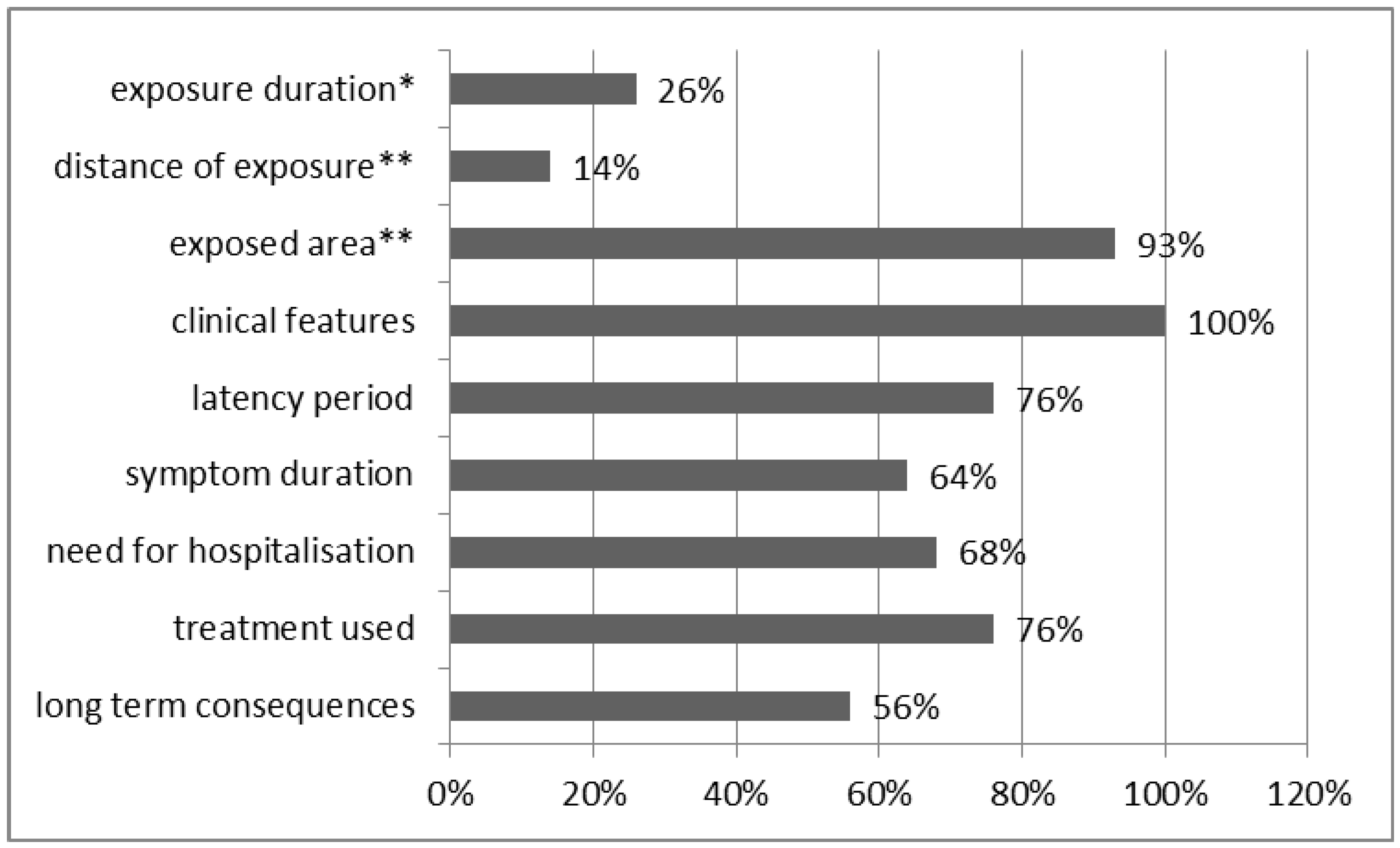
The objectives of epidemiology include the following:
- to identify the etiology or cause of disease.
- to determine the extent of disease.
- to study the progression of disease.
- to evaluate preventive and therapeutic measures for a disease or condition.
- to develop public health policy.
What are the key features of Epidemiology?
Apr 05, 2022 · What should be included in epidemiology? April 5, 2022 by suci Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials.
What is epidemiology Chapter 1?
The objectives of epidemiology include the following: to identify the etiology or cause of disease. to determine the extent of disease. to study the progression of disease. to evaluate preventive and therapeutic measures for a disease or condition. to develop public health policy.
What is the application of Epidemiology?
Nov 10, 2021 · Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials. What are the 4 important elements of epidemiology?
What is epidemiology in nursing?
As a measure of incidence, it includes only new cases of disease in the numerator. The denominator is the number of persons in the population at the start of the observation period. Because all of the persons with new cases of disease (numerator) are also represented in the denominator, a risk is also a proportion. More About Denominators
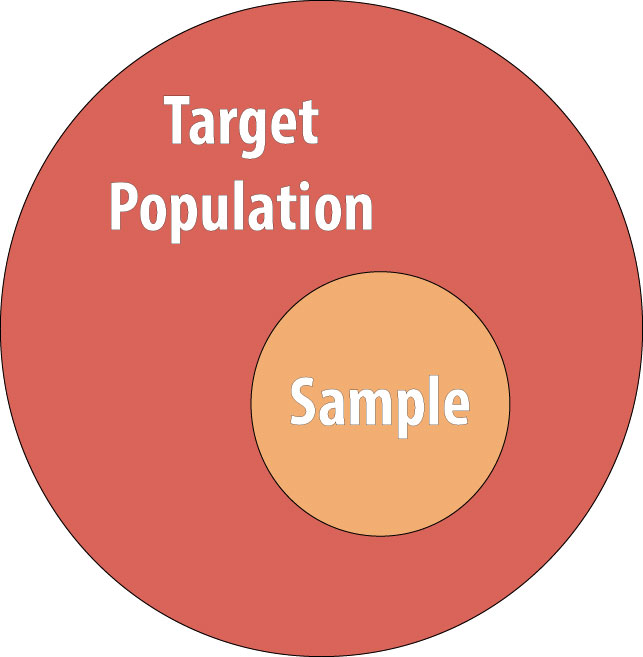
What are the 3 main elements of the definition of epidemiology?
The epidemiologic triangle is made up of three parts: agent, host and environment.
What are the 5 main objectives of epidemiology?
In the mid-1980s, five major tasks of epidemiology in public health practice were identified: public health surveillance, field investigation, analytic studies, evaluation, and linkages.
What are the 5 W's of epidemiology?
The difference is that epidemiologists tend to use synonyms for the 5 W's: diagnosis or health event (what), person (who), place (where), time (when), and causes, risk factors, and modes of transmission (why/how).
What are the 4 types of epidemiological data?
The tests of analytical epidemiology are carried out through four major types of research study designs: cross-sectional studies, case-control studies, cohort studies, and controlled clinical trials. Cross-sectional studies are used to explore associations of disease with variables of interest.
What are the basic tools of measurement in epidemiology?
The basic tools of measurement in epidemiology are: Rates. Ratios, and. Proportions....Basic Measurements in EpidemiologyMeasurement of mortality.Measurement of morbidity.Measurement of disability.Measurement of natality.Measurement of the presence, absence or distribution of the characteristics or attributes of the disease.More items...•Jan 30, 2019
What are the seven uses of epidemiology?
There are, he argues, seven main uses for the science of epidemiology: in historical study; in 'community diagnosis' or population studies; in the calculation of individual risks; for health services research; as an aid to clinical understanding; in the identification and labelling of disease; and, lastly and ...Dec 1, 2007
What do epidemiologists study?
By definition, epidemiology is the study (scientific, systematic, and data-driven) of the distribution (frequency, pattern) and determinants (causes, risk factors) of health-related states and events (not just diseases) in specified populations (neighborhood, school, city, state, country, global).
What are the steps in the epidemiological process?
Identify investigation team and resources.Establish existence of an outbreak.Verify the diagnosis.Construct case definition.Find cases systematically and develop line listing.Perform descriptive epidemiology/develop hypotheses.Evaluate hypotheses/perform additional studies as necessary.Implement control measures.More items...
What skills are needed to be an epidemiologists?
Below is a list of skills and traits that could be useful in launching a successful epidemiology career.Strong understanding of statistical concepts. ... Strong understanding of medical and biological processes. ... Critical thinking skills. ... Strong communication skills. ... Attention to detail. ... Computer skills.
What are some examples of epidemiology?
The term epidemiology is now widely applied to cover the description and causation of not only epidemic, infectious disease, but of disease in general, including related conditions. Some examples of topics examined through epidemiology include as high blood pressure, mental illness and obesity.
What is an epidemiological pattern?
Epidemiological patterns are models of morbidity-mortality or ways of measuring sickness and death that are more prevalent in a given society at specific historical moments.Jun 4, 2019
What is a source in epidemiology?
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Unpublished data; 1990. A propagated outbreak results from transmission from one person to another. Usually, transmission is by direct person-to-person contact, as with syphilis.
Why is epidemiology important?
Epidemiological research helps us to understand how many people have a disease or disorder, if those numbers are changing, and how the disorder affects our society and our economy. The epidemiology of human communication is a rewarding and challenging field.
What factors should be taken into account when calculating the cost of illness?
Ideally, the cost of illness would also take into account factors that are more difficult to measure, such as work-related costs, educational costs, the cost of support services required by the medical condition, and the amount individuals would pay to avoid health risks.
What is the burden of disease?
Burden of disease: The total significance of disease for society, beyond the immediate cost of treatment. It is measured in years of life lost to ill health, or the difference between total life expectancy and disability-adjusted life expectancy (DALY). (Adapted from the World Health Organization. (link is external)
Can you answer yes when asked if someone in your household has trouble hearing?
For instance, an epidemiological study may collect data on the number of people who answer, “Yes” when asked if someone in their household has trouble hearing. Each person providing such an answer may interpret “trouble hearing” differently.
What are the principles of epidemiology?
Principles of Epidemiology. Public health workers use epidemiologic principles as the foundation for disease surveillance and investigation activities. Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states or events in specified populations, and the application of this study to the control of health problems.
How does epidemiology help public health?
The information is used when planning how to control and prevent disease in the community. Through public health surveillance, a health systematically collects, analyzes, interprets and disseminates health data on an ongoing basis. By knowing the ongoing pattern of disease occurrence and disease potential, a health agency can effectively and efficiently investigate, prevent and control disease in the community.
What is frequency in epidemiology?
Frequency includes not only the number of events in a population, but also the rate or risk of disease in the population. Determining the rate of disease occurrences (number of events divided by size of the population) is critical for making valid comparisons across different populations. Determinants - Epidemiology is also used to search ...
What is the definition of disease surveillance?
Disease surveillance usually begins with descriptive epidemiology -- defining the what, who, when and where of health-related events. what - Define the disease events and/or its determinants. who - Descriptions of demographic characteristics are helpful in determining which groups are at risk for some outcome.
How to determine if a case is infectious?
There are two ways to assess the case's infectivity: estimation --uses the date of onset of illness, dates of known treatment, and known periods of infectiousness for an illness. For example, hepatitis A is no longer infectious after 1 week of the onset of symptoms.
What is distribution epidemiology?
Distribution - Epidemiology is concerned with the frequency and pattern of health events in a population. Frequency includes not only the number of events in a population, but also the rate or risk of disease in the population.
What are some examples of determinants?
Examples of determinants include host susceptibility to a disease, and opportunity for exposure to a microorganism, environmental toxin, insect vector or other infected individual that may pose a risk for acquiring disease.
How does an epidemiologist perform descriptive epidemiology?
This is done by developing a case definition. Then, using this case definition, the epidemiologist finds and collects information about the case-patients. The epidemiologist then performs descriptive epidemiology by characterizing the cases collectively ...
How does an epidemiologist determine the disease rate?
To calculate the disease rate, the epidemiologist divides the number of cases by the size of the population.
What is an indigenous case?
An indigenous case is defined as a case of measles that is not imported. Cases that are linked to imported cases should be classified as indigenous if the exposure to the imported case occurred in the reporting state. Any case that cannot be proved to be imported should be classified as indigenous.
What is a probable case?
Probable: A case that meets the clinical case definition, has noncontributory or no serologic or virologic testing, and is not epidemiologically linked to a confirmed case. Confirmed: A case that is laboratory confirmed or that meets the clinical case definition and is epidemiologically linked to a confirmed case.
What is the role of public health?
These counts, usually derived from case reports submitted by health-care workers and laboratories to the health department, allow public health officials to determine the extent and patterns of disease occurrence by time, place, and person. They may also indicate clusters or outbreaks of disease in the community.
What is a sensitive case?
A sensitive case definition is one that is broad or “loose,” in the hope of capturing most or all of the true cases. For example, the case definition for a suspected case of rubella (German measles) is “any generalized rash illness of acute onset.”.
How long is a febrile illness?
A febrile illness of greater than or equal to 5 days’ duration, with at least four of the five following physical findings and no other more reasonable explanation for the observed clinical findings:
What is the key feature of epidemiology?
A key feature of epidemiology is the measurement of disease outcomes in relation to a population at risk. The population at risk is the group of people, healthy or sick, who would be counted as cases if they had the disease being studied.
Why is epidemiology important?
Epidemiological information is used to plan and evaluate strategies to prevent illness and as a guide to the management of patients in whom disease has already developed. Like the clinical findings and pathology, the epidemiology of a disease is an integral part of its basic description. The subject has its special techniques ...
What is a gastroenterologist with Crohn's disease?
A gastroenterologist who has a special interest in Crohn’s disease may be referred patients whose cases are unusual or difficult, the clinical course and complications of which are atypical of the disease more generally.
What is the difference between clinical and epidemiological observations?
Clinical observations determine decisions about individuals. Epidemi ological observations may also guide decisions about individuals, but they relate primarily to groups of people. This fundamental difference in the purpose of measurements implies different demands on the quality of data.
Can a sample be unrepresentative?
The confidence that can be placed in conclusions drawn from samples depends in part on sample size. Small samples can be unrepresentative just by chance, and the scope for chance errors can be quantified statistically. More problematic are the errors that arise from the method by which the sample is chosen.
Can data recording change?
Unfortunately, standards of diagnosis and data recording may change, and conclusions from time trends call for particular wariness. The data from which epidemiology seeks to draw conclusions are nearly always collected by more than one person, often from different countries.
Can epidemiological conclusions be drawn from clinical data?
Epidemiological conclusions (on risk) cannot be drawn from purely clinical data (on the number of sick people seen). Implicit in any epidemiological investigation is the notion of a target population about which conclusions are to be drawn. Occasionally measurements can be made on the full target population.
What is epidemiology in health?
According to the World Health Organization, epidemiology is the study of the spread of disease and factors affecting states of health. Generally, epidemiology doesn’t just focus on illness; it primarily studies wellness and how to maintain it. In essence, it can be considered the basic science of public health.
When was epidemiology first used?
In essence, it can be considered the basic science of public health. Epidemiology was initially coined in the mid-19th century to refer to the study of epidemics. Today, it’s applied to all factors affecting the health and wellness of a particular demographic.
What is the role of nurse educators?
Nurse educators fill a similar role, in that they can leverage their understanding of etiology and epidemiology and their applications to advance the training of young nursing professionals.
What is the role of a nurse in an outbreak?
Nurses are on the front line of disease outbreaks, so they need to understand the basics of epidemiology and etiology and apply them where necessary. The journal Family Practice explores the idea of primary care epidemiology, including prevention, diagnosis, and etiology of a disease as a significant benefit to all physicians having to deal with the outbreak. Nurses may be the first responders to a disease occurrence, and determining the etiology of the disease and its method of containment as fast as possible can be crucial to avoid its spread.
What is the role of a nurse researcher?
Hunting down information, sourcing similar cases, and determining the overall factors and causes are critical elements to the job of nurse researchers. The American Nurses Association notes that nursing research aims to bring evidence-based care to patients — not merely individuals, but also communities as a whole.
What is intrinsic etiology?
Intrinsic — coming from within. Extrinsic — originating from external factors. Idiopathic — cause unknown. Etiology is not only disease specific but also person specific. While a particular cause may lead to a disease manifesting in an individual, a similar set of factors could lead to a different illness being manifested in another individual.
What is the role of a nurse practitioner?
Nurse practitioners (NPs) should always ensure that their patients maintain their health. Their role is similar to that of an epidemiologist, in that they try to identify the key factors affecting it. Nurse researchers or nurse educators may find themselves more comparable to an etiologist.
Why should research be reported transparently?
Research should be reported transparently so that readers can follow what was planned, what was done, what was found, and what conclusions were drawn. The credibility of research depends on a critical assessment by others of the strengths and weaknesses in study design, conduct, and analysis. Transparent reporting is also needed to judge whether ...
Is biomedical research observational?
Much biomedical research is observational. The reporting of such research is often inadequate, which hampers the assessment of its strengths and weaknesses and of a study's generalisability. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Initiative developed recommendations on what should be included in an ...
Is a checklist an instrument to evaluate the quality of observational research?
Also, while clarity of reporting is a prerequisite to evaluation, the checklist is not an instrument to evaluate the quality of observational research.