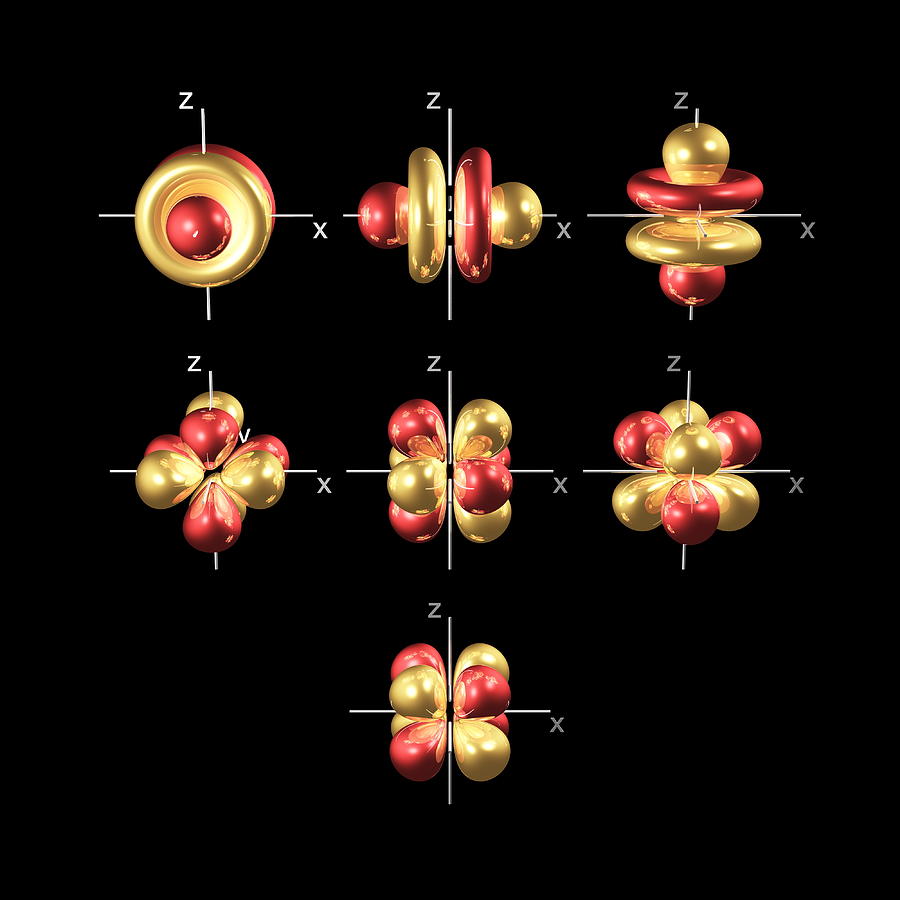Why are the f orbitals rarely shown in textbooks?
The exotic, complex f orbital shapes are rarely shown in textbooks. General (and organic) chemistry traditionally focuses on the lighter elements, but the f orbitals aren't occupied in the ground state until element 58 (cerium).
What is the difference between d orbital and f orbital?
Thus d orbital corresponds to 4 double dumb-belled shapes (d xy, d yz, d zx, d x2y2) with the atomic nucleus at its centre and one dumb belled with dough nut shaped (d z2 ). d orbital has two nodal planes. For f orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 3 and the magnetic quantum number m = -3. -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3.
How many nodal planes does an f orbital have?
d orbital has two nodal planes. For f orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 3 and the magnetic quantum number m = -3. -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3. Hence f orbitals have seven orientations in space. f orbital has complex shapes with the atomic nucleus at its centre. f orbital has three nodal planes.
How many f orbitals are there in the periodic table?
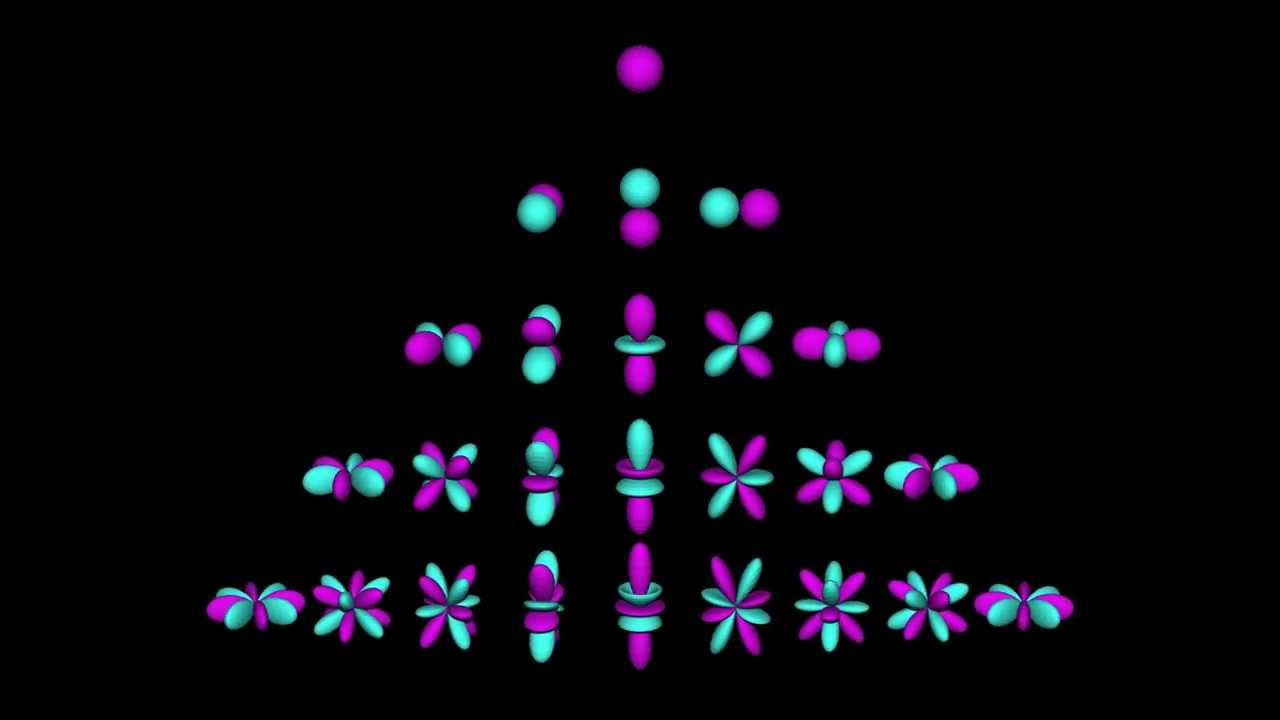
s, p, d, and f orbitals are available at all higher energy levels as well. Fortunately, you will probably not have to memorize the shapes of the f orbitals. Just remember that there seven f orbitals in each level from level 4 and onwards.
What type of orbital is F?
Orbitals and Electron Capacity of the First Four Principle Energy LevelsPrinciple energy level (n)Type of sublevelNumber of orbitals per type4p3d5f77 more rows
Can we draw the shape of f orbitals?
If you absolutely have to draw them, you can draw the shapes as below. One orbital looks like a p orbital with two doughnuts around its middle. Two orbitals have eight lobes pointing towards the corners of a cube. Four orbitals have six lobes oriented in various planes (easiest to draw).
What is the shape of d orbital and f orbital?
An s-orbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a p-orbitals is dumbbell-shaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped. The fifth d orbital is shaped like an elongated dumbbell with a doughnut around its middle. The orbitals in an atom are organized into different layers or electron shells.
Are there how many shapes or types of f orbitals?
The p orbital is a dumbbell shape. There are three p orbitals that differ in orientation along a three-dimensional axis. There are five d orbitals, four of which have a clover shape with different orientations, and one that is unique. There are seven f orbitals, all with different orientations.
What is the shape of f sub level?
tetrahedralThe f orbital has 15 protons to complete a fifth level of a tetrahedral structure. The f orbital is more complex, but follows the same rules based on proton alignment as the p and d orbitals. When completely full it is similar to the d orbital, but cut in half (eight lobes instead of four).
How many orbitals are in F?
7 orbitalsAn f sublevel has 7 orbitals.
What is the shape of G orbital?
The higher g-orbitals (6g and 7g) are more complex since they have spherical nodes. The shapes of the nine 5g orbitals.
What is shape of p orbital?
A p orbital has the approximate shape of a pair of lobes on opposite sides of the nucleus, or a somewhat dumbbell shape.
What is the d orbital shaped like?
The d orbital is a clover shape because the electron is pushed out four times during the rotation when an opposite spin proton aligns gluons with three spin-aligned protons.
How do you draw an orbital shape?
1:082:4512.1.5 Draw the shape of an s orbital and the shapes of the p x , p y and ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe have to be x 2py. And 2pz the x y&z refer to the axis. Along which the orbital lies. So the 2pxMoreWe have to be x 2py. And 2pz the x y&z refer to the axis. Along which the orbital lies. So the 2px orbital lies along the x axis. The 2py orbital lies on the y axis.
How do you draw af orbital?
1:256:05How to Draw Orbital Diagrams - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEnergy level or sublevel. Here is the 2s then we move up and we have 2p 3s. Go back up 3p. And weMoreEnergy level or sublevel. Here is the 2s then we move up and we have 2p 3s. Go back up 3p. And we think we should have the 3d next but it's actually going to be the 4s. Then we go to the 3d.
How do you draw an orbital diagram?
1:0212:12Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration - Basic IntroductionYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo what you want to do is you want to fill each orbital from the bottom all the way to the top. SoMoreSo what you want to do is you want to fill each orbital from the bottom all the way to the top. So the first orbital has two electrons. And you need to put opposite spins.
What shape is orbital?
Orbitals have shapes that are best described as spherical ( l = 0), polar ( l = 1), or cloverleaf ( l = 2) . They can even take on more complex shapes as the value of the angular quantum number becomes larger. Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations. Sponsored by Best Gadget Advice.
How many electrons does an F orbital hold?
This is an f orbital. It is oriented in 7 different ways and each orientation can hold 2 electrons. Therefore f orbitals together have 7 degenerates and hold 14 electrons. So these are the images of d and f orbitals. If you wanted to see a real d and f orbital, the truth is that orbitals are theoretical.
What is the quantum idea of an electron in an atom?
The quantum idea of an electron in an atom is more of a diffuse “wave” or a probability distribution, than of a solid particle in a well-defined position. The orbitals are solutions to the Schrodinger wave equation for the electrons in the electric field defined by the atomic nucleus. These solutions are not ea.
What are the three coordinates of Schr Dinger's wave equations?
The three coordinates that come from Schr�dinger's wave equations are the principal ( n ), angular ( l ), and magnetic ( m) quantum numbers. These quantum numbers describe the size, shape, and orientation in space of the orbitals on an atom. The principal quantum number ( n) describes the size of the orbital. ...
How are electrons held in place?
Electrons are held in place by the balance of two forces. Once is Entanglement and the other the Coulomb Force. The Coulomb Force is shorter range than the Entanglement Force and it what actually keeps Electrons apart. The main attractive force is the Entanglement force which is a form of polar gravity.
What is the name of the orbital of fluorine?
It’s called an f orbital; that’s its name (with a lower-case f, BTW). Unless you really did intend a capital F and meant “What is the name of a fluorine orbital”, in which case the answer is that fluorine has lots of orbitals, but only those up through 2p are occupied.
What are the D orbital atoms?
The d-orbital atoms are the so-called transition metals (scandium to zinc - period 4 - and yttrium to cadmium - period 5). f-orbitals make a late appearance in period 6 and above, and these elements are the lanthanides and actinides. The structure of the periodic table matches this number and sequence of orbitals.