
What is a codon in DNA?
Codon A codon is a triple sequence of DNA and RNA that corresponds to a specific Amino acid. It describes the relationship between DNA�s sequence bases (A, C, G, and T) in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes. The triplet of bases in DNA encoded amino acid.
How many base pairs of codons are in a strand?
Most images show 17 base pairs. For the Codonsanimation, the left-most two base pairs are hidden, leaving exactly five 3-base codons (15 base pairs). The coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above).
Which strand of RNA contains codons and which strand contains anticodons?
It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains anticodons. During transcription, RNA Pol II binds to the non-coding template strand, reads the anti-codons, and transcribes their sequence to synthesize an RNA transcript with complementary bases.
What are the three stop codons in mRNA?
The three stop codons in mRNA are UAG, UAA, and UGA. While 61 codons code for amino acids, humans only have 20 amino acids, so there are more codons than necessary. This is known as redundancy. An amino acid can have more than one codon that codes for it.
What is a codon in DNA?
Codon. A codon is a triple sequence of DNA and RNA that corresponds to a specific Amino acid. It describes the relationship between DNA�s sequence bases (A, C, G, and T) in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes. The triplet of bases in DNA encoded amino acid.
How are codons interpreted?
Codons have three letters the genetic code can be interpreted in three ways. These three ways are called Reading Frames. For an instant, the gene CGAGCCTCC, if we read from the first position (or frame), it contains the codons CGA, GCC, TCC. If we read from the second position (or frame), it contains the codons GAG and CCT. If read by third position (or frame), it contains AGC and CTC codons. Because the code is read as triplets codons each the second and third reading frames just contain two complete codons.
What is the sequence of nucleotides that are complementary to codons called?
Anticodon Definition Biology. Sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons are called anticodon. They are found in tRNAs and allow the tRNAs to take correct amino acid in a way with mRNA during protein production.
What is an anticodon?
Anticodon Definition. Anticodons are basically the section of a transfer RNA (t RNA) is a categorization of three bases which are corresponding to codons in the mRNA. During the translation process, the Anticodon bases form corresponding base sets among the bases of the codon by establishing the suitable hydrogen bonds.
What happens to RNA after transcription?
After transcription of RNA, translation follows when a ribosome latches itself to an mRNA strand. The ribosome moves to mRNA until it recognizes a start codon, and their translation starts. The start codons always work for methionine in eukaryotes and modified Met (fMet) in prokaryotes.
What is the function of anticodons?
The function of anticodons is to take correct amino acid together to create a protein, based on the instructions carried in mRNA. Every tRNA carries one anticodon and has one amino acid. When the anticodon successfully pairs up with mRNA codons, the correct amino acid is in place to be added to the growing protein.
What does it mean when two different codons do not use the same letter?
No overlapping: The genetic code never does overlapping, that�s mean the adjacent codon never overlap each other. A no overlapping code means that two different codons did not use the same letter. Non-Ambiguity: The same amino acid always coded by a particular codon.
What is the coding strand?
By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a DNA sequence. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction .
What is the position of the template and coding strands during transcription?
Position of the template and coding strands during transcription. When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil ). It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains ...
What is the difference between a coding strand and a template strand?
Where the helix is unwound, the coding strand consists of unpaired bases, while the template strand consists of an RNA:DNA composite, followed by a number of unpaired bases at the rear.
How does DNA rewound?
The DNA double helix is rewound by RNA polymerase at the rear of the transcription bubble. Like how two adjacent zippers work, when pulled together, they unzip and rezip as they proceed in a particular direction. Various factors can cause double-stranded DNA to break; thus, reorder genes or cause cell death.
Which direction does RNA polymerase travel?
The RNA polymerase, and with it the transcription bubble, travels along the noncoding strand in the opposite, 3' to 5', direction, as well as polymerizing a newly synthesized strand in 5' to 3' or downstream direction. The DNA double helix is rewound by RNA polymerase at the rear ...
How many codons are there in RNA?
Any of the four nucleotides in RNA may occupy one of three possible codon positions. Therefore, there are 64 possible codon combinations. Sixty-one codons specify amino acids and three (UAA, UAG, UGA) serve as stop signals to designate the end of protein synthesis.
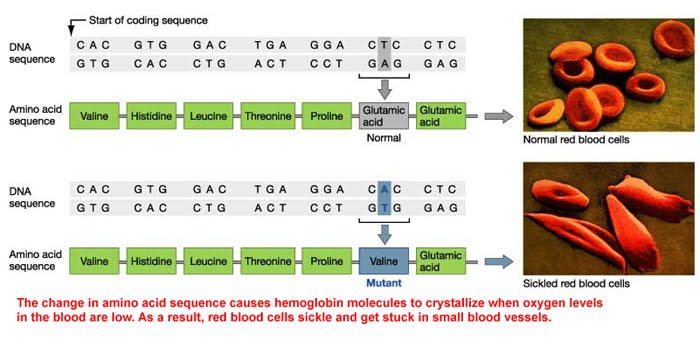
What happens when a codon is changed?
If the codons are changed, the amino acids and thus the proteins that are synthesized will not be the ones coded for in the original gene sequence. Gene mutations can be generally categorized into two types: point mutations and base-pair insertions or deletions. Point mutations alter a single nucleotide.
What is the codon UAC?
For example, the codon UAC (uracil, adenine, and cytosine) specifies the amino acid tyrosine. Some codons represent start (AUG) and stop (UAG) signals for RNA transcription and protein production. Gene mutations can alter codon sequences and negatively impact protein synthesis.
How does RNA translation work?
During translation, each RNA codon is read and the appropriate amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain by transfer RNA. The mRNA molecule will continue to be translated until a termination or stop codon is reached.
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is a sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA that code for the production of specific amino acids. Amino acids are linked together to form proteins.
What is the genetic code of a protein?
Updated November 05, 2019. The genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide bases in nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) that code for amino acid chains in proteins. DNA consists of the four nucleotide bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). RNA contains the nucleotides adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil (U).
What are the four bases that are stored in DNA?
Genetic information is stored as long, complex sequences of the four different bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine ( C). Triplets of these bases are interpreted by the genetic machinery as instructions to add a certain amino acid to a protein.
What is the start codon in protein?
One “ Start ” codon (AUG) marks the beginning of a protein. AUG encodes the amino acid, called Methionine.
Why are codons used in natural selection?
Codon usage biases could be the consequence of natural selection (tRNA abundance ). For laboratories to produce certain proteins in a large quantity, researchers may perform “codon optimization” to resynthesize genes in such a way that their codons are more appropriate for the desired expression host (i.e., making human proteins in E coli. bacteria).
What is the name of the mRNA molecule that Nirenberg discovered?
Nirenberg started with an mRNA molecule consisting only of the nucleotide uracil (called poly-U). When he added poly-U mRNA to the cell-free system, he found that the polypeptides made consisted exclusively of the amino acid – Phenylalanine (Phe). Nirenberg concluded that UUU might code for phenylalanine. Using the same approach, he discovered that triplet CCC codes for Proline (Pro).
What is the relationship between amino acids and codons called?
The full set of relationships between codons and amino acids (or stop signals) is called the genetic code . The genetic code is often summarized in a codon chart (or codon table), where codons are translated to amino acids.
What is the order of the protein translation?
mRNA codons are read from 5′ end to 3′ end, and its order specifies the order of amino acids in a protein from N-terminus to C-terminus.
What is the ribosome in mRNA?
Codons in an mRNA are read by a ribosome during translation. A ribosome is a particle-like cell organelle made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins. A ribosome consists of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Three binding sites for tRNA (A, P, and E sites) between the two subunits. Read more about ribosomes.
What is a short chain of amino acids called?
Note: A short chain of amino acids is often referred to as a “polypeptide”. When the number of amino acids adds up (usually > 30 units) and the polypeptide chain folds into a 3D structure, we call it a “protein”.
What is the codon at the end of a protein called?
And then at the end of the proteins we have a special codon called stop codons . There's actually three of those, three different triplets, that tell the translational machinery that's making the protein that here's the place to stop making the protein, and those are called stop codons.
What is the stop codon?
A stop codon is a trinucleotide sequence within a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that signals a halt to protein synthesis. The genetic code describes the relationship between the sequence of DNA bases (A, C, G, and T) in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes. The cell reads the sequence of the gene in groups of three bases.
How many nucleotides are in a genetic code?
The genetic code is made up of stretches of three nucleotides in a row, each of which specifies an amino acid to be plugged in to ultimately to make a protein. If we just continually made proteins, we'd have this giant long stretch of nonsense proteins, so we need some punctuation.

Overview
When referring to DNA transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand ) is the DNA strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the RNA transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It is this strand which contains codons, while the non-coding strand contains anticodons. During transcription, RNA Pol II binds to the non-coding template strand, reads t…
Strands in transcription bubble
During transcription, RNA polymerase unwinds a short section of the DNA double helix near the start of the gene (the transcription start site). This unwound section is known as the transcription bubble. The RNA polymerase, and with it the transcription bubble, travels along the noncoding strand in the opposite, 3' to 5', direction, as well as polymerizing a newly synthesized strand in 5' to 3' or downstream direction. The DNA double helix is rewound by RNA polymerase at the rear of th…
RNA-DNA hybrid
Where the helix is unwound, the coding strand consists of unpaired bases, while the template strand consists of an RNA:DNA composite, followed by a number of unpaired bases at the rear. This hybrid consists of the most recently added nucleotides of the RNA transcript, complementary base-paired to the template strand. The number of base-pairs in the hybrid is under investigation, but it has been suggested that the hybrid is formed from the last 10 nucleotides added.
See also
• Sense strand
• Sense (molecular biology)
Works cited
• Griffiths, A.J.F.; et al. (2005). Introduction to Genetic Analysis (8th ed.). W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-4939-4.
• Lewin, B. (2000). Genes VII. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-879277-8.