What hormone secretes glucagon?
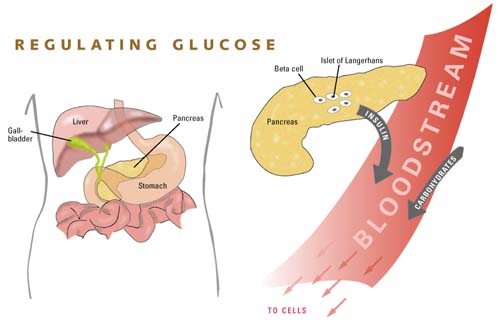
The pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon. Both hormones work in balance to play a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. If the level of one hormone is higher or lower than the ideal range,...
What i8s the stimulus for the release of glucagon?
The release of glucagon is stimulated by low blood glucose, protein-rich meals and adrenaline (another important hormone for combating low glucose). The release of glucagon is prevented by raised blood glucose and carbohydrate in meals, detected by cells in the pancreas. Click to see full answer.
What is the main function of glucagon?
The function of glucagon is to increase the blood glucose levels so that the body has enough energy to function properly. Glucagon supplies glucose to the body by promoting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Glycogenolysis: The liver stores glucose in the form of glycogen.
What is the stimulus for release of glucagon?
When glucagon is released it can perform the following tasks:
- Stimulating the liver to break down glycogen to be released into the blood as glucose
- Activating gluconeogenesis, the conversion of amino acids into glucose
- Breaking down stored fat (triglycerides) into fatty acids for use as fuel by cells
See more

What is the mechanism of glucagon release?
Glucagon secretion occurs as exocytosis of stored peptide vesicles initiated by secretory stimuli of the alpha cell. Stimulatory regulators of glucagon release include hypoglycemia, amino acids and the gut hormone glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), whereas hyperglycemia and GLP-1 inhibit glucagon release.
How does glucagon affect glucose?
Glucagon controls plasma glucose concentrations during fasting, exercise and hypoglycemia by increasing hepatic glucose output to the circulation. Specifically, glucagon promotes hepatic conversion of glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis), stimulates de novoglucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis), and inhibits glucose breakdown (glycolysis) and glycogen formation (glycogenesis) (Fig. 5) (26). Hepatic glucose production is rapidly enhanced in response to a physiological rise in glucagon; achieved through stimulation of glycogenolysis with minor acute changes in gluconeogenesis (27,28). This ability of glucagon is critical in the life-saving counterregulatory response to severe hypoglycemia. Additionally, it is a key factor in providing adequate circulating glucose for brain function and for working muscle during exercise (28). During prolonged fasting, glycogen stores are depleted, and gluconeogenesis takes over (29). The hyperglycemic property of glucagon is enhanced when hepatic glycogen levels are high and diminished when hepatic glycogen levels are low in conditions of fasting or liver diseases like cirrhosis (12).
How is glucagon secreted?
Glucagon is secreted in response to hypoglycemia, prolonged fasting, exercise and protein-rich meals (10) . Glucagon release is regulated through endocrine and paracrine pathways; by nutritional substances; and by the autonomic nervous system (11). Glucagon secretion occurs as exocytosis of stored peptide vesicles initiated by secretory stimuli of the alpha cell. Stimulatory regulators of glucagon release include hypoglycemia, amino acids and the gut hormone glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), whereas hyperglycemia and GLP-1 inhibit glucagon release. Additionally, glucagon release is inhibited in a paracrine fashion by factors like somatostatin, insulin, zinc and possibly amylin. Glucagon may regulate its own secretion indirectly via stimulatory effect on beta cells to secrete insulin (12,13). In contrast to glucose, non-glucose regulators of glucagon secretion seem to mediate their action through changes in cAMP levels rather than through the calcium-dependent pathway outlined below (14,15).
What is the role of glucagon in the body?
Hypoglycemia is physiologically the most potent secretory stimulus and the best known action of glucagon is to stimulate glucose production in the liver and thereby to maintain adequate plasma glucose concentrations. However, glucagon is also involved in hepatic lipid and amino acid metabolism and may increase resting energy expenditure. Based on satiety-inducing and food intake-lowering effects of exogenous glucagon, a role for glucagon in the regulation of appetite has also been proposed. This chapter provides an overview of the structure, secretion, degradation and elimination of glucagon, and reviews the actions of glucagon including its role in glucose metabolism and its effects on lipolysis, ketogenesis, energy expenditure, appetite and food intake. Finally, the role of glucagon in the pathophysiology of diabetes, obesity and hepatic steatosis is discussed and emerging glucagon-based therapies for these conditions are outlined. For complete coverage of all related areas of Endocrinology, please visit our on-line FREE web-text, WWW.ENDOTEXT.ORG.
What enzyme is used to make proglucagon?
In the pancreas proglucagon is processed into glucagon, glicentin-related pancreatic polypeptide (GRPP), intervening peptide 1 (IP1), and major proglucagon fragment (MPGF) by the processing enzyme prohormone convertase 2 (PC2) . In the intestine and in the brain proglucagon is processed by prohormone convertase 1/3 (PC1/3) into glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2), oxyntomodulin, intervening peptide 2 (IP2), and glicentin.
Where is the glucagon receptor located?
The glucagon receptor is a seven transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor (Fig. 4) predominantly expressed in the liver, but also found in varying amounts in the kidneys, heart (controversial), adrenal glands, adipose tissue (controversial), gastrointestinal tract, and pancreas (21).
Which cell is the most potent regulator of glucagon secretion?
Regulation of Glucagon Secretion by Glucose. The most potent regulator of glucagon secretion is circulating glucose. Hypoglycemia stimulates the pancreatic alpha cell to release glucagon and hyperglycemia inhibits glucagon secretion (Fig. 2) (11).
How to stimulate glucagon production?
So the first thing you need to do to stimulate the production of glucagon is to reduce total carbohydrates in your diet and be sure those you choose are low glycemic. But there’s another important step to crank up your body’s production of glucagon: Eat a protein-rich diet!
What hormones release fat?
Glucagon also signals the fat cells to release free fatty acids (a process called lipolysis). Glucagon signals the body to release stored fat to be used as fuel. Numerous research studies illustrate the effects of these two opposing hormones.
How to shift hormones from sugar burner to fat burner?
The key is to consume plenty of protein and healthy fats. And be sure that the carbs you choose are low glycemic and high in fiber. By eating this way, your hormonal state will shift from that of a “sugar burner” to a “fat burner.”
Why is it important to keep insulin levels low?
If you want to convert your body to a perpetual fat-burning state, it is essential that you keep your insulin and blood sugar levels low. That’s because burning sugar always takes precedence over burning fat. The more carbohydrates in your diet, the higher your blood sugar and insulin levels will be. And in the end, being a “sugar burner” means ...
What hormones are involved in the fat burning process?
The other half involves the “fat-burning hormone,” glucagon. By understanding the interplay between these two important hormones and how they are affected by the foods you eat, you can truly win the battle of the bulge.
What is the name of the fat storage and blocking hormone?
Insulin is a fat-storage and blocking hormone.
What hormone is used to burn fat?
Unlock Glucagon: Your Body’s Fat-Burning Hormone. This may come as a surprise, but burning body fat and sculpting a lean, healthy physique is not about eating less food. It’s about eating the right kinds of foods.
Which cell secretes glucagon?
Islet beta-cell secretion determines glucagon release from neighbouring alpha-cells. Homeostasis of blood glucose is maintained by hormone secretion from the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Glucose stimulates insulin secretion from beta-cells but suppresses the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood glucose, from alpha-cells.
Does pyruvate stimulate glucagon secretion?
We find that pyruvate, a glycolytic intermediate and principal substrate of mitochondria, stimulates glucagon secretion. Our analyses indicate that, although alpha-cells, like beta-cells, possess the inherent capacity to respond to nutrients, secretion from alpha-cells is normally suppressed by the simultaneous activation of beta-cells.
Does glucose stimulate insulin secretion?
Glucose stimulates insulin secretion from beta-cells but suppresses the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood glucose, from alpha-cells. The mechanism by which nutrients stimulate insulin secretion has been studied extensively: ATP has been identified as the main messenger and the ATP-sensitive potassium channel as an essential ...
Which system secretes products into ducts that lead to body surfaces or cavities?
D) The endocrine system secret es products into ducts that lead to body surfaces or cavities.
Which system produces immediate, short-lasting effects?
A) The endocrine system produces immediate, short-lasting effects.
