What is the average dose of cyclosporine in the US?
At the second week, the mean drug dose in patients with cyclosporine trough levels less than the target therapeutic level was 279.16 +/- 56.23 mg/d, while in the patients with cyclosporine levels higher than the therapeutic level, its dose was 302.08 +/- 66.61 mg/d (P < .05).
What are cyclosporin levels used for?
A: Cyclosporin levels are used by transplant physicians to guide them regarding the doses of cyclosporine usage. Cyclosporin levels may vary depending on the drug dose, intake with food, form of the drug and laboratory standardisation. I do hope you have not changed the chemist from whom you get cyclosporine and that your cyclosporine is genuine.
What is the normal range of cyclosporine in psoriasis?
In psoriasis patients, the circulating concentration of cyclosporine does not correlate reliably with the therapeutic response. Some patients may achieve an excellent response with blood levels in the range of 50 ng/ml; others may show little or no response despite blood levels as high as 200 ng/ml.
When should a blood sample be drawn for cyclosporine?
For example, if cyclosporine is given twice a day, a blood sample is usually drawn 12 hours after the last dose, before a new dose is given. On mornings when you are scheduled to have your cyclosporine level checked, do not take the medicine until after your blood is drawn. What is being tested?
What happens when cyclosporine level is high?
Some signs and symptoms of cyclosporine toxicity are: Kidney damage (nephrotoxicity) High blood pressure. Tremors.
When do you check cyclosporine levels?
For cyclosporine or tacrolimus trough-level monitoring, blood should be drawn 12 h after the last dose (i.e., immediately before the next dose).
What is cyclosporine toxicity?
High dosages of cyclosporine can cause liver and kidney toxicity. It can also increase someone's risk of certain types of cancer, especially lymphoma and skin cancer.
What causes high cyclosporine levels?
Taking cyclosporine with certain antifungal drugs may lead to higher levels of cyclosporine in your body. This could cause increased side effects or raise your risk of kidney damage. Examples of these drugs include: amphotericin B.
What are the long term side effects of cyclosporine?
However, cyclosporine is potentially toxic. Side effects include renal toxic effects, hypertension, and an increased risk of malignant neoplasm. The toxicity of cyclosporine is dose-related, yet the safe duration of treatment is undefined.
What are the side effects of taking cyclosporine?
Cyclosporine Side EffectsHigh blood pressure.Increased hair growth. ... Swollen or inflamed gums. ... Numbness or tingling of the hands or feet. ... Other common side effects are tremors, restlessness, stomach upset, nausea, cramps, diarrhea, headache, and changes in blood sugar.
How long can you take cyclosporine for?
The FDA recommends cyclosporine not be used for longer than one year. However, there are no specific guidelines for how long you should stay off cyclosporine before resuming treatment. Some doctors may prescribe the drug for more than one year.
Can cyclosporine make you gain weight?
Does cyclosporine cause weight gain? Yes, prolonged consumption of cyclosporine can lead to a gain in weight. Cyclosporine affects a patient's appetite because of which there may be either weight gain or weight loss. However, only rare cases of weight change have been reported so far.
Can cyclosporine cause liver damage?
Cyclosporine therapy can be associated with mild elevations in serum bilirubin and transient serum enzyme elevations, and to rare instances of clinically apparent cholestatic liver injury.
What organ is most susceptible to cyclosporine toxicity?
Cyclosporine is a very strong medicine. It can cause side effects that can be very serious, such as kidney problems.
Does cyclosporine cause anxiety?
Cyclosporine (Cyc) is a calcineurin inhibitor that is widely used in immunosuppressive therapy for organ transplantation and autoimmune diseases. These medications may cause neuropsychological problems such as tremor, confusion, anxiety, and depression in patients (1).
Does cyclosporine cause insomnia?
Mycophenolate is associated with several neurological side effects including headache, insomnia, dizziness, depression, confusion, hypertonia, and paresthesia.
How long does it take to get cyclosporine out of your system?
How long does cyclosporine stay in your system? The half-life cycle of cyclosporine ranges from 5–18 hours after consumption. After the first dose of cyclosporine, it takes around 2–3 days to achieve a stable state of blood concentration in the body.
How do you titrate cyclosporine?
Titration: If insufficient benefit is seen at 4 weeks and tolerability is good at the initial dose, the dose may be increased by 0.5 mg/kg/day at 2-week intervals based on patient response. Maximum dose: 4 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. Note: Doses below 2.5 mg/kg/day may also be effective.
How often is cyclosporine taken?
Cyclosporine is usually taken once a day. Cyclosporine (modified) is usually taken twice a day. It is important to take both types of cyclosporine on a regular schedule. Take cyclosporine or cyclosporine (modified) at the same time(s) each day, and allow the same amount of time between doses and meals every day.
How is cyclosporine cleared?
Elimination of Cyclosporine is primarily biliary with only 6% of the dose (parent drug and metabolites) excreted in urine. The disposition of Cyclosporine from blood is generally biphasic, with a terminal half-life of approximately 8.4 hours (range 5 to 18 hours).
Usual Adult Dose For Organ Transplant - Rejection Prophylaxis
ORAL FORMULATION (MODIFIED):-Note: The dose is dependent upon type of transplant and formulation; refer to local protocol for specific dosing.-Init...
Usual Adult Dose For Rheumatoid Arthritis
ORAL FORMULATION (MODIFIED):-Initial dose: 1.25 mg/kg orally 2 times a day; onset of action usually occurs between 4 and 8 weeks-Titration: If insu...
Usual Adult Dose For Psoriasis
ORAL FORMULATION (MODIFIED):-Initial dose: 1.25 mg/kg orally 2 times a day for at least 4 weeks-Titration: If insufficient benefit is seen at 4 wee...
Usual Pediatric Dose For Organ Transplant - Rejection Prophylaxis
The same dose and dosing regimen may be used in children as in adults although in several studies, children have required and tolerated higher dose...
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use cyclosporine if you are allergic to it. You may not be able to use cyclosporine if you have: 1. kidney disease; 2. untreated or...
How Should I Take Cyclosporine?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose to make sure you get the best results. Do not take...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to...
What Should I Avoid While Taking Cyclosporine?
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice may interact with cyclosporine and lead to unwanted side effects. Avoid the use of grapefruit products while taking...
Cyclosporine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.Ca...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Cyclosporine?
Cyclosporine can harm your kidneys. This effect is increased when you also use certain other medicines, including: antivirals, cholesterol-lowering...
How to monitor cyclosporine levels?
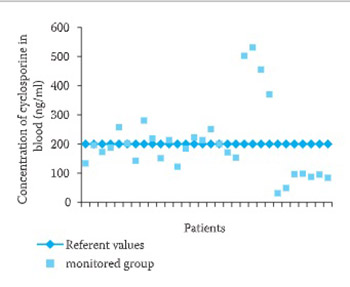
The following guidelines are recommended for laboratory monitoring of circulating levels of cyclosporine in dermatology patients. Measurements should be determined as trough levels in whole blood, not plasma or serum. The measurements should be performed with an assay that is specific for the parent cyclosporine compound (e.g., a high-performance liquid chromatography method or a specific monoclonal immunoassay). The results of nonspecific immunoassays that detect cyclosporine as well as its metabolites are difficult to interpret and cannot readily be compared among different studies or laboratories. In psoriasis patients, the circulating concentration of cyclosporine does not correlate reliably with the therapeutic response. Some patients may achieve an excellent response with blood levels in the range of 50 ng/ml; others may show little or no response despite blood levels as high as 200 ng/ml. In patients with a poor clinical response, monitoring of cyclosporine levels may be useful to confirm that the drug has been taken and may provide an estimate of the degree of absorption and metabolism of the parent compound. Because an upper limit of safety for the circulating concentration of cyclosporine has not been clearly defined, one should attempt to achieve a therapeutic response with the lowest possible dose. Clinicians must carefully monitor patients for signs of cyclosporine toxicity, regardless of the circulating concentration of the drug. Whole blood levels exceeding 250 ng/ml should be avoided.
Why is cyclosporine monitoring important?
In patients with a poor clinical response, monitoring of cyclosporine levels may be useful to confirm that the drug has been taken and may provide an estimate of the degree of absorption and metabolism of the parent compound.
Can cyclosporine be detected in immunoassays?
The results of nonspecific immunoassays that detect cyclosporine as well as its metabolites are difficult to interpret and cannot readily be compared among different studies or laboratories. In psoriasis patients, the circulating concentration of cyclosporine does not correlate reliably with the therapeutic response.
How long does it take for a syringe to stabilize?
Discontinue therapy if dose reduction is not effective. -Improvement is usually seen in 2 weeks; stabilization may take 12 to 16 weeks. -Discontinue therapy if a satisfactory response cannot be achieved after 6 weeks at 4 mg/kg/day or the maximum tolerated dose.
Does cyclosporine affect renal function?
Renal dysfunction, including structural kidney damage, is a potential consequence of cyclosporine, and therefore, renal function must be monitored during therapy. NON-MODIFIED/MODIFIED FORMULATION:
What is cyclosporine?
Cyclosporine lowers your body's immune system. The immune system helps your body fight infections. The immune system can also fight or "reject" a transplanted organ such as a liver or kidney. This is because the immune system treats the new organ as an invader.
What other drugs will affect cyclosporine?
This effect is increased when you also use certain other medicines, including: antivirals, cholesterol-lowering drugs, chemotherapy, injected antibiotics, medicine for bowel disorders, medicines to treat autoimmune disorders, medicine to prevent organ transplant rejection, stomach acid reducers ( Tagamet, Zantac ), and some pain or arthritis medicines (including aspirin, Tylenol, Advil, and Aleve ).
How to measure sandimmune?
Sandimmune oral solution may be mixed with milk, chocolate milk, or orange juice at room temperature to make the medicine taste better. Neoral "modified" (microemulsion) oral solution should be mixed with orange juice or apple juice that is at room temperature.
What medications can interact with cyclosporine?
heart or blood pressure medication, including a diuretic or "water pill"; seizure medication; or. steroid medication (oral, nasal, inhaled, or injectable). This list is not complete and many other drugs can interact with cyclosporine. This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products.
Can you take cyclosporine if you are allergic to it?
You should not use cyclosporine if you are allergic to it. You may not be able to use cyclosporine if you have:
Can cyclosporine cause a blood test?
While using cyclosporine, you will need frequent blood or urine tests to be sure cyclosporine is not causing harmful effects. Your condition may need to be treated with a combination of different drugs. Use all medications as directed by your doctor.
Can cyclosporine cause kidney failure?
Cyclosporine can cause serious side effects, including kidney failure or life-threatening infection. While using cyclosporine, you will need frequent blood tests to be sure cyclosporine is not causing harmful effects.
Why is cyclosporine used for RA?
Cyclosporine is used to prevent rejection of a transplanted organ. It’s also used to reduce inflammation in active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and severe psoriasis.
Can you take blood tests before taking cyclosporine?
Your doctor may monitor you with certain blood tests before and during treatment with cyclosporine. This is to make sure it’s safe for you to take. Tests may be done to check things such as your:
Can you take cyclosporine with protease inhibitors?
If you’re taking drugs called protease inhibitors to treat HIV, check with your doctor before taking cyclosporine. Your doctor may need to reduce your dose of cyclosporine to prevent side effects that can be caused by taking these drugs with cyclosporine. Examples of these drugs include:
Can you take cyclosporine with birth control?
Taking cyclosporine with drugs used for birth control may increase the amount of cyclosporine in your body. This may cause harmful side effects.
Can cyclosporine cause polyoma?
For people with serious infections: Cyclosporine may increase your risk of serious viral infections, such as polyomavirus infection. This may be very serious, even fatal.
Can you take cyclosporine with methylprednisolone?
Taking methylprednisolone with cyclosporine may increase the amount of cyclosporine in your body. This may cause harmful side effects.
Is cyclosporine safe for long term use?
Cyclosporine is used for long-term treatment. It comes with serious risks if you don’t take it as prescribed.
How long after CsA dose can you collect blood?
By collecting serial blood samples over this limited period (4hr after the dose) and estimating the AUC0-4, one can gain insight into how well CsA has been absorbed for each transplant recipient, and individualise CsA dosage. However, a recent survey of Australasian CsA laboratories revealed that such AUC0-4sampling strategies in the early post-dose period were poorly accepted in clinics across Australasia. The alternative that has proven to be more clinically acceptable is the use of a single sample 2-hours after the dose (C2). The C2 concentration has been demonstrated (particularly in kidney and liver transplant recipients) as correlating well with AUC0-4, allowing it to be used as a surrogate index of CsA absorption and exposure.
What is the bioavailability of Csa?
In this way we can accommodate, at least partially, the generally poor and variable rate and extent of absorption (bioavailability) of CsA both inter- and intra-patient. On average, only about 40% of CsA in the oral dose survives the barriers to absorption and first-pass metabolism, in the gut-wall and liver to reach the systemic circulation, from where it reaches the tissues to exert its actions.1–3Perhaps a better term for CsA would be "critical concentration drug", as the dosage schedule is typically adjusted up or down so as to attain the desired target blood CsA concentration, in the light of the patient's clinical indices. This variability with the dosage/concentration relationship of CsA is shared with other immunosuppressant drugs currently used in organ transplantation, including tacrolimus, sirolimus and mycophenolic acid, as well as newer drugs currently in clinical trials, (eg. FTY-720 and everolimus) as recently reviewed.4–6
What is the temperature dependent equilibrium between plasma and red blood cells?
there was a significant temperature-dependent equilibrium between plasma and red blood cells such that each 1°C reduction in the temperature that plasma was separated from the cellular fraction caused a 14 μg/L reduction in plasma CsA concentration, making it difficult to obtain representative plasma CsA concentrations that reflected in vivocirculating concentrations (ie. at 37°C),
Why is heparin anticoagulated blood variable?
heparin anti-coagulated blood showed variable results due to the presence of micro-clots causing significant inconsistencies in the fraction sampled for assay in the laboratory.
Is C2 better than C0?
Further arguments and recommendations favouring C2 monitoring are reviewed elsewhere, including the recent consensus papers from the CONCERT group, and our Australasian group, as well as other reviews and recommendations.5,33,38–40,48,59–63They have all supported the use of C2 strategies as a more useful tool than C0 for CsA monitoring. However, like many issues regarding CsA over the years, there is also a (minority) counter argument, including one extensive review that concluded: "C0 is currently the standard method of monitoring CsA therapy and there is no evidence demonstrating the superiority of any other method of monitoring CsA over C0 in terms of patient outcomes”.54Another lung transplant study concluded: “monitoring either the C2 or C6 concentration did not give a better indication of response to CsA therapy in patients with lung transplants compared with C0”.64
Is C2 a peak or a concentration?
Whilst some authors have referred to the C2 sample as the 'peak' or Cmax concentration, it is probably inappropriate to link such terms with C2.55,56Even with the more predictable Neoral®formulation, the CsA absorption profile is quite variable and so the actual peak concentration may frequently occur before or well after two hours for many reasons.41, 42Rather, it is important to simply think of C2 as an index, or surrogate marker, of AUC0-4which is in turn a marker of CsA absorption.
Can CSA be measured using HPLC?
Whilst CsA can be measured using chromatographic approaches [HPLC/UV or LCMS(MS)], these have proved unpopular internationally, with <5% of laboratories in the International CsA Proficiency Testing Program (www.bioanalytics.co.uk) employing them. In Australasia, HPLC is used by only one laboratory which also has the largest CsA service in the region. The vast majority of laboratories use one of the commercial CsA immunoassays (Figure 1and Table 2).19
Why is it important to test cyclosporine levels?
Testing cyclosporine levels in the blood can help ensure that drug levels are in a range that will be therapeutic. If the level is too low, organ rejection may occur (in the case of transplantation) or symptoms may reappear (autoimmune cases). It is also important to ensure that the level is not too high and will not result in toxicity.
How long can you stay on cyclosporine?
It is not advised that your stay on cyclosporine for more than a year due to an increase in the likelihood of toxic symptoms the longer you are on the medication. Short-term or intermittent courses of 12 weeks at a time are more advisable.
Why do you need a cyclosporine test?
Tests for cyclosporine are used to measure the amount of this drug in the blood to determine whether cyclosporine concentrations have reached therapeutic levels and are not in a toxic range. Cyclosporine is a drug that diminishes the body’s immune response. It is prescribed for organ transplant recipients to prevent organ rejection and for some people with autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, to alleviate symptoms.
What is cyclosporine used for?
Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant drug used to reduce the body’s natural defenses. This test measures the amount of cyclosporine in the blood.
How long after cyclosporine is tested?
A majority of laboratories use whole blood samples for cyclosporine testing instead of serum or plasma and will collect samples 12 hours after the last dose or just before the next dose (trough levels).
How long after a transplant can you test for cyclosporine?
High levels of cyclosporine in peak samples are correlated with reduced rejection rates, especially in the first year after transplant surgery.
Does cyclosporine help with a transplant?
When people undergo an organ transplant, their immune system recognizes the graft as “foreign” and will begin to attack it just as it would any invasive bacteria or virus. Cyclosporine diminishes the ability of certain white blood cells in the immune system to respond to this foreign tissue. The transplanted organ then has a better chance of survival and will not be as easily rejected by the transplant recipient’s immune system. Cyclosporine is used routinely in the transplantation of kidney, heart, liver, and other organs.
