
Do all ferns have roots?
All ferns have roots. The root system of a fern is made up of rhizomes, which are short underground stems that form from nodes at the base of the plant. There are also stolons (stems with leaves), which form at the tip of each rhizome. In addition, there are fronds, which are leafy structures formed at the tips of the stolons.
How do ferns reproduce?
The rhizomes (fibrous structures that resemble roots) can spread through soil, sprouting new ferns. Ferns grown from rhizomes are also identical to their parents. This is another method that permits quick reproduction. Ferns use both sexual and asexual reproduction methods.
What does a fertile fern look like?
Fronds that do have them are called fertile fronds . Spores are tiny structures that contain the genetic material needed to grow a new fern. They may be green, yellow, black, brown, orange, or red. Spores are encased in structures called sporangia, which sometimes clump together to form a sorus (plural sori).
What are the balls on roots of ferns?
Root Nodules On Boston Fern: What Are The Balls On Roots Of Fern Plants. Ferns are ancient plants that reproduce by generating and spreading spores, much like fungi and mushrooms. Boston fern, also known as sword fern, is a dependable plant with masses of long, graceful fronds.

What is the structure of a fern plant?
The structure of a fern. Ferns have 3 major parts – the rhizome, the fronds and the reproductive structures called sporangia. The characteristics of each of these 3 parts of the fern plant are used for classification and identification.
What type of roots does fern have?
The ferns produce numerous roots on the rhizome. These are adventitious roots. Each root emerges from deep within the stem tissue. The roots possess root hairs and have root caps at their growing tips.
Do ferns plants have roots?
Ferns generally reproduce by producing spores. Similar to flowering plants, ferns have roots, stems and leaves.
Do ferns have fibrous roots?
It is usually formed by thin, moderately branching roots growing from the stem. A fibrous root system is universal in monocotyledonous plants and ferns. The fibrous root systems look like a mat made out of roots when the tree has reached full maturity.
Why do ferns have roots?
Root nodules on Boston ferns aren't harmful. They are a natural adaptation that ensures the plant's survival. Boston fern nodules help the plant take up moisture and nutrients in the soil. They are important because they store water for the plant during periods of drought.
Do ferns have roots and rhizoids?
It doesn't have roots, stems or leaves, but it does have rhizoids that anchor it to the soil and help with absorption.
How does a fern grow?
Instead of growing from seed like most flowering plants, ferns come from a single spore. Spores become gametophytes, which produce male gametes and an egg structure. When fertilized, the gametophyte generates a sporophyte (the fern plant).
How deep are roots on ferns?
However, most ferns have roots that grow about six inches into the soil. This is deeper than the shallow roots of plants with a wide lattice of roots that remain near the surface yet it is farm shallower than the roots of plants that produce deep taproots.
What type of plant is a fern?
nonflowering vascular plantsfern, (class Polypodiopsida), class of nonflowering vascular plants that possess true roots, stems, and complex leaves and that reproduce by spores.
Are ferns monocots or dicots?
Ferns are neither monocots nor dicots. These labels refer to the embryonic leaves within the seeds of angiosperms, which are plants that reproduce with flowers and fruits.
Does a fern have adventitious roots?
Fern roots arise directly from the rhizome. These are adventitious roots. Like all roots, fern roots have a central region of xylem surrounded by phloem, an endodermis, cortex, and epidermis that is not covered with cuticle.
Do ferns have big roots?
Fern roots are generally thin and wiry, although some are fleshy and either slender (in the Ophioglossaceae) or as much as 13 mm (0.5 inch) in diameter (e.g., Acrostichum and Marattia).
Do ferns outgrow their pots?
Most species will with time do so. You can then remove them from the pot, divide them into clumps and replant them in new pots. This helps you mult...
What do you do with fern roots?
Normally you can plant them in new pots and they will yield new ferns. You can keep these or give them away. Alternatively, after you cut them off...
Can you trim the roots of a fern?
Yes. In many cases what you think is a root is actually a piece of the rhizome or a stolen. Either can be removed and planted to yield a new fern....
Do ferns need a lot of root space?
This will depend on the fern! Choose a fern that suits your space. There are 10500 species which range from being about 2 inches tall to giant tree...
Where do ferns grow?
Some are twining and vinelike; others float on the surface of ponds. The majority of ferns inhabit warm, damp areas of the Earth. Growing profusely in tropical areas, ferns diminish in number with increasingly higher latitudes and decreasing supplies of moisture. Few are found in dry, cold places. filmy fern.
How big are ferns?
In size alone they range from minute filmy plants only 1–1.2 cm (0.39–0.47 inch) tall to huge tree ferns 10 to 25 metres (30 to 80 feet) in height. Some are twining and vinelike; others float on the surface of ponds.
Where do athyriums live?
Most of the other families occur in both the tropics and the temperate zones. Only certain genera are primarily temperate and Arctic (e.g., Athyrium, Cystopteris, Dryopteris, and Polystichum ), and even these tend to extend into the tropics, being found at high elevations on mountain ranges and volcanoes.
Do ferns have vascular systems?
Ferns, like all tracheophytes, have vascular systems to bring water up to their leaves. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. fern, (class Polypodiopsida), class of nonflowering vascular plants that possess true roots, stems, and complex leaves and that reproduce by spores. The number of known extant fern species is about ...
Where do ferns grow?
Ecologically, the ferns are most commonly plants of shaded damp forests of both temperate and tropical zones. Some fern species grow equally well on soil and upon rocks; others are confined strictly to rocky habitats, where they occur in fissures and crevices of cliff faces, boulders, and taluses.
What are the adaptations of ferns?
Ingmar Holmasen. Both epipetric (growing on rocks) and epiphytic ferns may show structural adaptations to dry habitats similar to those of some desert plants. These adaptive features include such specializations as hard tissues and thick texture; the surface cells, or epidermis, may be provided with a very thick cuticle (a waxy layer);
How do fern gametophytes develop?
It develops in a microenvironment characterized by little competition from other plants (including even mosses and algae); exposed humus, decomposing plant materials, or fresh mineral surfaces; deep to moderate shade; and a humid atmosphere. Even ferns whose sporophytes tolerate sun and drought tend to have these requirements for their gametophytes. On rocks, for example, the gametophytes form in protected crevices in which light is minimal and moisture maximal. Because of their requirements for exposed soil, development of fern gametophytes is promoted by damage to mature vegetation, such as fallen trees in the forest, flooding, and deep erosion. Prothallia are observed in nature most commonly upon shaded soil banks in forests and along streams and upon rotting logs.
What is the name of the fungus that attacks ferns?
Fungi infect ferns, some of them producing soruslike (i.e., resembling the sorus, the sporangium cluster of ferns) dark bodies, or sclerotia. Snails and slugs commonly attack young, uncurling fronds (leaves) of some species, and various beetles have been observed to graze upon ferns.
Do ferns need shade?
Ferns that grow in the open are often referred to as sun ferns (e.g., Gleichenia) and, unlike most ferns, do not (at least as mature plants) require shade. Water ferns —waterclovers ( Marsilea ), water spangles ( Salvinia ), and mosquito ferns ( Azolla )—surprisingly are very commonly inhabitants of dry regions.
Do ferns reproduce sexually?
As the bulk of reproduction of ferns is probably vegetative, taking place in the sporophytic stage, the presence of a large stand of a particular kind of fern results not so much from sexual reproduction by gametophytes as from clone formation by rhizomes and in some cases by root or leaf proliferations.
What is a fern?
Ferns are ancient plants that reproduce by generating and spreading spores, much like fungi and mushrooms. Boston fern, also known as sword fern, is a dependable plant with masses of long, graceful fronds. One might also notice root nodules on Boston fern plants.
How to propagate dead ferns?
Sometimes, you can successfully propagate an old, dead fern by planting nodules, which may be fleshy and green even if the main plant is dry and shriveled. Plant the nodules in a pot with the green growth facing upward, just above the surface of sterile potting mix. Place the pot in a plastic bag and fill the bag with air.
How to propagate a rhizome?
You can also propagate the plant by planting the root nodules. Plant a small section of rhizome with attached root nodules in a pot filled with moist potting soil or equal parts sand and peat. A rhizome with at least three nodules is more likely to root.
How to grow a sage plant in a pot?
Place the pot in a plastic bag and fill the bag with air. Place the pot in indirect light and temperatures between 59 and 68 F. (15-20 C .). With any luck, you’ll notice small, white nodules in one to three months. When the nodules develop roots, remove the plastic bag and plant each rooted nodule in its own pot.
Are Balls on Boston Fern Roots Harmful?
Root nodules on Boston ferns aren’t harmful. They are a natural adaptation that ensures the plant’s survival. Boston fern nodules help the plant take up moisture and nutrients in the soil. They are important because they store water for the plant during periods of drought.
How do ferns grow?
Starting with the "fern" as we recognize it (the sporophyte), the life cycle follows these steps: 1 The diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis, the same process that produces eggs and sperm in animals and flowering plants. 2 Each spore grows into a photosynthetic prothallus (gametophyte) via mitosis. Because mitosis maintains the number of chromosomes, each cell in the prothallus is haploid. This plantlet is much smaller than sporophyte fern. 3 Each prothallus produces gametes via mitosis. Meiosis is not needed because the cells are already haploid. Often, a prothallus produces both sperm and eggs on the same plantlet. While the sporophyte consisted of fronds and rhizomes, the gametophyte has leaflets and rhizoids. Within the gametophyte, sperm is produced within a structure called an antheridium. The egg is produced within a similar structure called an archegonium. 4 When water is present, sperm use their flagella to swim to an egg and fertilize it. 5 The fertilized egg remains attached to the prothallus. The egg is a diploid zygote formed by the combination of DNA from the egg and sperm. The zygote grows via mitosis into the diploid sporophyte, completing the life cycle.
What are the parts of a fern called?
To understand fern reproduction, it helps to know the parts of fern. Fronds are the leafy "branches," consisting of leaflets called pinnae. On the underside of some pinnae are spots that contain spores. Not all fronds and pinnae have spores. Fronds that do have them are called fertile fronds .
What is the life cycle of a fern?
Starting with the "fern" as we recognize it (the sporophyte), the life cycle follows these steps: The diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by meiosis, the same process that produces eggs and sperm in animals and flowering plants. Each spore grows into a photosynthetic prothallus (gametophyte) via mitosis.
Why do ferns droop?
As the baby fern grows, its weight causes the frond to droop toward the ground. Once the baby fern roots itself, it can survive separate from the parent plant. The proliferous baby plant is genetically identical to its parent. Ferns use this as a method of quick reproduction.
How many generations does a fern have?
Ferns alternate generations as part of their life cycle. The fern life cycle requires two generations of plants to complete itself. This is called alternation of generations . One generation is diploid, meaning it carries two identical sets of chromosomes in each cell or the full genetic complement (like a human cell).
What are spores in ferns?
Spores are tiny structures that contain the genetic material needed to grow a new fern. They may be green, yellow, black, brown, orange, or red. Spores are encased in structures called sporangia, which sometimes clump together to form a sorus (plural sori). In some ferns, sporangia are protected by membranes called indusia. In other ferns, the sporangia are exposed to air.
How is a fertilized egg formed?
The fertilized egg remains attached to the prothallus. The egg is a diploid zygote formed by the combination of DNA from the egg and sperm. The zygote grows via mitosis into the diploid sporophyte, completing the life cycle. Before scientists understood genetics, fern reproduction was mystifying.
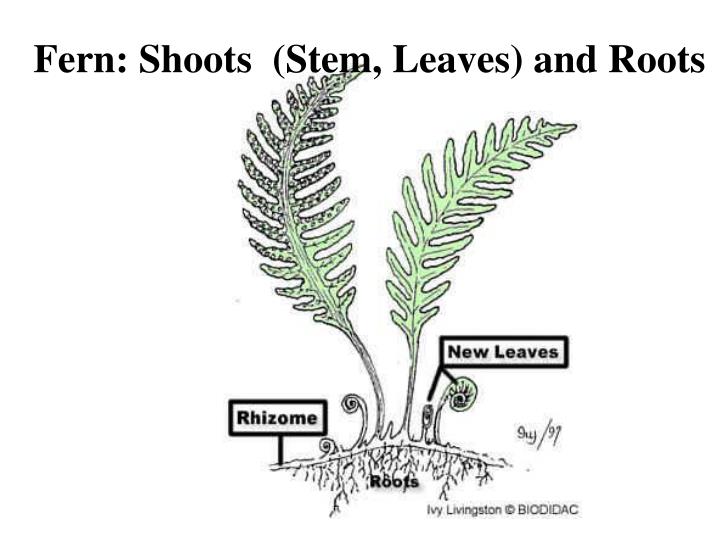
Roots of Ferns
Structure of Fern Roots
- Fern roots consist of three main parts: Rhizoid, cortex, and xylem. These are the three main parts of the root system. 1. The rhizoidsare the longest roots and they are responsible for the uptake of nutrients. 2. The cortexis the next largest part of the root. It consists of cortical cells and these cells form the outer wall of the root. Cortical c...
Caring For Roots of Ferns
- Caring for roots for ferns and other plants that are in full sun is no easy task. To protect the roots from too much moisture, it’s important to keep the soil dry. If the roots are allowed to sit in water for long periods of time, they will rot. The best way to prevent this is by watering the soil in a way that allows the soil to dry out between waterings. It’s also important to ensure the roots don’t sit …
Take Home – Roots of Ferns
- This article demystifies all the info about the roots of ferns and their needs to thrive. Ferns are the most ancient plants on earth. They have survived in the wild for more than 200 million years and are found in almost every habitat. There are hundreds of species that grow in a wide variety of conditions. In some parts of the world, there are more than 30 species growing in one area. Fern…