stuck so tightly to the lungs that it cannot be peeled off. The outer layer (parietal pleura) lines the inside of the chest wall.
What is the cavity located between the lungs?
The pleural cavity is the potential space between the two pleurae (visceral-parietal) of the lungs. The pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered membrane structure.
What is the membrane around the lungs called?
The chest cavity is lined by a thin shiny membrane called the pleura, which covers the inside surface of the rib cage and spreads over the lungs as well. Normally, the pleura produces a small amount of fluid which serves as a lubricant to the lungs as they move back and forth against the chest wall during respiration.
What is the membrane on the surface of the lung called?
A pleura is a serous membrane that folds back on itself to form a two-layered membranous pleural sac. The outer layer is called the parietal pleura and attaches to the chest wall. The inner layer is called the visceral pleura and covers the lungs, blood vessels, nerves, and bronchi.
What does the pleural membrane do?
The function of the pleura is to allow optimal expansion and contraction of the lungs during breathing. The pleural fluid acts as a lubricant, allowing the parietal and visceral pleura to glide over each other friction free.
Are lung lobes connected?
Each lung is divided into lobes separated from one another by a tissue fissure. The right lung has three major lobes; the left lung, which is slightly smaller because of the asymmetrical placement of the heart, has two lobes. Internally, each lobe further subdivides into hundreds of lobules.
Why does the left lung have 2 lobes and the right 3?
The left lung has only two formal lobes because of the space taken up in the left side of the chest cavity by the heart, though it does have the lingula, which is similar to a lobe.
How are the left and right lungs different?
The lungs are not equal in size. The right lung is shorter, because the liver sits high, tucked under the ribcase, but it is broader than the left. The left lung is smaller because of the space taken up by the heart (see diaphragm for an image of this).
What are the 5 lobes of the lungs?
The lung consists of five lobes. The left lung has a superior and inferior lobe, while the right lung has superior, middle, and inferior lobes. Thin walls of tissue called fissures separate the different lobes.
Where do all the structures enter and leave the lung?
All these structures enter or leave the lung via the hilum – a wedge shaped area on its mediastinal surface.
Where are the lungs located?
Log In. The lungs are the organs of respiration. They are located in the thorax, either side of the mediastinum. The function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood. They achieve this by bringing inspired air into close contact with oxygen-poor blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
How are the medial surfaces of the lungs suspended?
They are suspended from the mediastinum by the lung root – a collection of structures entering and leaving the lungs. The medial surfaces of both lungs lie in close proximity to several mediastinal structures:
Which bronchioles are terminal?
The segmental bronchi give rise to many conducting bronchioles, which eventually lead into terminal bronchioles. Each terminal bronchiole gives off respiratory bronchioles, which feature thin walled outpocketings that extend from their lumens. These are the alveoli – the site of gaseous exchange.
How many lobes does the right lung have?
The right and left lungs do not have an identical lobular structure. The right lung has three lobes; superior, middle and inferior. The lobes are divided from each other by two fissures: Oblique fissure – Runs from the inferior border of the lung in a superoposterior direction, until it meets the posterior lung border.
What is the role of the lungs in pulmonary embolism?
The lungs are the organs of respiration. They are located in the thorax, either side of the mediastinum. The function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood. They achieve this by bringing inspired air into close contact with oxygen-poor blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
Which bronchus has a higher incidence of foreign body inhalation?
Note: The right bronchus has a higher incidence of foreign body inhalation due to its wider shape and more vertical course.
What is the lobe of the left lung called?
Instead there is a small projection of the upper lobe of the left lung which is known as lingula. Lingula means ‘little’ in Latin. It is also known as tongue of the lung because of its shape. It is further divided into two segments, upper or superior and lower or inferior.
Why is the right lung shorter than the left?
The right lung is shorter than the left lung by about five centimeters. This is due to the diaphragm rising higher on the right side so as to accommodate the liver. However, the right lung is broader due to the inclination of the heart on the left side.
What are the lungs made of?
The lungs are basically made up of parenchymatous tissue that is present in this form on the right and left, which thus, constitutes the right and left lungs. Each lung has a specific number of lung lobes.
Why is the left lung smaller than the right?
The reason why there is no middle lobe, which makes the left lung smaller than the right, is that it makes room for the heart as the human heart is placed slightly towards the left side of the chest. The left lung is divided into two lobes: The upper and lower lobe is divided by a fissure known as an oblique fissure.
How many lobes are there in the lungs?
The lungs are divided into the right lung and left lung. The right lung has three lobes, whereas the left lung has only two lobes. However, all the lobes help in the exchange of gases and aid breathing. The lungs are one of the most important organs present in the body. These are the organs of the respiratory system that are responsible ...
Which lobe of the lung is the smallest?
On the mediastinal surface of the lung, it may be traced backwards to the hilum. The middle lobe is the smallest of all the lung lobes of the right lung. It is wedge-shaped and includes the lower part of the anterior border and the anterior part of the base of the lung.
Where is the fissure in the lung?
This fissure begins on the mediastinal surface of the lung at the upper and posterior part of the hilum and then runs backwards and upwards to the posterior border which it crosses at a point about six centimeters below the apex of the left lung.
What is the lining of the left lung called?
Your left lung is a bit smaller, with two lobes, with your heart nearby. A thin lining called the pleura covers both lungs. Swipe to advance.
What are the tiny hairs inside the lungs called?
Tiny hairs inside (cilia) help trap dust and germs that you cough up, sneeze out, or swallow. The smallest tubes are called bronchioles. These end in tiny air sacs called alveoli. This is where your lungs deliver oxygen to your blood and take back carbon dioxide.
What Are Lungs Made Of?
Your lungs are made of a special sponge-like tissue that stretches easily and keeps its shape without damage. Your right lung is divided into three sections, or “lobes.” Each lobe expands like a balloon when you breathe in and deflates when you breathe out. Your left lung is a bit smaller, with two lobes, with your heart nearby. A thin lining called the pleura covers both lungs.
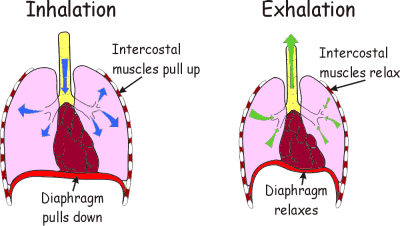
How Do You Breathe In and Out?
Together, this draws air in through your nose and mouth. To breathe out, your diaphragm pushes back up and your chest wall muscles relax to force CO2-rich air out of your lungs.
What happens to your lungs as you age?
Your Lungs as You Age. Muscles like your diaphragm, your main breathing muscle, start to weaken. Lung tissue starts to lose stretchiness, which can narrow your airways. Bones and muscles in your rib cage can shrink, leaving less space for lungs to expand.
What are the tiny sacs in the lung?
When you have lung disease -- whether from smoking, chemicals, mold, bacteria, or a virus like the one that causes COVID-19 -- it’s often the alveoli that start to break down.
How does breathing out air work?
To breathe out, your diaphragm pushes back up and your chest wall muscles relax to force CO2-rich air out of your lungs. Swipe to advance.