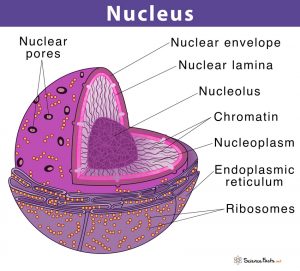
- Nucleus consists of a double-membrane organelle which is referred to as the nuclear envelope or the nuclear membrane which encircles it.
- Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus, which occupies around 25 per cent of the nuclear volume.
- Chromatin is dense thread-like structures which are found inside the nucleus and contain DNA and protein.
What is the structure that surrounds the nucleus?
A structure called the nuclear envelope/ nuclear membrane surrounds the nucleus. It is a double-membraned organelle. Within the nucleus lies the nucleolus, which takes up 25% per cent of the volume. Also found within the nucleus are dense, thread-like structures called chromatins that contain DNA and proteins.
What is the structure of the nucleolus?
Nucleus consists of a double-membrane organelle which is referred to as the nuclear envelope or the nuclear membrane which encircles it. Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus, which occupies around 25 per cent of the nuclear volume. Chromatin is dense thread-like structures which are found inside the nucleus and contain DNA and protein.
What organelles make up the nucleus?
A double-membraned organelle known as the nuclear membrane/envelope engirdles the nucleus. The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25% per cent of the volume. Thread-like, dense structures known as chromatins are found within the nucleus containing proteins and DNA.
What are the properties of nucleus in biology?
Properties. The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is generally the most prominent organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a structure called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.

What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes. It is exclus...
Outline the structure of the Nucleus.
A double-membraned organelle known as the nuclear membrane/envelope engirdles the nucleus. The nucleolus is found within the nucleus, occupying 25%...
Highlight the functions of the nucleus.
The nucleus has 2 primary functions: It is responsible for storing the cell’s hereditary material or the DNA. It is responsible for coordinating ma...
What is the cell nucleus?
Updated November 06, 2019. The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains a cell's hereditary information and controls its growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is usually the most notable cell organelle in both size and function.
What is the nucleus membrane?
Nuclear Envelope and Nuclear Pores. The cell nucleus is bound by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance containing all other organelles. The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane.
What is the nucleoplasm?
The nucleolus and chromosomes are surrounded by nucleoplasm, which cushions and protects nuclear contents. Like the nuclear envelope, the nucleoplasm supports the nucleus to hold its shape.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope consists of phospholipids that form a lipid bilayer much like that of the cell membrane. This lipid bilayer has nuclear pores that allow substances to enter and exit the nucleus, or transfer from the cytoplasm to the nucleoplasm. The nuclear envelope helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus.
What is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope?
Nucleoplasm is the gelatinous substance within the nuclear envelope. Also called karyoplasm, this semi-aqueous material is similar to cytoplasm in that it is composed mainly of water with dissolved salts, enzymes, and organic molecules suspended within.
What is the name of the structure that houses chromosomes?
Chromatin. The nucleus houses chromosomes containing DNA. DNA holds heredity information and instructions for cell growth, development, and reproduction. When a cell is "resting", or not dividing, its chromosomes are organized into long entangled structures called chromatin .
What is the function of the nucleus?
The key function of the nucleus is to control cell growth and multiplication. This involves regulating gene expression, initiating cellular reproduction, and storing genetic material necessary for all of these tasks. In order for a nucleus to carry out important reproductive roles and other cell activities, it needs proteins and ribosomes.
What is the structure of the nucleus?
Structure Of Nucleus. Typically, it is the most evident organelle in the cell. The nucleus is completely bound by membranes. It is engirdled by a structure referred to as the nuclear envelope. The membrane distinguishes the cytoplasm from the contents of the nucleus. The cell’s chromosomes are also confined within it.
What is a Nucleus?
The most integral component of the cell is the nucleus (plural: nuclei). It is derived from a Latin word which means “ kernel of a nut ”.
What are the functions of the nucleus?
Following are the important nucleus function: 1 It contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. 2 The nucleus has been clearly explained as a membrane-bound structure that comprises the genetic material of a cell. 3 It is not just a storage compartment for DNA, but also happens to be the home of some important cellular processes. 4 First and foremost, it is possible to duplicate one’s DNA in the nucleus. This process has been named DNA Replication and produces an identical copy of the DNA. 5 Producing two identical copies of the body or host is the first step in cell division, where every new cell will get its own set of instructions. 6 Secondly, the nucleus is the site of transcription. Transcription creates different types of RNA from DNA. Transcription would be a lot like creating copies of individual pages of the human body’s instructions which may be moved out and read by the rest of the cell. 7 The central rule of biology states that DNA is copied into RNA, and then proteins.
What is the classification of every cell?
Mostly, every type of cell that exists is categorized on the basis of the absence or presence of the nucleus within its cell (categorized either as a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.)
Which organelle contains genetic material?
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material and other instructions required for cellular processes. It is exclusively found in eukaryotic cells and is also one of the largest organelles.
Which organisms have a nucleus diagram?
A nucleus diagram highlighting the various components. Moreover, only eukaryotes have the nucleus, prokaryotes have the nucleoid
What is the function of the cytoplasmic cytoplasm?
It is responsible for storing the cell’s hereditary material or the DNA.
What are the two parts of the nucleus?
Chromosomes are the most important parts of the cell nucleus. Each chromosome has two components: 1) an axis formed by protein fibers, and 2) long loops of a molecule called DNA that hang off of the chro mosome’s axis. There are 46 chromosomes in each human cell. Each chromosome is plastered onto the interior of the nuclear envelope in its own special place. Information on the DNA is used to control the function of the cell. This information is copied onto other molecules (messenger RNA molecules) and sent to the cytoplasm of the cell. In the cytoplasm, this information is used to make the proteins that operate the cell machinery.
Why do molecules move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm?
However, molecules can still move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm because the nuclear envelope is pierced by hundreds of hollow structures called nuclear pores that allow traffic between the cytoplasm and nucleus. The nuclear pores are suspended in a framework found on the inside of the nuclear envelope. This framework, composed of lamin proteins, governs the overall shape of the nucleus. If the lamin proteins change their function, this causes the nuclear envelope to change its shape or to even disappear, as occurs during cell division! These features help explain why cell nuclei look so different in different types of cells.
What is the name of the molecule that links amino acids together?
The sequence of bases on the DNA is copied onto a similar molecule called messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA). Then, the mRNA travels through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, tiny machines called ribosomes use the information on the mRNA to link together hundreds of amino acids into long chains. A long chain of amino acids is called a protein. Proteins are the building blocks of the cell. They can form rigid structures inside the cell, which help organize its structure. Alternatively, they can form enzymes that accelerate chemical reactions and provide the cell with energy.
What are the 4 types of bases in DNA?
These bases are called adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymidine (T). The sequence of bases found on the strands of sugars, which can be thousands of bases long, represents a coded form of information that is used to control the cell. The encoded information on the DNA is called a gene, and there are about 20,000 active genes in human chromosomes. How is the information in the DNA of a gene used?
Is DNA a sugar molecule?
DNA is partly composed of thousands of sugar molecules, all linked together into long strands by molecules of phosphate. The name of each sugar molecule is deoxyribose. The molecules of phosphate that join the sugars together are very acidic. Thus, DNA represents an acidic molecule found in the nucleus that contains deoxyribose. In other words, DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid.
