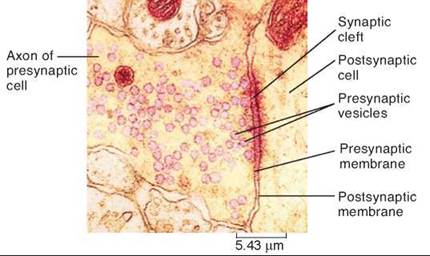
What is the difference between the presynaptic membrane and postsynaptic membrane?
At a synapse, the presynaptic membrane is separated from the postsynaptic membrane by the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitters are released at the presynaptic membrane, while the postsynaptic membrane has receptors for the neurotransmitters.
What is the difference between synapse and neuromuscular junction?
At a synapse, the presynaptic membrane is separated from the postsynaptic membrane by the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitters are released at the presynaptic membrane, while the postsynaptic membrane has receptors for the neurotransmitters. At a neuromuscular junction, the axon terminal is much more structurally complex.
What is the function of the postsynaptic neuron?
Postsynaptic neuron is the neuron that takes part in receiving the neurotransmitter during the nerve impulse transmission. The postsynaptic neuron receives the neurotransmitter at the synapse to facilitate the transmission of the action potential.
What causes vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane?
A) Neurotransmitter causes vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane. B) Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic cell membrane.

What is the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes?
There is a small gap between the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron and the membrane of the postsynaptic cell, and this gap is called the synaptic cleft.
Are presynaptic and postsynaptic cell membranes physically separated?
At a synapse, the presynaptic membrane is separated from the postsynaptic membrane by the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitters are released at the presynaptic membrane, while the postsynaptic membrane has receptors for the neurotransmitters.
What is the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes quizlet?
-A space called synaptic cleft separates the presynaptic terminal from postsynaptic neuron.
Where is the presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane located?
In a chemical synapse, the presynaptic membrane is the cell membrane of an axon terminal that faces the receiving cell. The postsynaptic membrane is separated from the presynaptic membrane by the synaptic cleft.
What does the synaptic gap do?
The main function of the synaptic cleft is to provide space for chemical transmission of messages from the nervous system. The synaptic cleft also provides opportunity for these signals to be modulated, such as increasing or decreasing the duration of the signal or summing of additional signals.
Which is the gap between neurons across which they had to communicate?
Synapse is the gap between two neurons.
What is the area between the presynaptic nerve cell and the postsynaptic muscle cell called?
The area between the pre-synaptic nerve cell and the post-synaptic muscle cell is termed the synaptic cleft. Receptors that bind the neurotransmitter at the post-synaptic cell membrane are voltage-gated.
What is a synapse?
Synapses are microscopic gaps that separate the terminal buttons of one neuron from receptors (usually, located on the dendrites) of another neuron. When neurons communicate, they release chemicals that must travel across this gap to stimulate the post-synaptic receptors.
What are the three parts of a synapse?
Synapses are composed of three main parts: The presynaptic ending that contains neurotransmitters. The synaptic cleft between the two nerve cells. The postsynaptic ending that contains receptor sites.
Where is the postsynaptic membrane usually found?
Excitatory synapses are characterized by a morphological and functional specialization of the postsynaptic membrane called the postsynaptic density (PSD), which is usually located at the tip of the dendritic spine.
What is presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron?
As a convention, the neuron transmitting or generating a spike and incident onto a synapse is referred as the presynaptic neuron, whereas the neuron receiving the spike from the synapse is referred as the postsynaptic neuron (see Figure 2.3).
What is located on the postsynaptic membrane?
The postsynaptic membrane contains specific ACh receptors (AChR), concentrated opposite the active zones. These are one of the best-characterized ionic channels. Their opening allows ions to flow following the specific binding of ACh.
What happens to acetylcholine after it is released from the presynaptic membrane?
What happens to acetylcholine (ACh) after it is released from the presynaptic membrane? ACh is broken down and the choline is reabsorbed.
Where is the postsynaptic membrane located?
Excitatory synapses are characterized by a morphological and functional specialization of the postsynaptic membrane called the postsynaptic density (PSD), which is usually located at the tip of the dendritic spine.
Where is the presynaptic membrane located?
axon terminalA presynaptic membrane is a specialized area of membrane of the axon terminal that faces the plasma membrane of the neuron or muscle fiber with which the axon terminal establishes a synaptic junction.
What kind of membrane transport occurs when presynaptic neurons release neurotransmitters?
Communication at chemical synapses requires release of neurotransmitters. When the presynaptic membrane is depolarized, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and allow Ca2+ to enter the cell. The calcium entry causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release neurotransmitter molecules into the synaptic cleft.
What is the difference between a presynaptic neuron and a post-synapt?
The key difference between presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron is that the presynaptic neuron is involved in releasing the neurotransmitter while the postsynaptic neuron is involved in receiving the neurotransmitter.
What is a Presynaptic Neuron?
The presynaptic neuron is the neuron that opens the synapse and mainly functions in releasing the neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter released to the synapse from the presynaptic neuron. The release of the neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron ending takes place in response to the action potential reaching the end of the axon. Thus, the presynaptic neuron’s primary function is to conduct and transmit the incoming nerve impulse to the synapse.
Which neurons border the synapse?
Both presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons border the synapse
Which neuron receives the neurotransmitter at the synapse?
Postsynaptic neuron is the neuron that takes part in receiving the neurotransmitter during the nerve impulse transmission. The postsynaptic neuron receives the neurotransmitter at the synapse to facilitate the transmission of the action potential.
Which membrane is separated from the post synaptic membrane?
At a synapse, the presynaptic membrane is separated from the postsynaptic membrane by the synaptic cleft. Neurotransmitters are released at the presyna ptic membrane, while the postsynaptic membrane has receptors for the neurotransmitters. At a neuromuscular junction, the axon terminal is much more structurally complex.
Which arrangement of the presynaptic membrane appears prior to the postsynaptic membrane?
The converse arrangement, whereby the presynaptic membrane appears prior to the postsynaptic, is far less frequently encountered (Fig. 8e ). A commonly quoted illustration of this is the membrane-vesicle clusters described in the cervical spinal cord of Xenopus laevis embryos ( Hayes and Roberts, 1973 ). A similar sequence of events has been described as part of the pattern for photoreceptor synaptogenesis in developing chick retina ( McLaughlin, 1976 ).
What is the mechanism by which synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane?
The mechanism by which synaptic vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane is complex and relies on a group of proteins belonging to the SNARE ( SNAP receptor) family. The vesicle and presynaptic membranes ‘kiss’ and the interaction between complimentary proteins creates a small fusion pore. This quickly expands as the lipid membranes unite to form a large opening through which the contents of the vesicle are discharged into the synaptic cleft. After exocytosis the vesicle membrane thus becomes part of the presynaptic membrane. However, a similar amount of membrane is reclaimed from the axon terminal to make new vesicles, so there is no net increase in the size of the axon terminal.
What is the function of neuromuscular junction?
At a neuroglandular junction, one neuron controls or regulates activity of a secretory cell. Neurons also innervate many other cell types, including adipocytes. The axon terminal of a presynaptic cell, into the synaptic cleft, releases chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are contained in synaptic vesicles inside the axon terminal.
What is the synapses of one neuron and another neuron?
Axosomatic synapses have junctions at an axon terminal of one neuron and the cell body of another. In an axodendritic synapse, synaptic contact occurs between an axon terminal of one neuron and a dendrite of another neuron. A neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a neuron and a skeletal muscle cell.
How does chemical signaling occur in a synapse?
Chemical signaling at a synapse occurs when a synaptic vesicle fuses with the presynaptic membrane in response to calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels. Vesicle fusion results in the formation of a fusion pore through which neurotransmitter packaged in the vesicle can escape into the synaptic cleft. The released neurotransmitter then diffuses through the synaptic cleft and binds to ligand-gated receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, which then lead to current flow across the postsynaptic membrane. To understand synaptic transmission, it is necessary to determine the spatiotemporal pattern of channel opening. However, physical limitations preclude direct observation of the dynamics of neurotransmitter release and receptor activation at single synapses. With the vast amount of biophysical and structural data that are now available, it is possible to make constrained models with sufficient biological realism that can be used to answer the following questions about the generation of synaptic responses:
What is the mechanical stability of synapses?
The mechanical stability of synapses and the precise apposition of pre- and postsynaptic membrane domains implies that adhesion molecules might bridge the synaptic cleft and thereby keep both sides of the synapse in register. Ultrastructural studies revealed the presence of different sites of cell-cell adhesion at the synapse—including the linkage across the synaptic cleft, as well as at puncta adherentia that flank the synaptic cleft. A third site of cellular adhesion at central synapses are the end feet of glial cells that tightly enclose the synaptic junctions.
Which protein is released and moves across the synaptic cleft bound to a transport protein?
A) Acetylcholine is released and moves across the synaptic cleft bound to a transport protein.
Which molecule diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to chemically gated channels on?
D) Calcium diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to chemically gated channels on the postsynaptic cell.
How is acetylcholine transported into the postsynaptic neuron?
B) Acetylcholine is transported into the postsynaptic neuron by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
What causes vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane?
A) Calcium influx into the synaptic terminal causes vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane and the release of neurotransmitter.
When does action potential propagation cease?
Action potential propagation in a skeletal muscle fiber ceases when acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft. Which of the following mechanisms ensures a rapid and efficient removal of acetylcholine?
When the action potential reaches the end of the axon terminal, what happens?
D) When the action potential reaches the end of the axon terminal, voltage-gated sodium channels open and sodium ions diffuse into the terminal
Where does the sarcolemma extend?
A) extend from the brain or spinal cord to the sarcolemma of a skeletal muscle fiber
Which membrane releases neurotransmitter by exocytosis?
the presynaptic membrane releases neurotransmitter by exocytosis
Which cell process divides into two branches?
structure: one cell process that divides into two branches, both branches are axons; receptive endings of peripheral branch are dendrites
Where is the myelin sheath produced?
produce the myelin sheath around axons in the CNS
What is the role of phagocytes in the CNS?
act as phagocytes; protects the CNS from disease-causing microorganisms
Which layer surrounds an entire nerve?
connective tissue layer that surrounds an entire nerve
Where do neurons communicate with each other?
neurons communicate with each other at the special junctions
Which nerve fibers are located in the anterior and lateral horns of the spinal cord?
contains motor nerve fibers from the anterior and lateral horns of the spinal cord to a spinal nerve