What is the Phillips curve theory?
What is the Phillips Curve? The Phillips curve is an economic concept developed by A. W. Phillips stating that inflation and unemployment have a stable and inverse relationship. The theory claims that with economic growth comes inflation, which in turn should lead to more jobs and less unemployment.
Does Phillips curve really exist?
Though the Phillips curve has played an important role in the decision-making process on macroeconomic policy, there have been critics who doubted the existence of the “Phillips curve”. Despite a number of studies on the Phillips curve, there has been a lack of research that probed the hypothesis in the developing countries' context.
Can the Phillips curve help forecast inflation?
Yet, some Phillips curve specifications can offer systematic improvements over a univariate model; in other words, measures of economic activity do help to forecast inflation.
Why the Phillips curve is flattening in the US?
With inflation having only modestly picked up in the past few years as the economy has become more robust, many believe the Phillips curve relationship has weakened, with the curve becoming flatter. I show that the flattening can be due to very different types of structural changes and that knowing the type of change that has occurred is crucial for choosing the appropriate monetary policy.
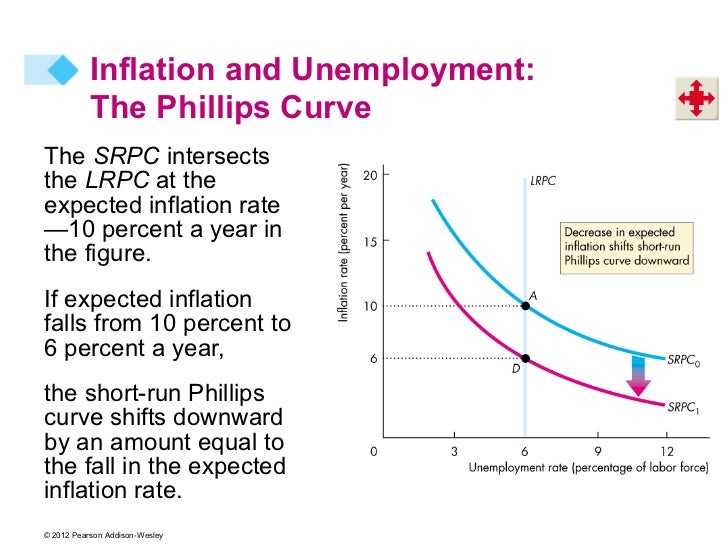
What shifts the long-run Phillips curve to the left?
For example, if frictional unemployment decreases because job matching abilities improve, then the long-run Phillips curve will shift to the left (because the natural rate of unemployment decreases).
What shifts the short-run Phillips curve upwards?
The Phillips curve shows the short-run relationship between inflation and unemployment. As price level rises, unemployment decreases (point A to point B on Phillips curve). Movement up along the supply curve is mirrored by movement up along the Phillips curve.
What causes the Phillips curve to shift to the right?
A decrease in energy prices, a positive supply shock, would cause the AS curve to shift out to the right, yielding more real GDP at a lower price level. This would shift the Phillips curve down toward the origin, meaning the economy would experience lower unemployment and a lower rate of inflation.
What causes the short-run Phillips curve to shift up or down?
If inflation expectations increase, the Phillips curve shifts upward. Of course, a positive supply shock can shift the Phillips curve down as inflation expectations fall.
When did the Phillips curve shift to the right?
Shift in Phillips Curve to the right (the 1970s) In the early 2000s , the trade-off seemed to improve. Helped by low global inflation, unemployment in the UK fell without any rise in inflation. Some argued this period of stability had ended the boom and bust cycles with the classic trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
Why was the Phillips curve broken in the 1970s?
In the 1970s, there seemed to be a breakdown in the Phillips curve as we experienced stagflation (higher unemployment and higher inflation). The Phillips Curve was criticised by monetarist economists who argued there was no trade-off between unemployment and inflation in the long run.
Why is there a trade-off between unemployment and inflation?
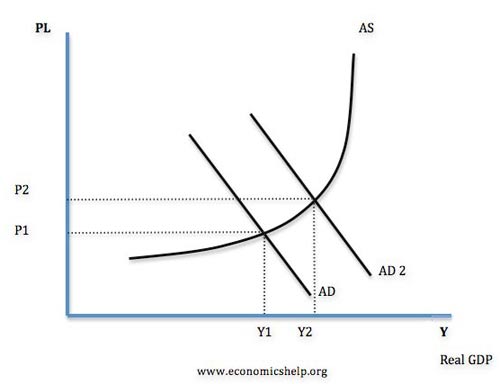
An increase in aggregate demand (AD to AD2) causes higher real GDP (Y1 to Y2). Therefore firms employ more workers and unemployment falls.
Why do monetarists work longer?
Monetarists argue that if there is an increase in aggregate demand, then workers demand higher nominal wages. When they receive higher nominal wages, they work longer hours because they feel real wages have increased. (their price expectations are based on last year)
What does the Phillips curve show about unemployment?
The Phillips curve suggests there is an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
What happens to real output after inflation expectations increase?
The increase in AD only causes a temporary increase in real output to Y1. After inflation expectations increase, SRAS shifts to left (SRAS2), and we end up with higher inflation (P3) and output of Y1. This AD/AS model explains why we only get a temporary fall in unemployment.
What would happen if the economy was operating below full capacity?
If the economy is operating below full capacity, a significant increase in aggregate demand is likely to cause a reduction in unemployment and higher inflation. Most economists would agree that in the short term, there can be a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
What is the Phillips curve?
The Phillips Curve is the graphical representation of the short-term relationship between unemployment and inflation. Fiscal Policy Fiscal Policy refers to the budgetary policy of the government, which involves the government controlling its level of spending and tax rates. within an economy.
Why is the Phillips curve important?
After the publication of “The General Theory” by John Maynard Keynes, most economists and policymakers believed that in order for the economy to grow, aggregate demand must be increased in the market. However, if policymakers stimulated aggregate demand using monetary and fiscal policy, ...
What would happen if policymakers stimulated aggregate demand using monetary and fiscal policy?
However, if policymakers stimulated aggregate demand using monetary and fiscal policy, the rise in employment and output was accompanied by a rapidly increasing price level . If policymakers then wanted to reduce inflation, then they would need to reduce output and employment in the short run.
Who published the article on the relationship between unemployment and inflation?
In 1958, Alban William Housego Phillips, a New-Zealand born British economist, published an article titled “The Relationship between Unemployment and the Rate of Change of Money Wages in the United Kingdom, 1861-1957” in the British Academic Journal, Economica. In the article, A.W. Phillips showed a negative correlation between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation – the years with high unemployment showed low inflation, and the years with low unemployment experienced high inflation.
Who published the article on inflation and unemployment?
In 1960, American economists Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow published an article titled “Analytics of Anti-Inflation Policy” in the American Economic Review (AER). This article, too, reported a negative correlation between inflation and unemployment in the United States. Subsequently, researchers from other countries also found ...
Who was the first to propose the Phillips curve?
The Long-term Phillips Curve. In 1968, the Nobel Prize-winning economist and the chief proponent of monetarism, Milton Freidman, published a paper titled “The Role of Monetary Policy.”. In his paper, Freidman claimed that in the long run, monetary policy could not lower unemployment by raising inflation. Freidman’s claim was heavily influenced by ...
Which theory influenced Freidman's claim?
Freidman’s claim was heavily influenced by the classical macroeconomic theory that believed that the amount of money in an economy (the money supply) was a nominal variable and could not influence a real variable such as employment or output.
Who created the Phillips curve?
The Phillips curve is named after economist A.W. Phillips, who examined U.K. unemployment and wages from 1861-1957. Phillips found an inverse relationship between the level of unemployment and the rate of change in wages (i.e., wage inflation). 1. Phillips, A.W. “ The Relation Between Unemployment and the Rate of Change ...
Why Has the Phillips Curve Flattened?
“If you put it in a murder mystery framework —‘Who Killed the Phillips Curve? ’—it was the Fed that killed the Phillips curve,” Bullard said.
What is the trade off between unemployment and inflation?
Louis Fed. This trade-off is the so-called Phillips curve relationship.
Why does weighing the usefulness of the Phillips curve matter?
Why does weighing the usefulness of the Phillips curve matter? Because it could lead to different monetary policy recommendations for how best to achieve the Fed’s dual mandate of maximum sustainable employment and price stability.
What is the price stability of the economy?
Price stability can be thought of as low and stable inflation, where inflation refers to a general, sustained upward movement of prices for goods and services in an economy. U.S. monetary policymakers believe an inflation rate of 2% is consistent with price stability, hence the Fed’s 2% inflation target.
Is there a relationship between labor market performance and inflation?
That has resulted in lower, more stable inflation in the U.S., he said, adding “so there isn’t much of a relationship anymore between labor market performance and inflation.”. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell has been asked about the Phillips curve, including during his July 2019 testimony before Congress. 2.
Is the Phillips curve useful?
It is useful, both as an empirical basis for forecasting and for monetary policy analysis.”. —New York Fed President John Williams, remarks delivered on Feb. 22, 2019.
Why does the Phillips curve shift to the left?
For example, if frictional unemployment decreases because job matching abilities improve, then the long-run Phillips curve will shift to the left (because the natural rate of unemployment decreases). Or, if there is an increase in structural unemployment because workers’ job skills become obsolete, then the long-run Phillips curve will shift to the right (because the natural rate of unemployment increases).
Why use the Phillips curve?
We can also use the Phillips curve model to understand the self-correction mechanism. Perhaps most importantly, the Phillips curve helps us understand the dilemmas that governments face when thinking about unemployment and inflation.
What does shift in SRPC mean?
The shift in SRPC represents a change in expectations about inflation. For example, suppose an economy is in long-run equilibrium with an unemployment rate of 4% and an inflation rate of 2%.
What happens when inflation moves to point?
An economy is initially in long-run equilibrium at point , but an increase in aggregate demand decreases unemployment and increases inflation, resulting in the move to point . When people expect there to be inflation permanently, will decrease (shift left) and the shifts to the right.
What is the LRPC curve?
a curve illustrating that there is no relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation in the long-run; the LRPC is vertical at the natural rate of unemployment.
What model is used to illustrate long run adjustment?
That long-run adjustment mechanism can be illustrated using the Phillips curve model also. When shifts, the shifts in the opposite direction, as summarized in the table below:
How many schedules are there in Phillips curve?
There are two schedules (in other words, "curves") in the Phillips curve model:
Phillips Curve
The Phillips curve is an economic model named after the economist William Phillips during the 1960s. Phillips collected statistical data on unemployment and inflation, or rising wages. From this data, there was a noticeable inverse correlation between rates of unemployment and inflation.
Short Run Phillips Curve Graph
A short-run Phillips curve is an easy model to illustrate the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment, and merely measures the relationship over a short period of time (because other factors may cause changes in the long run). The graph has the inflation rate values at the y-axis, and the unemployment rates on the x-axis.
Phillips Curve Shifts
The slow economic growth or stagflation of the 1970s demonstrated the flaw of the Phillips curve. The reasoning economists give now is that the expectations of workers and consumers plays a role in the relationship between unemployment and inflation.

History of The Phillips Curve
Importance of The Phillips Curve
- After the publication of “The General Theory” by John Maynard Keynes, most economists and policymakers believed that in order for the economy to grow, aggregate demand must be increased in the market. However, if policymakers stimulated aggregate demand using monetary and fiscal policy, the rise in employment and output was accompanied by a rapidly increasing pri…
Example
- Point A represents a situation where the economy faces high unemployment but low inflation. Policymakers make the decision that the economy must prioritize output. Thus, the policymakers raise government spending and cut taxes to stimulate demand in the market. As a result of these policies, employment and output increase within the economy. However, there is a limit to how …
The Long-Term Phillips Curve
- In 1968, the Nobel Prize-winning economist and the chief proponent of monetarism, Milton Freidman, published a paper titled “The Role of Monetary Policy.” In his paper, Freidman claimed that in the long run, monetary policy could not lower unemployment by raising inflation. Freidman’s claim was heavily influenced by the classical macroeconomic theo...
Related Reading
- CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)®certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To continue learning and advance your career, see the following free CFI resources: 1. Consumer Surplus Formula 2. GDP Formula 3. Market Economy 4. Law of Supply
Historical Relationship Between Inflation and Unemployment
Then and Now
- Kliesen noted that a trade-off seemed to exist in the U.S. in the 1950s and 1960s. Take a look at the graph below, which shows the unemployment rate in blue and the inflation rate in red since 1950. (The inflation rate is measured using the percentage change from a year ago in the personal consumption expenditures price index.) Figure 1: Inflation and Unemployment, Q1 195…
Why Has The Phillips Curve Flattened?
- St. Louis Fed President James Bullard has previously discussed the flattening of the empirical Phillips curve, including during an NPR interviewin October 2018. “If you put it in a murder mystery framework—‘Who Killed the Phillips Curve?’—it was the Fed that killed the Phillips curve,” Bullard said. “The Fed has been much more mindful about targeting inflation in the last 20 years,” he exp…
What Does All of This Mean For Monetary Policy?
- There is debate among policymakers regarding how useful the Phillips curve is as a reliable indicator of inflation—a debate that is not limited to recent years.3Meade, Ellen E.; and Thornton, Daniel L. “The Phillips curve and US monetary policy: what the FOMC transcripts tell us,” Oxford Economic Papers, April 2012, Vol. 64, No. 2, pp. 197-216. Why does weighing the usefulness of t…