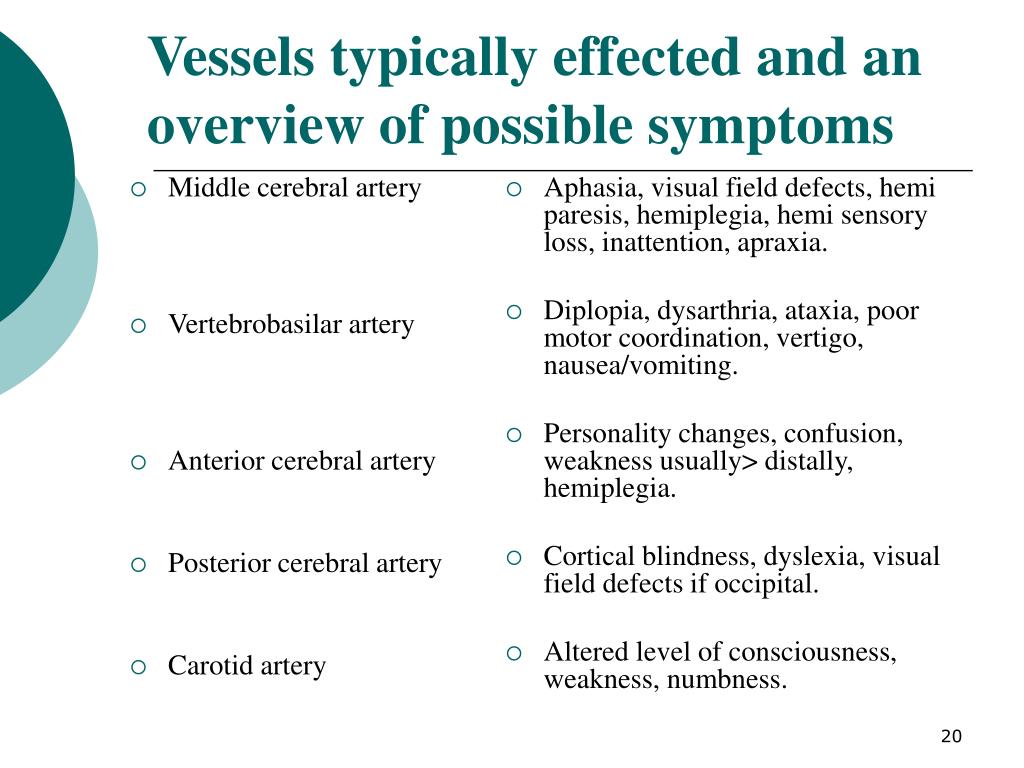
The cerebellum is mainly perfused by the posterior circulation including vertebral and basilar arteries and their branches. Comparison of micro-CT images of different brain samples in the cerebellum as depicted in Fig. 2 demonstrates a high variability of the perfused vessels with contrast agent.
What blood vessels supply the posterior cerebral artery?
The posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries that combine to form the basilar artery which then divides into the posterior cerebral arteries. From these main vessels, many smaller vessels supply the posterior structures of the brain, including: posterior inferior cerebellar artery. anterior inferior cerebellar artery.
What is posterior cerebral circulation?
Posterior cerebral circulation. The posterior cerebral circulation (or simply, posterior circulation) is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobes, cerebellum and brainstem. The posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries that combine to form the basilar artery which then divides...
How do posteromedial central arteries enter the brain?
Posteromedial central arteries arising from the proximal posterior cerebral artery and the posterior communicating artery enter the substance of the brain via the posterior perforated substance. They go on to perfuse the lateral wall of the third ventricle, globus pallidus, along with the anterior thalamus and its associated subthalamus.
How are the posterior communicating arteries connected to the circulations?
Both circulations are connected by the posterior communicating arteries (PCOM), which make up the circle of Willis. When there is an occlusion in the cerebral vasculature, the circle of Willis, as well as collateral circulations, provide blood to the occluded areas.
What is the process of posterior circulation?
What is the communication between the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries?
What is the P1 segment of the cerebral artery?
What is the distal part of the basilar artery?
How many segments are there in the posterior cerebral artery?
Which artery branches off in a lateral direction?
Which branch of the vertebral artery supplies the falx cerebelli and surrounding bone?
See 4 more
About this website

What does the posterior circulation of the brain supply?
The posterior circulation of the brain supplies the posterior cortex, the midbrain, and the brainstem; it comprises arterial branches arising from the posterior cerebral, basilar, and vertebral arteries.
Which of the following blood vessel is part of the posterior circulation?
Posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries (VA), posterior inferior cerebellar arteries (PICA), basilar artery (BA), anterior inferior cerebellar arteries (AICA), pontine branches of the basilar artery, superior cerebellar arteries (SCA), PCA, and PCOM.
What does posterior communicating artery supply?
The posterior communicating artery supplies blood and oxygen to the brain in instances where the internal carotid or posterior cerebral arteries are blocked. The posterior cerebral arteries provide blood to the occipital and temporal lobes, midbrain, thalamus, and choroid plexus.
Which of the following Gyral structures is supplied by the posterior cerebral artery?
The posterior cerebral artery, via its cortical branches, supplies the inferior and medial surfaces of the temporal and occipital lobes, together with a small area on the lateral surface of the hemisphere. It also gives rise to the thalamoperforating vessels.
What is a posterior circulation stroke?
A posterior circulation (PC) stroke is classically defined by infarction occurring within the vascular territory supplied by the vertebrobasilar (VB) arterial system.
What areas does the PCA supply?
The cortical branches of PCA supply the posterior medial parietal lobe and the splenium of the corpus callosum, inferior and medial part of the temporal lobe including the hippocampal formation, and the medial and inferior surfaces of the occipital lobe.
What does the anterior communicating artery supply?
To summarize, the ACA supplies the medial and superior parts of the frontal lobe, and the anterior parietal lobe.
Which cerebral artery gives the posterior communicating artery?
The posterior communicating artery (PCoA) is a smaller branch of the internal carotid artery (ICA). It runs backward to anastomoses with the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) to contribute in the formation of circle of Willis (CW).
What does the posterior inferior cerebellar artery supply?
The PICA supplies the medulla, the choroid plexus and tela choroidea of the fourth ventricle, the tonsils, the inferior vermis, and the inferior aspects of the cerebellar hemispheres 1, 7.
What are the functions of the postcentral gyrus?
The postcentral gyrus is the primary somatosensory cortex and receives the majority of the somatic sensory relay information from the thalamus. The body is somatotopically represented on the gyrus in an inverted pattern with regions receiving sensory information from the head located in the lower portions.
Which of the following structures is supplied by the middle cerebral artery?
The primary function of the MCA is to supply specific regions of brain parenchyma with oxygenated blood. The cortical branches of the MCA irrigate the brain parenchyma of the primary motor and somatosensory cortical areas of the face, trunk and upper limbs, apart from the insular and auditory cortex.
Which Gyral structures is supplied by the middle cerebral artery?
The middle cerebral artery supplies the body of the caudate and most of the putamen, most of the globus pallidus, the middle part (or genu) of the internal capsule, and the anterior hypothalamus.
Is the aorta Part of the systemic circulation?
The systemic circulation is the part of the vascular system that carries blood from the left ventricle to organs and tissues of the body. As outlined above, the aorta is the major artery of the systemic circulation.
Where is the femoral artery?
thighThe femoral artery is a major blood vessel in your body. It carries blood from the bottom of your abdomen down through your lower limbs. This artery starts in the upper front part of your thigh, near the groin.
Which of the following blood vessels carries blood from the tissues back to the heart?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart and veins carry blood back to the heart.
Which of the following blood vessels receives blood directly from the right ventricle?
When the right ventricle contracts, blood is forced through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary artery. Then it travels to the lungs. In the lungs, the blood receives oxygen then leaves through the pulmonary veins.
Posterior cerebral circulation | Radiology Reference Article ...
The posterior cerebral circulation (or simply, posterior circulation) is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobes, cerebellum and brainstem.. Due to the anastomotic circle of Willis, the posterior circulation connects via the posterior communicating arteries to the anterior circulation.. The posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral ...
Poor Circulation: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and More - Healthline
Poor circulation is most common in your extremities, such as your legs and arms. Learn more about the symptoms and causes of poor circulation.
Posterior Communicating Artery: Anatomy, Function - Verywell Health
The posterior communicating artery is part of a group of arteries in the brain. It provides blood and oxygen to the brain.
Neuroanatomy, Posterior Cerebral Arteries - NCBI Bookshelf
The cerebral circulation is composed of a multitude of arteries that provide oxygenated blood to the brain. The cerebral vasculature is unique because it has a circular ring of anastomosing arteries that provide collateral circulation to the brain, known as the circle of Willis. Both anterior and posterior circulations of the brain are connected by the posterior communicating arteries, which ...
Which arteries supply the posterior circulation?
The posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries that combine to form the basilar artery which then divides into the posterior cerebral arteries. From these main vessels, many smaller vessels supply the posterior structures of the brain, including:
Which arteries connect the posterior circulation to the anterior circulation?
Due to the anastomotic circle of Willis, the posterior circulation connects via the posterior communicating arteries to the anterior circulation. The posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries that combine to form the basilar artery which then divides into the posterior cerebral arteries. From these main vessels, many smaller ...
What is the cerebral circulation?
The posterior cerebral circulation (or simply, posterior circulation) is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain, including the occipital lobes, cerebellum and brainstem. Due to the anastomotic circle of Willis, the posterior circulation connects via the posterior communicating arteries to ...
What are the major arteries of the posterior circulation?
The major arteries of the posterior circulation are the vertebral, posterior inferior cerebellar, basilar, and the posterior cerebral arteries. The posterior circulation is generally thought of as split in three divisions: proximal, middle, and distal. The most common areas of the posterior circulation affected in ischemic stroke are: distal (41%) multiple territories (25%), proximal (18%) and middle (16%).6The major areas of the brain supplied include the brainstem, cerebellum, thalamus, occipital visual cortex, medial temporal lobe, and auditory/vestibular structures. The diversity of function of these structures helps explain how posterior circulation deficits can present in many different ways.
How many strokes occur in the posterior circulation?
Approximately 20–25% of all acute strokes occur in the posterior circulation. These strokes can be rather difficult to diagnose because they present in such diverse ways, and can easily be mistaken for more benign entities. A fastidious history, physical exam, high clinical suspicion, and appropriate use of imaging are essential for the emergency physician to properly diagnose and treat these patients. Expert stroke neurologist consultation should be utilized liberally.
What are the symptoms of a basilar artery occlusion?
Basilar artery occlusion affects the middle portion of the circulation and is characterized by unilateral limb weakness, dizziness, dysarthria, diplopia, headache, cranial nerv e VII findings, Babinski’s sign, and oculomotor findings.6When the ventral pons is involved, basilar artery occlusion can also cause “locked in” syndrome in which the patient is fully conscious, yet completely paralyzed, except for blinking and sometimes facial movements.6A second syndrome, lateral medullary infarction (Wallenberg’s syndrome) is caused by occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery or the vertebral artery. The classic findings are the crossed findings of decreased pain and temperature on the ipsilateral face and the contralateral side of the trunk and limbs. Additional findings include severe vertigo, unilateral arm weakness, dysphagia, dysarthria, dysphonia, nystagmus (horizontal and rotary), and ataxia. Respiratory function and cardiovascular abnormalities can also occur. Finally, vertebral basilar syndrome is caused by a disruption of the proximal posterior circulation. It is sometimes known as “beauty parlor syndrome” since it is associated with head turning and resultant occlusion of the vertebral artery. It presents with dizziness, nausea and vomiting, unilateral limb weakness and/or ataxia, cranial nerve V findings, nystagmus, and gait ataxia.6Despite these general patterns it should be noted that it is rare that the above syndromes present in their purely classic forms.
Where should PCS patients be admitted?
All PCS patients should be admitted to a facility that has expertise in stroke care, preferably to a primary or comprehensive stroke center so that the patient can be managed in a dedicated stroke unit. If the facility that the patient initially presents to does not have these capabilities, the patient should be transferred to the nearest, most appropriate stroke center from the ED once they are stable for transport. If the patient is to be transferred, consultation with the accepting neurologist should be obtained prior to the administration of thrombolytics in most cases, as the best treatment modality for individual patients, their particular lesions, and their particular clinical presentations may vary.
Which branch of the optic radiation receives blood from the PCA?
PCA and deep branches of MCA supply the optic radiations. The lower part of the optic radiations receives blood supply from the PCA. The upper part gets blood supply from the MCA.
Which lobe of the brain is affected by PCA?
Patients may present with different signs or symptoms when PCA restricts the blood supply of multiple brain regions (the occipital lobe, the inferomedial temporal lobe, a large portion of the thalamus, and the upper brainstem and midbrain).
How many strokes are caused by PCA?
The incidence of PCA strokes can be estimated between 5% to 10%.[1] Some studies include only pure PCA. One study shows that pure PCA strokes account for 232 (6.1%) cases of stroke (n = 3808). Other factors, such as being male and the mean age, are also shown in the same study 128/232 (55.2%) and 73.9 (11.9 SD), respectively.
Where do VAs originate?
The VAs arise from the subclavian arteries and fuse into the BA within the cranium. The BA typically divides into PCAs near the pituitary stalk at the pontomesencephalic junction. PCAs can originate from BA 70 percent of the time, 20 percent of the time from PCOMs, and 10 percent of the time from a mix of the two.[1] .
What is PCA stroke?
Introduction. A solid understanding of the pathophysiology of a posterior cerebral artery (PCA) stroke as well as the syndrome relating to it, requires adequate knowledge of the structures and vascular anatomy of the brain. Anterior and posterior circulations provide the primary blood circulation of the brain.
How many segments are there in PCA?
PCA is divided into four segments, P1 to P4. The segments can be further categorized into deep and superficial segments or proximal and distal, respectively.
What is the circle of Willis?
Both circulations are connected by the posterior communicating arteries (PCOM), which make up the circle of Willis. When there is an occlusion in the cerebral vasculature, the circle of Willis, as well as collateral circulations, provide blood to the occluded areas.
Which circulations have embolism?
Both the anterior and posterior circulations have embolism from the heart, aorta, and proximal arteries as the main cause of infarction. These two systems share the same vascular coats and are under the same arterial pressures 3.
What are the symptoms of arterial blood flow occlusion?
Common symptoms and signs include dizziness/vertigo, dysarthria, dysphagia, unilateral limb weakness, ataxia, gaze palsy/diplopia, and/or visual field deficits. Less than 1% of patients present with one symptom 4.
What is a POCI stroke?
Posterior circulation infarction (POCI), also referred as posterior circulation stroke, corresponds to any infarction occurring within the vertebrobasilar vascular territory, which includes the brainstem, cerebellum, midbrain, thalami, and areas of temporal and occipital lobes.
How much blood goes into the ICA?
When comparing the amount of blood carried by each system, ~40% of brain blood flow goes into each ICA (totalising ~80% of brain blood flow provided by the anterior circulation) and only 20% into the vertebrobasilar system. So, just by chance, we could expect around 1/5th of cardiac origin emboli going to the posterior circulation 3.
Which brain imaging modality is used to assess strokes?
Radiographic features. CT, which is the main brain imaging modality in hyperacute stroke, unfortunately, has a known limited sensitivity to assess strokes involving the posterior circulation, especially in the posterior fossa structures 1-3 .
What is the process of posterior circulation?
The posterior circulation is formed in a distal to proximal fashion (i.e. from posterior communicating and posterior cerebral → basilar → vertebral). This process is initiated by the growing brain stem and occipital lobe. Within the 4th gestational week, the superior cerebellar artery perfuses the primitive cerebellum without any assistance. The foetal posterior cerebral artery will become the posterior communicating artery. It fuses with the adult posterior cerebral artery, which is formed from the fusion of nearby adjacent embryonic vessels.
What is the communication between the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries?
There is a major communication between the dual supply to the brain. The anterior communicating artery provides communication between the contralateral anterior cerebral arteries. The posterior communicating artery bridges each ipsilateral internal carotid artery with the posterior cerebral artery. The completed structure is known as the circle of Willis.
What is the P1 segment of the cerebral artery?
From the origin of the vessel at the basilar bifurcation to the junction with the posterior communicating artery is known as P1. The P2 segment extends from the junction with the posterior communicating artery to the segment in the perimesencephalic cistern. The P3 segment continues in the calcarine fissure.
What is the distal part of the basilar artery?
The distal part of the basilar artery is formed from the fusion of the posterior communicating and the posterior cerebral arteries. The aforementioned hypoglossal, otic, and trigeminal arteries break down after the posterior communicating artery initiates contact with the distal basilar artery. During the 5th gestational week, ...
How many segments are there in the posterior cerebral artery?
The posterior cerebral arteries have been divided into three segments for clinical purposes.
Which artery branches off in a lateral direction?
At the distal aspect of the basilar artery (prior to its bifurcation), the superior cerebellar artery branches off in a lateral direction, caudal to CN III. It courses around the pedunculi cerebri (cerebral peduncles). It passes below CN IV to access the superior aspect of the cerebellum, which it supplies, along with the tela choroidea of the 3rd ventricle, the pineal body, pons, and superior medullary velum. It also forms an anastomosis with derivatives of the inferior cerebellar arteries.
Which branch of the vertebral artery supplies the falx cerebelli and surrounding bone?
Contributes meningeal branches near the foramen magnum that supplies the falx cerebelli and the surrounding bone. Posterior meningeal branch of vertebral artery (lateral-right view) May give off the posterior spinal artery; although this vessel usually arises from the posterior inferior cerebellar artery.