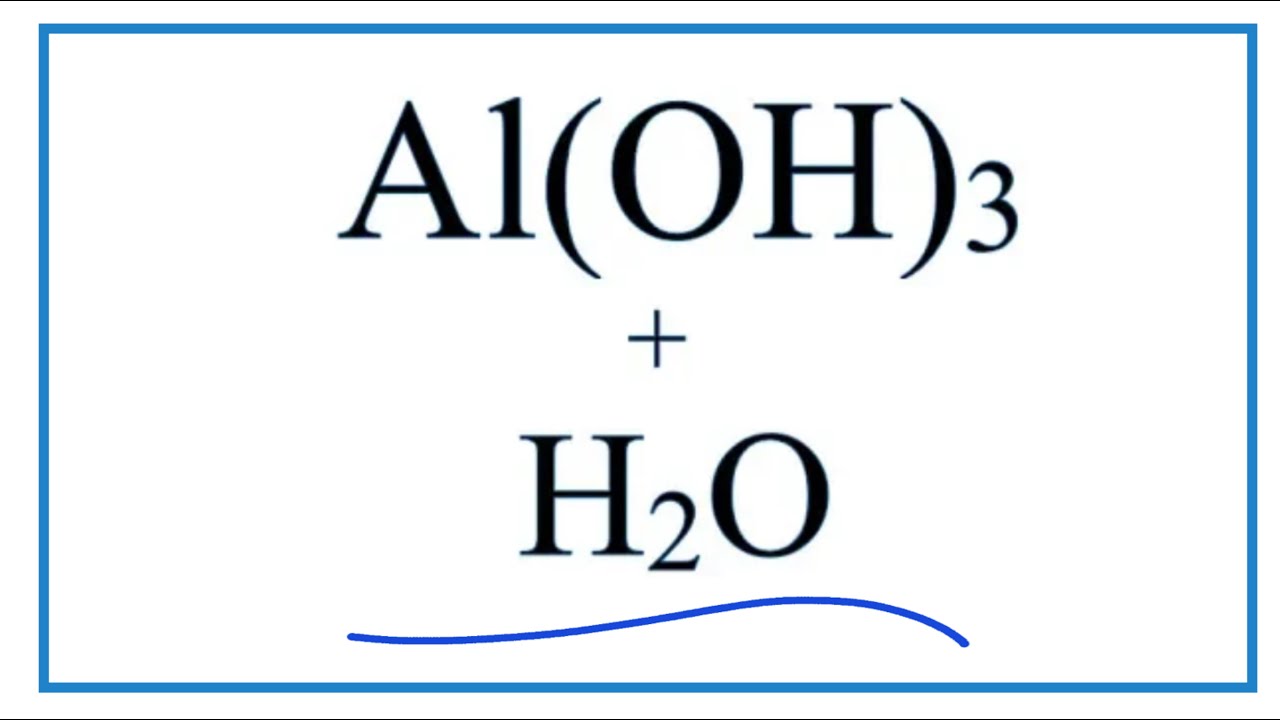
What is the name of the compound Al OH 3?
Aluminium hydroxide. Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH) 3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric in nature, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties.
What is the standard state of Al (OH) 3?
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). ?) Aluminium hydroxide, Al (OH) 3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite.
What is the balanced equation for Al (OH) 3 + HCl?
Al (OH)3 + HCl = AlCl3 + H2O | Chemical reaction and equation Aluminium hydroxide react with hydrogen chloride Al (OH) 3 + 3HCl → AlCl 3 + 3H 2 O [ Check the balance ]
What is Al2O3 used for?
Al 2 O 3 is significant in its use to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. [7] Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide. [8]
Is Aluminium hydroxide a solid or aqueous?
solidAluminum hydroxide is a compound that has the molecular formula of Al(OH)3. It is commonly known as an ingredient in antacid medication. The molecular weight of aluminum hydroxide is 78.0 g/mol. As a solid substance, it is white in color.
What is al2 oh3?
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is the most stable form of aluminium in normal conditions. It is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite). Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide, Al2O3, differing only by loss of water.
What element is Al oh3?
Aluminum HydroxideAluminum hydroxide is a stable form of aluminum and is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite. The compound has both basic and acidic properties.
Is aluminum a solid liquid or gas?
solidAluminum is a solid at room temperature. A solid is the state of matter that holds its own shape and has a fixed volume. You can bend and tear a sheet of aluminum foil, but the total volume of aluminum does not change.
How is Al oh3 made?
It is carried out by dissolving bauxite in sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature range up to 270 °C. The waste is removed and the sodium aluminate solution is allowed to precipitate. Therefore, the precipitate obtained is aluminium hydroxide.
How is Al oh3 amphoteric?
Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties....Aluminium hydroxide.NamesRelated compoundsSodium oxide, aluminium oxide hydroxide48 more rows
Is aluminum sulfide soluble in water?
Aluminum sulfide or aluminium sulphide is a chemical compound with the formula Al2S3....Aluminium sulfide.NamesMelting point1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K)Boiling point1,500 °C (2,730 °F; 1,770 K) sublimesSolubility in waterdecomposesSolubilityinsoluble in acetone31 more rows
Is aluminum hydroxide soluble in water?
AcidHydrochloric acidSulfuric acidAlkaliAluminium hydroxide/Soluble in
Is magnesium hydroxide soluble in water?
WaterMagnesium hydroxide / Soluble inIt is very slightly soluble in water at 0.00122 g/100 ml and has a solubility product of 5.61 × 10−12. Crystals of Mg(OH)2 have a refractive index of 1.559. Its heat of formation is –925 kJ/mol with an entropy of 63 J/mol·K. Magnesium hydroxide is a common component of antacids and laxatives.
Is aluminum a liquid?
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13....AluminiumMelting point933.47 K (660.32 °C, 1220.58 °F)Boiling point2743 K (2470 °C, 4478 °F)Density (near r.t. )2.70 g/cm3when liquid (at m.p. )2.375 g/cm352 more rows
Is aluminum a matter?
Aluminum is concentrated in the outer 16 km (10 miles) of Earth's crust, of which it constitutes about 8 percent by weight; it is exceeded in amount only by oxygen and silicon....Read a brief summary of this topic.atomic number13atomic weight26.9815384melting point660 °C (1,220 °F)boiling point2,467 °C (4,473 °F)3 more rows
What type of element is aluminum?
Aluminium is a silvery-white metal, the 13 element in the periodic table. One surprising fact about aluminium is that it's the most widespread metal on Earth, making up more than 8% of the Earth's core mass. It's also the third most common chemical element on our planet after oxygen and silicon.
What is meta aluminate?
Answer: Sodium meta aluminate is a commonly accepted type of sodium aluminate (NaAlO2). It is a white crystalline solid with a formula given as NaAlO2, NaAl(OH)4 in the hydrated form, Na2O·Al2O3 or Na2Al2O4 in various forms.
What are the side effects of aluminum hydroxide?
Common side effects or health problems may include:Nausea.Vomiting.Rebound hyperacidity.Aluminum-intoxication.Low blood phosphates (hypophosphatemia)Chalky taste.Constipation (this could lead to hemorrhoids or bowel obstruction)Fecal impaction.More items...
Is Aluminium hydroxide toxic?
Seizures, osteomalacia, and encephalopathy are well-documented toxic effects of aluminum hydroxide.
When Should aluminum hydroxide gel be taken?
Take this medication by mouth between meals and at bedtime. Follow all the directions on the product package or use as directed by your doctor. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Shake the bottle well before each dose.
What is the structure of aluminum hydroxide?
Aluminic hydroxide has a typical structure of metal hydroxide consisting of hydrogen bonds. It comprises double layers of hydroxyl groups along with aluminium ions which occupy 2/3rd of the octahedral holes which are formed between the two layers.
What is Aluminium Hydroxide?
Al (OH) 3 is amphoteric in nature with chemical name Aluminium hydroxide.
What are the uses of Al?
Al (OH) 3 Uses (Aluminium hydroxide) 1 Aluminium hydroxide is used as a flame retardant in plastics. 2 Used as an antacid. 3 Used in aluminium Hydroxide gel. 4 Used to manufacture activated alumina. 5 Used as a filler in cosmetics. 6 Used as a chemical intermediate. 7 Used as a soft abrasive for plastics. 8 Used in glass additive to increase resistance to thermal shock. 9 Used in waterproofing fabrics. 10 Used in the manufacturing of glass.
What is the process of making aluminium hydroxide?
Commercially used aluminium hydroxide is manufactured by the Bayer process. It is carried out by dissolving bauxite in sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature range up to 270 °C. The waste is removed and the sodium aluminate solution is allowed to precipitate. Therefore, the precipitate obtained is aluminium hydroxide.
Does aluminium hydroxide cause constipation?
Side effects of aluminium hydroxide include intense stomach pain or constipation, lack of appetite; discomfort while urinating; muscle weakness, fatigue; extreme drowsiness. Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of Al (OH) 3 from the experts at BYJU’S. Test your knowledge on aluminium hydroxide!
Is aluminium an antacid?
Aluminium is a metal that occurs naturally. The antacid is the hydroxide of aluminium. Aluminium hydroxide is used in the treatment of heartburn, stomach pain, sore stomach or indigestion with acid. Aluminium hydroxide is also used in humans with other kidney disorders to reduce phosphate levels.
Is Gibbsite an amphoteric base?
Gibbsite is amphoteric and acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base to yield a salt by picking up hydrogen ions and neutralizing the acid. The reaction is as follows: It acts as a Lewis acid in bases. It takes away an electron pair from the hydroxide ions.
What is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide?
Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide. Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms of corundum, which owe their characteristic colors to trace impurities. Rubies are given their characteristic deep red color and their laser qualities by traces of chromium. Sapphires come in different colors given by various other impurities, such as iron and titanium. An extremely rare, δ form, occurs as the mineral deltalumite.
What is the oxide layer of aluminum?
Aluminium oxide is responsible for the resistance of metallic aluminium to weathering. Metallic aluminium is very reactive with atmospheric oxygen, and a thin passivation layer of aluminium oxide (4 nm thickness) forms on any exposed aluminium surface in a matter of hundreds of picoseconds. This layer protects the metal from further oxidation. The thickness and properties of this oxide layer can be enhanced using a process called anodising. A number of alloys, such as aluminium bronzes, exploit this property by including a proportion of aluminium in the alloy to enhance corrosion resistance. The aluminium oxide generated by anodising is typically amorphous, but discharge assisted oxidation processes such as plasma electrolytic oxidation result in a significant proportion of crystalline aluminium oxide in the coating, enhancing its hardness .
How to grow aluminium oxide?
Aluminium oxide can be grown as a coating on aluminium by anodizing or by plasma electrolytic oxidation (see the "Properties" above). Both the hardness and abrasion-resistant characteristics of the coating originate from the high strength of aluminium oxide, yet the porous coating layer produced with conventional direct current anodizing procedures is within a 60-70 Rockwell hardness C range which is comparable only to hardened carbon steel alloys, but considerably inferior to the hardness of natural and synthetic corundum. Instead, with plasma electrolytic oxidation, the coating is porous only on the surface oxide layer while the lower oxide layers are much more compact than with standard DC anodizing procedures and present a higher crystallinity due to the oxide layers being remelted and densified to obtain α-Al2O3 clusters with much higher coating hardness values circa 2000 Vickers hardness.
What is the chemical formula for aluminium oxide?
Chemical compound. Aluminium oxide is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al 2 O 3. It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium (III) oxide.
When was aluminum oxide removed from the EPA list?
Aluminium oxide was taken off the United States Environmental Protection Agency 's chemicals lists in 1988 . Aluminium oxide is on the EPA's Toxics Release Inventory list if it is a fibrous form.
Is aluminium oxide an acid?
Aluminium oxide is an amphoteric substance, meaning it can react with both acids and bases, such as hydrofluoric acid and sodium hydroxide, acting as an acid with a base and a base with an acid, neutralising the other and producing a salt.
Is aluminum oxide soluble in water?
Aluminium oxide is insoluble in water. In its most commonly occurring crystalline form, called corundum or α-aluminium oxide, its hardness makes it suitable for use as an abrasive and as a component in cutting tools. Aluminium oxide is responsible for the resistance of metallic aluminium to weathering.
What is aluminum hydroxide used for?
Aluminum hydroxide is used to treat heartburn, upset stomach, sour stomach, or acid indigestion. Aluminum hydroxide is also used to reduce phosphate levels in people with certain kidney conditions. Aluminum hydroxide may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
How should I take aluminum hydroxide?
Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor.
What are the side effects of aluminum hydroxide?
Aluminum hydroxide side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficult breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Stop using the medicine and call your doctor at once if you have: severe stomach pain or constipation, loss of appetite; pain when you urinate;

Overview
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or alumina (Al2O3), the latter of which is also amphoteric. The…
Structure
Al(OH)3 is built up of double layers of hydroxyl groups with aluminium ions occupying two-thirds of the octahedral holes between the two layers. Four polymorphs are recognized. All feature layers of octahedral aluminium hydroxide units, with hydrogen bonds between the layers. The polymorphs differ in terms of the stacking of the layers. All forms of Al(OH)3 crystals are hexagonal :
• gibbsite is also known as γ-Al(OH)3 or α-Al(OH)3
Properties
Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric. In acid, it acts as a Brønsted–Lowry base. It neutralizes the acid, yielding a salt:
3 HCl + Al(OH)3 → AlCl3 + 3 H2O
In bases, it acts as a Lewis acid by binding hydroxide ions:
Al(OH)3 + OH → Al(OH)4
Production
Virtually all the aluminium hydroxide used commercially is manufactured by the Bayer process which involves dissolving bauxite in sodium hydroxide at temperatures up to 270 °C (518 °F). The waste solid, bauxite tailings, is removed and aluminium hydroxide is precipitated from the remaining solution of sodium aluminate. This aluminium hydroxide can be converted to aluminium oxide or al…
Uses
Aluminium hydroxide also finds use as a fire retardant filler for polymer applications. It is selected for these applications because it is colorless (like most polymers), inexpensive, and has good fire retardant properties. Magnesium hydroxide and mixtures of huntite and hydromagnesite are used similarly. It decomposes at about 180 °C (356 °F), absorbing a considerable amount of heat in the process and giving off water vapour. In addition to behaving as a fire retardant, it is very effectiv…
Safety
In the 1960s and 1970s it was speculated that aluminium was related to various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease. Since then, multiple epidemiological studies have found no connection between exposure to environmental or swallowed aluminium and neurological disorders, though injected aluminium was not looked at in these studies.
Neural disorders were found in experiments on mice motivated by Gulf War illness (GWI). Alumin…
External links
• International Chemical Safety Card 0373
• "Some properties of aluminum hydroxide precipitated in the presence of clays", Soil Research Institute, R C Turner, Department of Agriculture, Ottawa
• Effect of ageing on properties of polynuclear hydroxyaluminum cations
What Is Aluminium hydroxide?
Table of Contents
Properties of Aluminium Hydroxide – Al(OH)3
- Aluminic hydroxide has a typical structure of metal hydroxide consisting of hydrogen bonds. It comprises double layers of hydroxyl groups along with aluminium ions which occupy 2/3rd of the octahedral holes which are formed between the two layers. Gibbsite is amphoteric and acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base to yield a salt by picking up hydrogen ions and neutralizing the acid. The re…
Production of Aluminium Hydroxide
- Commercially used aluminium hydroxide is manufactured by the Bayer process. It is carried out by dissolving bauxite in sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature range up to 270 °C. The waste is removed and the sodium aluminate solution is allowed to precipitate. Therefore, the precipitate obtained is aluminium hydroxide. Alumina or aluminium oxide can be obtained from …
Al
- Aluminium hydroxide is used as a flame retardant in plastics.
- Used as an antacid.
- Used in aluminium Hydroxide gel.
- Used to manufacture activated alumina.
Health Hazards
- Prolonged exposure to Aluminium(III) hydroxide it causes irritation in eyes, respiratory system, and skin. When comes in contact with water it causes a violent explosion.