Cranial cavity This consists of the cranium which protects the brain and its boundaries are formed by the bones of the skull. Anteriorly – 1 Frontal Bone.
What is the structure of the cranial cavity?
Cranial cavity is contained by the frontal, parietal, sphenoid, temporal and occipital bones, and in part the ethmoid, all lines by fibrous endocranium, external zone of dura mater and pericranium. Cranial cavity forms the floor of brain, while the roof of brain is formed by skull cap or calvaria.
What are the boundaries of the middle cranial fossa?
The middle cranial fossa consists of three bones – the sphenoid bone and the two temporal bones. Its boundaries are as follows: Anteriorly and laterally it is bounded by the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. These are two triangular projections of bone that arise from the central sphenoid body.
What are your cranial bones?
Your cranial bones are eight bones that make up your cranium, or skull, which supports your face and protects your brain. We’ll go over each of these bones and where they’re located.
What bones make up the front of your head?
Frontal bone. This is the flat bone that makes up your forehead. It also forms the upper portion of your eye sockets. Parietal bones. This a pair of flat bones located on either side of your head, behind the frontal bone. Temporal bones. This is a pair of irregular bones located under each of the parietal bones.
What forms cranial cavity?
The neurocranium forms the cranial cavity that surrounds and protects the brain and brainstem. The neurocranium consists of the occipital bone, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, the sphenoid, ethmoid, and frontal bones—all are joined together with sutures.
What separates the cranial cavity?
Its full name is tentorium cerebelli. It separates the posterior cranial fossa from the rest of the cranial cavity, and separates two major parts of the brain, the cerebrum above from the cerebellum below. This opening in the tentorium is called the tentorial incisure.
What are the boundaries of the middle cranial fossa?
The middle cranial fossa is bounded anteriorly by the sphenoid ridge, medially by the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus and Meckel's cave, posteriorly by the sphenoid wing and petrous bone, and laterally by the greater wing of sphenoid and squamous temporal bone.
Which bones help form the cranial cavity?
The eight bones of the cranium form the “vault” that encloses the brain. They include the frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid and ethmoid bones.
How many bones form the cranial cavity?
There are eight cranial bones, each with a unique shape: Frontal bone. This is the flat bone that makes up your forehead. It also forms the upper portion of your eye sockets.
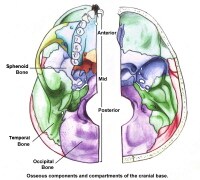
What are the boundaries of the 3 major cranial fossa seen on the internal surface of the base of the skull?
Three cranial fossae and its boundaries.... Sphenoidal limbus (anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove) Posterior borders of the lesser wings of the sphenoid. Dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. Superior borders of the petrous part of the temporal bone. Groove for transverse sinus of the occipital bone.
Which bone forms the anterior boundary of the middle cranial fossa?
Boundaries — extracranial aspects The anterior boundary of the middle cranial fossa is the posterolateral wall of the maxillary sinuses; the petro-occipital sutures form its posterior boundary. The lateral margin consists of primarily the squamous and petrous portions of the temporal bone.
Which structure is found in the middle cranial fossa of the skull?
The middle cranial fossa is a butterfly-shaped depression of the skull base, which is narrow in the middle and wider laterally. It houses the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.
Is the pituitary gland in the cranial cavity?
The pituitary gland is within the sella turcica or the hypophyseal fossa. This structure is present near the center at the base of the cranium and is fibro-osseous.
What organ is found in the cranial cavity?
the BrainContain the Brain The brain is arguably the most important organ in the human body. Fortunately for us, the brain has its own special “container,” called the cranial cavity. The cranial cavity enclosing the brain is just one of several cavities in the human body that form “containers” for vital organs.
Is the spinal cord in the cranial cavity?
In the posterior (dorsal) cavity, the cranial cavity houses the brain, and the spinal cavity encloses the spinal cord. Just as the brain and spinal cord make up a continuous, uninterrupted structure, the cranial and spinal cavities that house them are also continuous.
What does cranial cavity mean?
The cranial cavity, or intracranial space, is the space formed inside the skull. The brain occupies the cranial cavity, which is lined by the meninges and which contains cerebrospinal fluid to cushion blows.
What is the floor of the cranial cavity called?
The Anterior Cranial Fossa. The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior c ranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What are the three depressions in the cranial cavity?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What bone is the anterior border of the prechiasmatic sulcus?
Posteriorly and medially it is bounded by the limbus of the sphenoid bone. The limbus is a bony ridge that forms the anterior border of the prechiasmatic sulcus (a groove running between the right and left optic canals).
What is the frontal bone?
There are several bony landmarks present in the anterior cranial fossa. The frontal bone is marked in the midline by a body ridge , known as the frontal crest. It projects upwards, and acts as a site of attachment for the falx cerebri (a sheet of dura mater that divides the two cerebral hemispheres).
Which part of the anterior cranial fossa is most likely to fracture?
The cribriform plate of the ethmoid is the thinnest part of the anterior cranial fossa, and therefore most likely to fracture. There are two major consequences of cribriform plate fracture: Anosmia - the olfactory nerve fibres run through the cribriform plate, and can be 'sheared', resulting in loss of sense of smell.
Which bone contains the main foramina?
The ethmoid bone in particular contains the main foramina (openings that transmit vessels and nerves) of the anterior cranial fossa. The cribriform plate is a sheet of bone seen either side of the crista galli which contains numerous small foramina – these transmit olfactory nerve fibres (CN I) into the nasal cavity.
Which bone supports the olfactory bulb?
On either side of the crista galli is the cribriform plate which supports the olfactory bulb and has numerous foramina that transmit vessels and nerves. The anterior aspect of the sphenoid bone lies within the anterior cranial fossa. From the central body, the lesser wings arise.
What is the floor of the cranial cavity called?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What are the bones of the middle cranial fossa?
The middle cranial fossa consists of three bones – the sphenoid bone and the two temporal bones. Its boundaries are as follows: Anteriorly and laterally it is bounded by the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. These are two triangular projections of bone that arise from the central sphenoid body.
What bone is the anterior border of the chiasmatic sulcus?
Anteriorly and medially it is bounded by the limbus of the sphenoid bone. The limbus is a bony ridge that forms the anterior border of the chiasmatic sulcus (a groove running between the right and left optic canals).
What bone is bounded by the dorsum sellae?
Posteriorly and medially it is bounded by the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. This is a large superior projection of bone that arises from the sphenoidal body.
How many foramina are there in the middle cranial fossa?
Immediately lateral to the central part of the middle cranial fossa are four foramina:
What is the site of many foramina?
It is the site of many foramina - small holes by which vessels and nerves enter and leave the cranial cavity. Foramina. There are many foramina that transmit vessels and nerves into and out of the middle cranial fossa. These foramina will be discussed in relation to the bones they are situated in.
Where is the middle cranial fossa located?
Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain. The middle cranial fossa is located, as its name suggests, centrally in the cranial floor. It is said to be "butterfly shaped", with a middle part accommodating the pituitary gland and two lateral parts accommodating the temporal lobes of the brain.
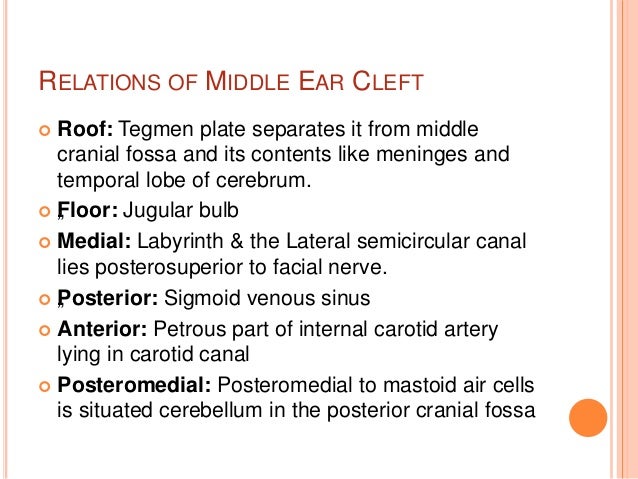
What are the two parts of the tympanic cavity?
Parts: Tympanic cavity is divided into two parts: Tympanic cavity proper – lies opposite to the tympanic membrane. Epitympa nic recess – lies above the level of the tympanic membrane. It contains the upper half of the malleus and the greater part of the incus.
Where is Tympanic cavity/midle ear located? Whatis its shape and dimensions?
Location: The middle ear or tympanic cavity is a narrow slit-like air-filled cavity located inside the petrous part of the temporal bone.
What nerves are in the tympanic plexus?
Nerves: chorda tympani (br. of facial N.) and tympanic plexus (formed by br. of glossopharyngeal and caroticotympanic nerves from sympathetic plexus around internal carotid artery).
What is the name of the branch of the facial nerve that emerges from the facial canal?
Chorda tympani a branch of facial nerve, leaves emerges from facial canal through posterior canaliculus.
Which nerve makes the tympanic membrane taut?
Makes the tympanic membrane taut. Mandibular nerve (nerve to medial pterygoid. Stapedius. Pyramidal eminence on posterior wall of tympanic cavity. Neck of Stapes. Pulls the stapes laterally (dampens the vibrations of stapes, thus helping to control the amplitude of sound).
What is the name of the wall that separates the middle ear from the internal ear?
6.Medial /labyrinthine wall: separates middle ear from the internal ear. It presents following features:
Which tegmen separates the middle ear from the temporal lobe of the cerebrum?
1.Roof /tegmental wall: is formed by tegmen tympani which separates middle ear from middle cranial fossa and temporal lobe of cerebrum.
How are cranial bones held together?
Your cranial bones are held together by unique joints called sutures, which are made of thick connective tissue. They’re irregularly shaped, allowing them to tightly join all the uniquely shaped cranial bones. The sutures don’t fuse until adulthood, which allows your brain to continue growing during childhood and adolescence.
What is the structure of the skull?
The bones in your skull can be divided into the cranial bones, which form your cranium, and facial bones, which make up your face.
What is the main defense system for the brain?
Your cranial bones are the main defense system for your brain, so it’s important to maintain their health by:
What type of synostosis causes a flat forehead?
Bicoronal synostosis. Infants with this type may have a flattened and elevated forehead.
How many cranial bones are there?
There are eight cranial bones, each with a unique shape:
Why does my forehead look elongated?
Sagittal synostosis. This type may cause the forehead to bulge out. The area around the temples might also appear very narrow, making the head look elongated.
What causes the back of the skull to tilt?
Lambdoid synostosis. This can lead to flattening on one side of the back of the skull. It can also affect the positioning of the ear or cause the skull to tilt sideways.
