
What lab tests are done after thoracentesis?
After thoracentesis, a lab test called a pleural fluid analysis may be performed to figure out the cause of fluid accumulation around one or both of your lungs. Your doctor may also perform a pleural biopsy. Though not commonly performed, it can help identify the underlying cause of pleural effusion. Potential causes include:
What happens after a thoracentesis procedure?
What happens after thoracentesis? After the procedure, your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing will be watched. The dressing over the puncture site will be checked for bleeding or other fluid. If you had an outpatient procedure, you will go home when your healthcare provider says it’s OK.
How should the patient be positioned for a thoracentesis?
If the patient is unable to sit, the patient may be placed in a side-lying position on the edge of the bed on unaffected side. The skin at the puncture site will be cleansed with an antiseptic solution. The patient will receive a local anesthetic at the site where the thoracentesis is to be performed.
Can a follow-up X-ray be performed Right after thoracentesis?
A follow-up X-ray may be performed right after the thoracentesis. What are the risks of the procedure? Every invasive procedure has risks, but side effects are uncommon with thoracentesis.
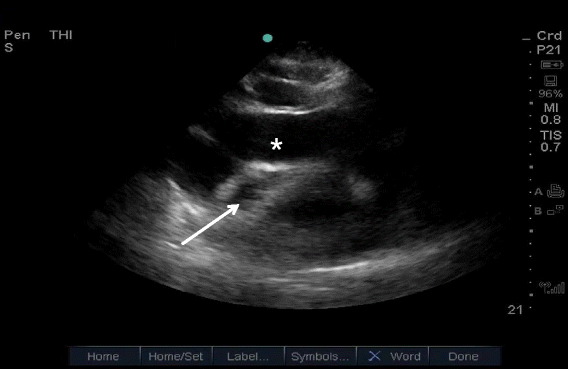
What should I monitor immediately after thoracentesis?
What happens after thoracentesis?Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as advised by your healthcare provider.Redness or swelling of the needle site.Blood or other fluid leaking from the needle site.Feeling short of breath.Trouble breathing.Chest pain.
What do you observe after thoracentesis?
After the procedure, the doctor will observe the insertion site for signs of bleeding and assess your breathing for signs of lung collapse (pneumothorax) or other complications. A routine chest X-ray is not necessary for patients who tolerate thoracentesis well.
What is the most common complication from thoracentesis?
Pneumothorax is the most common complication of thoracentesis, with historical incidence rates as high as 19% [19]. Iatrogenic pneumothorax significantly impacts patient outcomes. A recent meta-analysis found that up to one-third of cases require chest tube drainage [2].
What is the nurses responsibility during a thoracentesis?
Nursing Interventions Tell the patient to immediately report difficulty of breathing. Immediately report signs and symptoms of pneumothorax, tension pneumothorax, and pleural fluid reaccumulation. Monitor the patient for reexpansion pulmonary edema (RPE), a rare but serious complication of thoracentesis.
Is coughing normal after thoracentesis?
Key points. Re-expansion pulmonary edema is an uncommon complication following drainage of a pneumothorax or pleural effusion. Clinical presentations include cough, chest discomfort and hypoxemia; if the edema is severe, shock and death may ensue. Symptoms are usually noted within 24 hours after thoracentesis.
What is the best position for thoracentesis?
Positioning for Thoracentesis Best done with the patient sitting upright and leaning slightly forward with arms supported. Recumbent or supine thoracentesis (eg, in a ventilated patient) is possible but best done using ultrasonography or CT to guide procedure.
What can go wrong with thoracentesis?
Though thoracentesis is generally considered safe, these complications can happen: Pulmonary edema, or fluid in the lungs. Pneumothorax, or collapsed lung. Infection at the site where the needle pierced your skin.
Why does thoracentesis cause pneumothorax?
Major causes of pneumothorax in patients undergoing thoracentesis are direct puncture during needle or catheter insertion, the introduction of air through the needle or catheter into the pleural cavity, and the inability of the ipsilateral lung to fully expand after drainage of a large volume of fluid, known as ...
When caring for a client who has just undergone thoracentesis which of these interventions does the nurse perform first?
R: After thoracentesis, the nurse first makes sure a chest x-ray is performed to rule out possible pneumothorax and mediastinal shift (shift of central thoracic structures toward one side).
Why does thoracentesis cause hypotension?
Patients may also experience transient hypoxia associated with thoracentesis. Finally, hypotension or pulmonary edema can occur if too much fluid is removed too quickly. In an adult-sized patient, no more than 1000 to 1500 mL of fluid should be removed at a time.
What should the nurse do to prepare a client for thoracentesis?
Sitting while leaning forward over a pillow. Rationale: During a thoracentesis a needle is inserted into the intercostal space, so the nurse should assist the client to sit at the edge of the bed while leaning forward with their arms supported on a bedside table and a pillow or folded towel.
What can cause a pneumothorax?
A pneumothorax can be caused by:Chest injury. Any blunt or penetrating injury to your chest can cause lung collapse. ... Lung disease. Damaged lung tissue is more likely to collapse. ... Ruptured air blisters. Small air blisters (blebs) can develop on the top of the lungs. ... Mechanical ventilation.
Why does thoracentesis cause pneumothorax?
Major causes of pneumothorax in patients undergoing thoracentesis are direct puncture during needle or catheter insertion, the introduction of air through the needle or catheter into the pleural cavity, and the inability of the ipsilateral lung to fully expand after drainage of a large volume of fluid, known as ...
What color should fluid drained from lungs be?
A thoracentesis is a procedure used to drain excess fluid from the space outside of the lungs but inside the chest cavity. Normally, this area contains about 20 milliliters of clear or yellow fluid.
What are the complications of pleural effusion?
Complications of pleural effusion may include:Lung damage.Infection that turns into an abscess, called an empyema.Air in the chest cavity (pneumothorax) after drainage of the effusion.Pleural thickening (scarring of the lining of the lung)
How much fluid is removed during thoracentesis?
Traditional guidelines recommend that the volume of fluid removed during a thoracentesis should be limited to <1.5 liters, to avoid re-expansion pulmonary edema.
What will happen during a thoracentesis?
You will be asked to sit in a chair and rest your arms on a table in front of you. Local anesthesia will be given to numb the area where the needle will be inserted. Your healthcare provider will insert the needle and move it between your ribs. He or she may use an ultrasound to help guide the needle.
How long does a thoracentesis take?
This is to help prevent a lung injury. A thoracentesis usually only takes about 15 minutes. Tell your provider if you have any concerns about being able to stay still and breathe as directed during the procedure.
What is a thoracentesis?
A thoracentesis is a procedure to remove extra fluid or air from between your lungs and your inner chest wall. Air or fluid buildup may make it hard for you to breathe. A thoracentesis allows your lungs to expand fully so you can breathe more easily.
What to tell your healthcare provider about anesthesia?
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to anesthesia or a numbing medicine. Also tell your provider about any lung conditions you have, such as COPD.
How to breathe easier?
Breathing treatments may help open your airways so you can breathe easier. A machine is used to change liquid medicine into a mist. You will breathe the mist into your lungs through tubing and a mouthpiece. Inhaled mist medicines act quickly on your airways and lungs to relieve your symptoms.
Why do you need an x-ray after lung surgery?
A chest x-ray may be needed to check that your lungs were not damaged during the procedure. You may also need any of the following after your procedure:
How to prepare for blood clot surgery?
Your healthcare provider will tell you how to prepare for your procedure. You may need tests to check how well your blood clots. Tell your provider about all medicines you are taking, including blood thinners. You may need to stop taking certain medicines before the procedure. Your provider will tell you if you need to stop any medicines, and when to stop them. He or she will also tell you when to start taking them again after your procedure.
What is thoracentesis procedure?
Thoracentesis is a procedure that takes out fluid from the space between your chest wall and lung. This space is called the pleural cavity.
How long does it take for a thoracentesis to stop?
Coughing after the thoracentesis procedure is normal. It’s how your body helps your lung expand again. It should stop after about an hour.
What is the space called when you take a sample of fluid?
This space is called the pleural cavity. The procedure can be done to relieve shortness of breath caused by the fluid. It may also be done to take a sample of the fluid for testing if your healthcare provider requests it. Back to top.
When do you get a call before a pulmonary procedure?
You will get a phone call the day before your procedure to confirm your appointment time. If you don’t get a call by 12:00 pm, call the location where you’re scheduled to have your procedure. Read the resource Instructions for Pulmonary Procedures at Memorial Hospital for more information about your procedure. Back to top.
Can you go home after a thoracentesis?
This is to make sure that all the fluid was taken out and that your lungs are working the way they should be. You will be able to go home after your x-ray is done.
Can you feel pain after a shoulder insertion?
You may feel discomfort or pain in your shoulder or the area where the needle was inserted. This might happen toward the end of your procedure. It should go away when the procedure is finished, and you shouldn’t need medication for it. Let your healthcare provider know if you feel a lot of pain and they may pause the procedure.
Where is thoracentesis performed?
Depending on the situation, it may be performed in a hospital or at a doctor’s office. 3
What are the complications of thoracentesis?
The most common potentially serious complication of thoracentesis is pneumothorax. Some other possible problems include: 1 Re-expansion pulmonary edema (REPE) 2 Damage to the spleen or liver 3 Infection 4 Air embolism 5 Shortness of breath 6 Pain 7 Bleeding 5
How does thoracentesis help with pleural effusion?
Thoracentesis removes some of the excess fluid surrounding the lungs when there is a pleural effusion. Sometimes thoracentesis is used as a treatment to decrease symptoms from a pleural effusion. All that extra fluid may make you feel short of breath. Removing some of it may help you feel more comfortable. 1 .
What is a thoracentesis?
Interpreting Results. Thoracentesis is a medical procedure to remove some fluid between the lungs and the chest wall. The name derives from the Greek words thorax (“chest”) and centesis (“puncture”). It is used to help diagnose and treat medical conditions causing this fluid buildup, called a “pleural effusion.”.
How long does it take for a thoracentesis to come back?
If you are having a diagnostic thoracentesis, your fluid will be sent to the lab for analysis. The tests done here may take a day or more to come back. Your clinician can let you know about the specific results in your situation. These results may help your healthcare provider diagnose your specific medical condition.
What is the most common potentially serious complication of thoracentesis?
The most common potentially serious complication of thoracentesis is pneumothorax. Some other possible problems include:
Is a thoracentesis diagnostic inconclusive?
Sometimes a diagnostic thoracentesis is inconclusive. That just means that your physician needs more information to determine the cause of your medical problems. Depending on the context, you might need one or more of the following:
Why do we do thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis may be performed for diagnostic and/or therapeutic reasons. The diagnostic use of a thoracentesis involves pleural fluid analysis to distinguish between exudate, which may result from inflammatory or malignant conditions, and transudate, which may result from failure of organ systems that affect fluid balance in the body.
Where do you get local anesthesia for thoracentesis?
The patient will receive a local anesthetic at the site where the thoracentesis is to be performed.
What is a thoracentesis needle?
Matt Vera, BSN, R.N. Updated on March 20, 2019. 2. ADVERTISEMENTS. Thoracentesis, also known as pleural fluid analysis, is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the back of the chest wall into the pleural space (a space that exists between the two lungs and the anterior chest wall) to remove fluid or air.
How much fluid should be removed from a pleural edema?
8. Remove the necessary amount of pleural fluid (usually 100 mL for diagnostic studies), but generally not remove more than 1500 mL of fluid at any one time because of increased risk of pleural edema or hypotension. A pneumothorax from needle laceration of the visceral pleura is more likely to occur if an effusion is completely drained.
Where is the needle inserted in the pleura?
Next anesthetize the superior surface of the rib and the pleura. The needle is inserted over the top of rib (superior margin) to avoid the intercostals nerves and blood vessels that run on the underside of the rib (the intercostals nerve and the blood supply are located near the inferior margin). As the needle is inserted, aspirate back on ...
How to place a patient in a sitting position?
Place the patient in a sitting position with arms raised and resting on an overbed table. This position aids in spreading out the spaces between the ribs for needle insertion. If the patient is unable to sit, the patient may be placed in a side-lying position on the edge of the bed on unaffected side.
How long to keep patient in side lying position?
Position the patient in a side-lying position with the unaffected side down for an hour or longer.
What is the procedure called when you have fluid in your chest?
Thoracentesis (say "thor-uh-sen-TEE-sis") is a procedure to remove fluid from the space between the lungs and the chest wall (pleural space). This procedure may also be called a "chest tap.". It is normal to have a small amount of fluid in the pleural space. Too much fluid can build up because of problems such as infection, heart failure, ...
What to do if you have shortness of breath?
Call your doctor or nurse call line now or seek immediate medical care if: You have shortness of breath that is new or getting worse. You have new or worse pain in your chest, especially when you take a deep breath. You are sick to your stomach or cannot keep fluids down. You have a fever over 38°C.
What to do if you take blood thinners?
If you take blood thinners, ask your doctor if and when to start taking them again. Make sure that you understand exactly what your doctor wants you to do. Take pain medicines exactly as directed. If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed.
How long does it take for a chest catheter to heal?
Your chest may be sore where the doctor put the needle or catheter into your skin (the procedure site). This usually gets better after a day or two. You can go back to work or your normal activities as soon as you feel up to it.
What to do if you think pain medicine is making you sick?
If you think your pain medicine is making you sick to your stomach: Take your medicine after meals (unless your doctor has told you not to). Ask your doctor for a different pain medicine. If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you feel better.
Can you take a bath after a syringe?
You may shower. Do not take a bath until the procedure site has healed, or until your doctor tells you it is okay.
Can you breathe if you have pleural fluid removed?
If a large amount of pleural fluid was removed during the procedure, you will probably be able to breathe more easily.
What is a thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a needle into the pleural space around your lungs. The goal is to drain fluid or air in order to make it easier for you to breathe. In some cases, the procedure will also help your doctor discover the cause of your fluid buildup.
What are the risks of the procedure?
Every invasive procedure has risks, but side effects are uncommon with thoracentesis. Possible risks include:
How long does it take to get a pleural effusion?
The amount of fluid drained varies depending on the reasons for performing the procedure. It typically takes 10 to 15 minutes, but it can take longer if there’s a lot of fluid in the pleural space.
What is abnormal on a pleural biopsy?
Abnormal results on a pleural biopsy can indicate certain causes for the effusion, including: the presence of cancer cells, such as lung cancer.
Can you drive home after pleural surgery?
You’ll need someone else to drive you home after the procedure if you’re sedated. After sitting in a chair or lying on a table, you’ll be positioned in a way that allows the doctor to access the pleural space. An ultrasound may be done to ascertain the correct area where the needle will go.
Can you stay overnight after thoracentesis?
To ensure there are no complications, you may be asked to stay overnight in the hospital to be monitored. A follow-up X-ray may be performed right after the thoracentesis.
Is there a special preparation for thoracentesis?
There’s no special preparation for a thoracentesis. However, you should talk to your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about the procedure. You should also tell your doctor if you:

Purpose of Thoracentesis
Procedure to remove excess fluid accumulated in pleural space.
Treatment for: Pleurisy · Tuberculosis · Pneumonia · Pleural Empyema
Type of procedure: Minimally invasive
Recovery time: About one day
Duration: Few minutes
Hospital stay: Not typically needed
Risks and Contraindications
Before The Procedure
During The Procedure
After The Procedure
- People with certain medical conditions cannot have thoracentesis safely. For example, thoracentesis is not usually recommended for people with severe respiratory failure or people who don’t have adequate blood pressure. People who are unable to sit still for the procedure are also not able to have it safely. Healthcare providers are also very cautious in giving thoracentesi…
Interpreting Results
- Before the thoracentesis, your healthcare provider will talk to you about all your medical conditions, perform a physical exam, and assess your health. This will help ensure that thoracentesis makes sense for you. You should also review your medications with your clinician. If you take medications that affect your blood (like Coumadin), you might n...