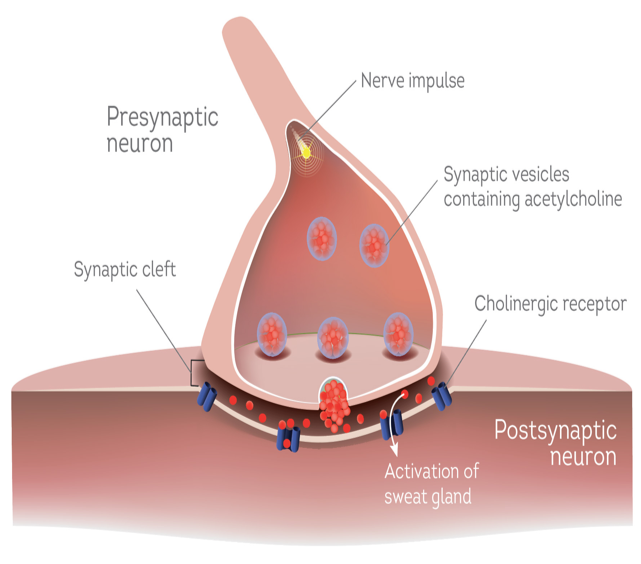
What type of peptide is VIP?
View/Edit Mouse. Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors.
What is the function of VIP in humans?
VIP is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas, and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain. VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder.
What is the effect of VIP on the stomach?
VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation ( lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice and bile, and cause inhibition of gastric acid secretion and absorption from the intestinal lumen.
What is the effect of VIP on the heart?
It causes coronary vasodilation as well as having a positive inotropic and chronotropic effect. Research is being performed to see if it may have a beneficial role in the treatment of heart failure. VIP provokes vaginal lubrication in normal women, doubling the total volume of lubrication produced.
What is the role of vip in the heart?
What is the effect of VIP on the digestive system?
What is the signaling pathway in SCN?
What is a vasoactive peptide?
Where is the VIP neuropeptide released?
Where are VIP cascades activated?
Which neurons are responsible for social behavior?
See 4 more
About this website

What triggers the release of VIP?
VIP, released in response to gut distention, is a potent vasodilator and is responsible for the relaxation of vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle of the intestinal tract. It is also a potent stimulator of water and electrolyte secretion, activating adenylate cyclase through stimulation of cAMP.
What causes high VIP levels?
A very high level is usually caused by a VIPoma . This is an extremely rare tumor that releases VIP. VIP is a substance found in cells throughout the body. The highest levels are normally found in cells in the nervous system and gut.
How do you increase vasoactive intestinal peptides?
We have previously shown that plasma vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) is increased in normal subjects by low-frequency transcutaneous nerve stimulation. The latter may also increase short-term physical performance in athletes (running, swimming and ergometer cycling).
Does VIP stimulate insulin release?
GIP directly stimulates insulin secretion through the β cell GIPR. Indirectly, GIP potentiates α cell activity to enhance α to β cell communication through the GLP-1R/GCGR. Thus, GIP indirectly stimulates insulin secretion through the α cell.
What does VIP do to your body?
A hormone found in the pancreas, intestine, and central nervous system. It has many actions in the body, such as helping to control the secretion of water, salts, enzymes, and gastric acid during digestion. It also causes smooth muscles in the digestive tract, the heart, and the blood vessels to relax.
What does high vasoactive intestinal peptide mean?
Values above 75 pg/mL may indicate the presence of an enteropancreatic tumor causing hypersecretion of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Values above 200 pg/mL are strongly suggestive of VIP-producing tumors (VIPoma).
Does VIP stimulate appetite?
VIP plays a key role in the regulation of body weight and mass composition phenotype by significantly enhancing body weight and fat mass accumulation. Therefore, VIP signaling is critical for the modulation of appetite/satiety and body mass phenotype and is suggested to be a target for future treatment of obesity.
What is VIP medication?
An abbreviation for a chemotherapy combination used to treat advanced testicular cancer. It is often used in patients who cannot receive bleomycin. It includes the drugs etoposide (VePesid), ifosfamide, and cisplatin (Platinol). Also called VIP.
Does VIP increase gastric motility?
In the stomach VIP produced a gastric relaxation and a blood flow increase. The motility response was similar to that observed when eliciting the vago-vagal reflex relaxation by distending the esophagus.
What stimulates release of gastric inhibitory peptide?
glucoseThe intake of glucose stimulates secretion of gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP), which passes to the pancreas causing the B cells to secrete insulin (Fig. 24.5). The presence of glucose (and fatty acids also) in the ileum stimulates the release of enteroglucagon: this too increases insulin release.
What stimulates GLP-1 release?
In the L-cells, GLP-1 is generated by tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon gene (1). Nutrients, including glucose, fatty acids, and dietary fiber, are all known to upregulate the transcription of the gene encoding GLP-1, and they can stimulate the release of this hormone (2).
What does GLP-1 and GIP do?
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) are the two primary incretin hormones secreted from the intestine on ingestion of glucose or nutrients to stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells.
What is VIP disease?
VIPoma is a type of neuroendocrine tumour (NET) that usually starts in the pancreas. Its symptoms can be vague. See your GP if you are worried. VIPomas usually make large amounts of a hormone called vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). VIP relaxes the muscles in the stomach and bowel.
What does VIP mean in medical terms?
An abbreviation for a chemotherapy combination used to treat advanced testicular cancer. It is often used in patients who cannot receive bleomycin. It includes the drugs etoposide (VePesid), ifosfamide, and cisplatin (Platinol). Also called VIP regimen.
How do you treat VIPoma?
Initial treatment of VIPomas is directed toward correcting volume and electrolyte abnormalities. Octreotide acetate controls diarrhea in up to 90% of patients with VIPomas. Glucocorticoids reduce symptoms in 50%. Systemic chemotherapy may be needed in cases of unresectable or progressive disease.
How is VIPoma diagnosed?
Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and somatostatin receptor scintigraphy are imaging modalities that can be used in the diagnosis of VIPoma. Reports have demonstrated successful VIPoma localization with99m Tc sestamibi. No formal staging criteria for VIPoma have been generally accepted.
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide - You Are The Healer
The content of this website is for informational purposes only. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any illness or disease. Information is shared for educational purposes only, and is believed to be accurate at the time it was developed, but it should be viewed as general information, which may need to be adjusted to fit individual circumstances.
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Tumor (VIPoma) - NCBI Bookshelf
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is a neurotransmitter which is present in the neurons in the central nervous system, the lung, intestine, adrenals, pancreas, and liver and in neuroendocrine cells in the pancreas. In the gastrointestinal tract, VIP stimulates contraction of enteric smooth muscle cells, secretion from the exocrine pancreas, gastrointestinal blood flow, and inhibition of ...
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Alan W. Partin MD, PhD, in Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology, 2021 Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide. The penis is richly supplied with nerves containing vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and VIP-related peptides such as pituitary adenylate cyclase–activating polypeptide. Most of these nerves also contain immunoreactivity to NOS (Andersson, 2001).Two subtypes of VIP receptors, VPAC1 and VPAC2 ...
VIP - Overview: Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide, Plasma
1. Smith SL, Branton SA, Avino AJ, et al: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide secreting islet cell tumors: a 15-year experience and review of the literature.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide | C147H237N43O43S - PubChem
Vasoactive intestinal peptide | C147H237N43O43S | CID 53314964 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature ...
What is the role of vip in the heart?
VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the VIP gene. VIP has a half-life (t ½) in the blood of about two minutes.
What is the effect of VIP on the digestive system?
VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation ( lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice and bile, and cause inhibition of gastric acid secretion and absorption from the intestinal lumen.
What is the signaling pathway in SCN?
Signaling pathway. In SCN, there is an abundant amount of VPAC2. The presence of VPAC2 in ventrolateral side suggests that VIP signals can actually signal back to regulate VIP secreting cells. SCN has neural multiple pathways to control and modulate endocrine activity.
What is a vasoactive peptide?
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors.
Where is the VIP neuropeptide released?
The production and release of the neuropeptide VIP is centralized in the hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic regions of the brain and from there it is able to modulate the release of prolactin secretion. Once secreted from the pituitary gland, prolactin can increase many behaviors such as parental care and aggression.
Where are VIP cascades activated?
Studies suggest that VIP cascades can be activated in the brain in response to a social situation that stimulates the areas of the brain that are known to regulate behavior. This social circuit includes many areas of the hypothalamus along with the amygdala and the ventral tegmental area.
Which neurons are responsible for social behavior?
Social behavior. Ventromedial hypothalamus (VM), optic chiasm (OC), anterior pituitary (AP), and posterior pituitary (PP) are shown here. VIP neurons located in the hypothalamus, specifically the dorsal anterior hypothalamus and ventromedial hypothalamus, have an effect on social behaviors in many species of vertebrates.
What is the role of vip in the heart?
VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the VIP gene. VIP has a half-life (t ½) in the blood of about two minutes.
What is the effect of VIP on the digestive system?
VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation ( lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice and bile, and cause inhibition of gastric acid secretion and absorption from the intestinal lumen.
What is the signaling pathway in SCN?
Signaling pathway. In SCN, there is an abundant amount of VPAC2. The presence of VPAC2 in ventrolateral side suggests that VIP signals can actually signal back to regulate VIP secreting cells. SCN has neural multiple pathways to control and modulate endocrine activity.
What is a vasoactive peptide?
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors.
Where is the VIP neuropeptide released?
The production and release of the neuropeptide VIP is centralized in the hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic regions of the brain and from there it is able to modulate the release of prolactin secretion. Once secreted from the pituitary gland, prolactin can increase many behaviors such as parental care and aggression.
Where are VIP cascades activated?
Studies suggest that VIP cascades can be activated in the brain in response to a social situation that stimulates the areas of the brain that are known to regulate behavior. This social circuit includes many areas of the hypothalamus along with the amygdala and the ventral tegmental area.
Which neurons are responsible for social behavior?
Social behavior. Ventromedial hypothalamus (VM), optic chiasm (OC), anterior pituitary (AP), and posterior pituitary (PP) are shown here. VIP neurons located in the hypothalamus, specifically the dorsal anterior hypothalamus and ventromedial hypothalamus, have an effect on social behaviors in many species of vertebrates.

Overview
Function
VIP has an effect on several tissues:
In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation (lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice and bile, and cause inhibition of gastric acid secretion and absorption from the intestinal lumen. Its role in the intestine is to greatly stimulate secretion of water and electrolytes, as well as relaxation of enteri…
Mechanisms
VIP binds to both VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors. When VIP binds to VPAC2 receptors, a G-alpha-mediated signaling cascade is triggered. In a number of systems, VIP binding activates adenyl cyclase activity leading to increases in cAMP and PKA. The PKA then activates other intracellular signaling pathways like the phosphorylation of CREB and other transcriptional factors. The mPer1 promoter has CRE domains and thus provides the mechanism for VIP to regulate the molecular …
Social behavior
VIP neurons located in the hypothalamus, specifically the dorsal anterior hypothalamus and ventromedial hypothalamus, have an effect on social behaviors in many species of vertebrates. Studies suggest that VIP cascades can be activated in the brain in response to a social situation that stimulates the areas of the brain that are known to regulate behavior. This social circuit includes many areas of the hypothalamus along with the amygdala and the ventral tegmental area. …
Pathology
VIP is overproduced in VIPoma.
In addition to VIPoma, VIP has a role in osteoarthritis (OA). While there is existing conflict in whether down-regulation or up-regulation of VIP contributes to OA, VIP has been shown to prevent cartilage damage in animals.
See also
• Hypothalamic–pituitary–prolactin axis
• Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor
• VPAC1
• VPAC2
Further reading
• Watanabe J (1 January 2016). Subchapter 18E - Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide. Handbook of Hormones. Academic Press. pp. 150–e18E–10. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-801028-0.00146-x. ISBN 9780128010280.
• Fahrenkrug J (2001). "Gut/brain peptides in the genital tract: VIP and PACAP". Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. Supplementum. 61 (234): 35–9. doi:10.1080/003655101317095392. PMID 11713978.
• Watanabe J (1 January 2016). Subchapter 18E - Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide. Handbook of Hormones. Academic Press. pp. 150–e18E–10. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-801028-0.00146-x. ISBN 9780128010280.
• Fahrenkrug J (2001). "Gut/brain peptides in the genital tract: VIP and PACAP". Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. Supplementum. 61 (234): 35–9. doi:10.1080/003655101317095392. PMID 11713978. S2CID 7249967.
External links
• Pathway at biocarta.com
• Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 6/6ch2/s6ch2_34". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
• Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P01282 (VIP peptides) at the PDBe-KB.