What happens to the sugars that are made during photosynthesis?
what happens to the sugars that are made during photosynthesis || Answer:The correct answer is c they are used for cellular respiration.Explanation:The light independent reaction or the dark reaction of photosynthesis also called calvin cycle which consist of many enzyme catalyzed biochemical steps that ultimately result in the …
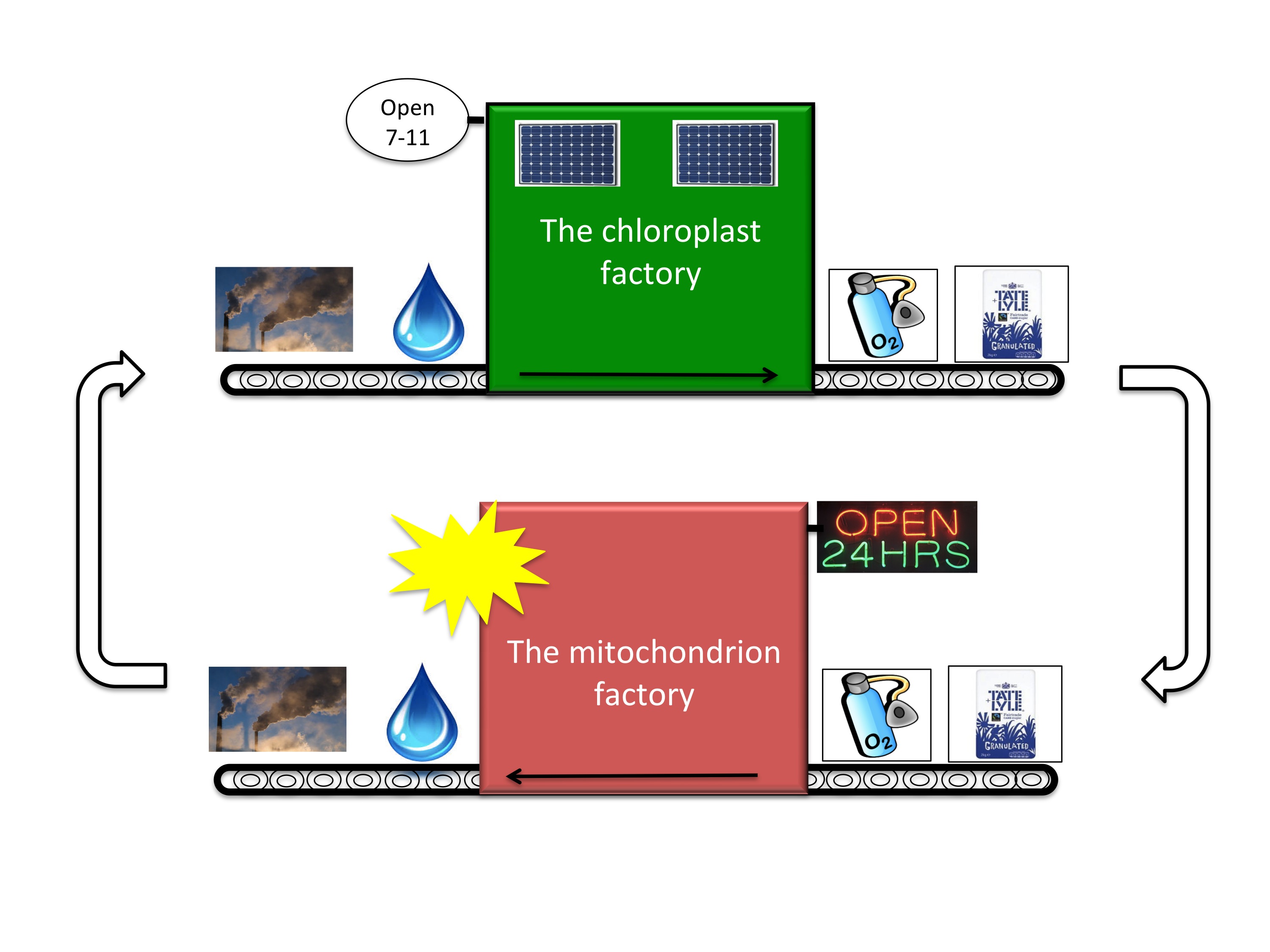
What substances are produced and consumed in photosynthesis?
What are the three things needed for photosynthesis highlight them on the diagram in green?
- Chlorophyll. Chlorophyll, the pigment in plants that makes them green, is essential to the photosynthetic process. …
- Sunlight. The process cannot work without an energy input, and this comes from the sun. …
- Water. …
- Carbon Dioxide.
Is sugar being converted into energy after photosynthesis?
The portions of glucose that are not immediately converted to energy are converted to complex sugar compounds, called starches. These are produced after the photosynthesis cycle. Plants then store starches for future energy needs or use them to build new tissues. Photosynthesis Plants are photoautotrophs.
What type of sugar is formed in photosynthesis?
- The products of photosynthesis are called as photosynthates; they are usually in the form of simple sugars, such as sucrose.
- Sucrose must be delivered to growing parts of the plant or either it is stored in storage areas (roots, tubers, and bulbs).
- These sugars are transported through the plant via the phloem in a process called as translocation.

What sugar is formed into photosynthesis?
glucosePlants use a process called photosynthesis to make food. During photosynthesis, plants trap light energy with their leaves. Plants use the energy of the sun to change water and carbon dioxide into a sugar called glucose. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to make other substances like cellulose and starch.
What 3 sugars are produced during photosynthesis?
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma and uses the ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide, producing three-carbon sugars—glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, or G3P, molecules.
Where are sugars formed in photosynthesis?
chloroplastsInside the chloroplasts within leaves, light, water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) are transformed into energy and sugar (glucose). Using water, sunlight is converted into energy-storing molecules within the plant cells. The energy from these molecules is then used to create glucose from CO2.
Does sugar made in photosynthesis?
Sugar is produced by all green plants and photosynthetic bacteria in a reaction sequence capable of forming carbon-carbon bonds. The very first steps occur independently of solar energy input, but to sustain the reaction, the products of initial fixation are phosphorylated and undergo a reduction in oxidation state.
What is produced in photosynthesis?
During the process of photosynthesis, cells use carbon dioxide and energy from the Sun to make sugar molecules and oxygen. These sugar molecules are the basis for more complex molecules made by the photosynthetic cell, such as glucose.
Is glucose the only sugar made during photosynthesis?
Little free glucose is produced in plants; instead, glucose units are linked to form starch or are joined with fructose, another sugar, to form sucrose (see carbohydrate).
What simple sugar is produced?
The prefix mono means one. Monosaccharides (simple sugars) are made up of a single sugar molecule. The most common simple sugars that make up carbohydrates are glucose (what we commonly call blood sugar), fructose and galactose. Both glucose and fructose are simple sugars and each has the molecular formula: C6H12O6.
What happens to the sugar made in photosynthesis?
The sugar goes through the process of cellular respiration and is used to make energy in the form of ATP.
What is the end product of photosynthesis?
Glucose and oxygen are the final products of photosynthesis.
Is sucrose the end product of photosynthesis?
Sucrose is the end product of photosynthesis and the primary sugar transported in the phloem of most plants. Sucrose synthase (SuSy) is a glycosyl transferase enzyme that plays a key role in sugar metabolism, primarily in sink tissues.
What sugar is made of?
The common 'sugar' (sucrose) used is made up from glucose and fructose and is extracted from sugar cane or sugar beetbeetremolacha f (plural remolachas) beet (Beta vulgaris) sugar beet. red beet.https://en.wiktionary.org › wiki › remolacharemolacha - Wiktionary. Sugar cane is grown in tropical and sub-tropical parts of the world, including South Africa, Brazil, India, Mauritius and the West Indies.
What is sugar in plants?
Sucrose is the chemical name for sugar and is a naturally occurring carbohydrate found in fruits and vegetables. Plants produce sucrose through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process where plants make their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight.
What are the 3 products of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose. Glucose is used as food by the plant and oxygen is a by-product.
What simple sugar is produced?
The prefix mono means one. Monosaccharides (simple sugars) are made up of a single sugar molecule. The most common simple sugars that make up carbohydrates are glucose (what we commonly call blood sugar), fructose and galactose. Both glucose and fructose are simple sugars and each has the molecular formula: C6H12O6.
What are the end products of photosynthesis?
Glucose and oxygen are the final products of photosynthesis.
What 3 factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The main factors affecting rate of photosynthesis are light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature.
What is the process of green plants synthesizing glucose from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water in the presence of?
Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants synthesize glucose from simple substances like carbon dioxide and water in presence of light.
Where does the light reaction occur?
Light reaction occurs in granum part of chloroplast where chlorophyll pigment is present. Chlorophyll entraps solar energy from light and converts that energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP.
Is the dark reaction preceded by the light reaction?
Dark reaction thus must be preceded by light reaction. Dark reaction simply involves reduction of carbon dioxide into glucose molecule, utilizing reducing power (NADPH+H) and ATPs produced during light reaction. It occurs in a series of steps, which together constitute Calvin cycle.
What is the most important organic product of photosynthesis?
As has been stated, carbohydrates are the most-important direct organic product of photosynthesis in the majority of green plants. The formation of a simple carbohydrate, glucose, is indicated by a chemical equation, Little free glucose is produced in plants; instead, glucose units are linked to form starch or are joined with fructose, ...
What is the complex mechanism of photosynthesis?
As has been mentioned, the complex mechanism of photosynthesis includes a photochemical, or light-harvesting, stage and an enzymatic, or carbon-assimilating, stage that involves chemical reactions.
What were the first oxygen cells?
The first oxygenic (oxygen-producing) cells probably were the blue-green algae (cy anobacteria), which appeared about two billion to three billion years ago. These microscopic organisms are believed to have greatly increased the oxygen content of the atmosphere, making possible the development of aerobic (oxygen-using) organisms. Cyanophytes are prokaryotic cells; that is, they contain no distinct membrane -enclosed subcellular particles ( organelles ), such as nuclei and chloroplasts. Green plants, by contrast, are composed of eukaryotic cells, in which the photosynthetic apparatus is contained within membrane-bound chloroplasts. The complete genome sequences of cyanobacteria and higher plants provide evidence that the first photosynthetic eukaryotes were likely the red algae that developed when nonphotosynthetic eukaryotic cells engulfed cyanobacteria. Within the host cells, these cyanobacteria evolved into chloroplasts.
How did green plants evolve?
Although life and the quality of the atmosphere today depend on photosynthesis, it is likely that green plants evolved long after the first living cells. When Earth was young, electrical storms and solar radiation probably provided the energy for the synthesis of complex molecules from abundant simpler ones, such as water, ammonia, and methane. The first living cells probably evolved from these complex molecules ( see life: Production of polymers ). For example, the accidental joining (condensation) of the amino acid glycine and the fatty acid acetate may have formed complex organic molecules known as porphyrins. These molecules, in turn, may have evolved further into coloured molecules called pigments —e.g., chlorophylls of green plants, bacteriochlorophyll of photosynthetic bacteria, hemin (the red pigment of blood), and cytochromes, a group of pigment molecules essential in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
How is the rate of photosynthesis determined?
In the light-dependent range before saturation, therefore, the rate of photosynthesis is determined by the rates of photochemical steps. At high light intensities, some of the chemical reactions of the dark stage become rate-limiting.
What are the molecules of chlorophyll?
Molecules of chlorophyll, the key photosynthetic pigment in green plants, are arranged within a leaf such that they minimize the plant's need to transport incoming solar radiation while also increasing a leaf's photosynthetic output.
What are some examples of organic molecules that have evolved from the accidental joining of amino acids?
For example, the accidental joining (condensation) of the amino acid glycine and the fatty acid acetate may have formed complex organic molecules known as porphyrins. These molecules, in turn, may have evolved further into coloured molecules called pigments —e.g., chlorophylls of green plants, bacteriochlorophyll of photosynthetic bacteria, ...
How is sugar used in photosynthesis?
Uses of the sugar produced by photosynthesis The sugar can be broken down in plant cells by the process of respiration to generate ATP. The chemical energy released by respiration can be used by the plant for cellular activities such as protein synthesis or cell division. The sugar produced by photosynthesis can be converted into the sugar glucose. Thousands of glucose molecules can be linked together to form the complex carbohydrate starch. Starch The sugar produced by photosynthesis can be converted into the sugar glucose. Thousands of glucose molecules can be linked together to form the complex carbohydrate cellulose. Cellulose is a very tough molecule that is used to build the cell wall of plant cells. A leaf magnified to show a plant cell, microfibril and cellulose molecule : it contains the chemical elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Plant cells can convert the sugar into another type of energy storage molecule - fat. Plant cells can also combine sugars with nitrates to make amino acids and use these to produce proteins. Continue reading >>
How Can A Plant Use The Sugars Made In Photosynthesis?
How can a plant use the sugars made in photosynthesis? During the process of photosynthesis, plants utilize sunlight and convert it into useful products, according to the following well-balanced chemical equation: `6CO_2 + 6H_2O + sunlight -> C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2` In this reaction, glucose (a common sugar) is produced. These glucose molecules are used by the plant in a number of ways. The most common use is the production of energy (in the form of ATP molecules) through the process of cellular respiration. This process... During the process of photosynthesis, plants utilize sunlight and convert it into useful products , according to the following well-balanced chemical equation: `6CO_2 + 6H_2O + sunlight -> C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2` In this reaction, glucose (a common sugar) is produced. These glucose molecules are used by the plant in a number of ways. The most common use is the production of energy (in the form of ATP molecules) through the process of cellular respiration. This process can be summarized by the following equation: `C_6H_12O_6 + 6O_2 -> 6CO_2 + 6H_2O + ATP` Note that most of the processes require energy, including the process of photosynthesis. During the daytime hours, when photosynthesis is taking place, plants produce more glucose than they can consume. This extra glucose is stored in the plant in the form of starch. Cell walls are made up of starch and that is where much of the extra glucose is used. Sugars are also stored in other parts of the plant. Apart from starch, sugars can be also be stored as fats and oils. Glucose can also be converted to sucrose and stored in fruits, stem, roots, seeds, etc. Glucose can also be used in the formation of amino acids, which are then used for protein synthesis in the plants. Plants are made of eukaryotic cells that con Continue reading >>
How does photosynthesis capture energy?
These chemicals can move in and out of cells by the process of diffusion. Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion. Photosynthesis is a process used by plants in which energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into molecules needed for growth . These molecules include sugars, enzymes and chlorophyll. Light energy is absorbed by the green chemical chlorophyll. This energy allows the production of glucose by the reaction between carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen is also produced as a waste product. This reaction can be summarised in the word equation: The chemical equation for photosynthesis is: Glucose is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Glucose made by the process of photosynthesis may be used in three ways: It can be converted into chemicals required for growth of plant cells such as cellulose It can be converted into starch, a storage molecule, that can be converted back to glucose when the plant requires it It can be broken down during the process of respiration, releasing energy stored in the glucose molecules Plants cells contain a number of structures that are involved in the process of photosynthesis: Diagram of a plant cell involved in production of glucose from photosynthesis Chloroplasts - containing chlorophyll and enzymes needed for reactions in photosynthesis. Nucleus - containing DNA carrying the genetic code for enzymes and other proteins used in photosynthesis Cell membrane - allowing gas and water to pass in and out of the cell while controlling the passage of other molecules Vacuole - containing cell sap to keep the cell turgid Cytoplasm - enzymes and other proteins used in photosynthesis made here Continue reading >>
What are the basic needs for photosynthesis?
Key Concepts Section 2 Chapter 1 Photosynthesis THE BASIC NEEDS FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS Plants, as well as some Protists and Monerans, can take small molecules from the environment and bind them together using the energy of light . The incoming light energy is transformed into the energy holding the new molecules together, and the organisms use those molecules as an energy "fuel." The basic process can be represented this way: CO2 + H2O light > C6H12O6 + O2 Carbon Water Glucose Oxygen Dioxide (sugar) In the case of organisms that live in water, the carbon dioxide and water are from their immediate surroundings; for most land plants, the water is absorbed from the soil and the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The glucose is used for two major purposes: 1) it serves as an energy reserve for periods of darkness (don't forget that photosynthesizers, like any living things, require energy and get it through respiration processes, commonly aerobic respiration; and 2) it is used as a major component of structure: the cell walls that surround almost all photosynthetic cells are made of starches, huge molecules made up of hundreds, commonly thousands, of sugar molecules bound together. This is why plant fibers are great sources of nutrition if you can break them down. Breaking down plant fibers is chemically difficult - we humans can't, being limited to the more digestible starches put into seeds and fruits and tubers. Plants use those starches as sources of fuel and structure components, and so build them into a molecule that is much easier to break down than the structural starches that hold them together. Keep in mind that photosynthetic organisms are still living things, with protein-based chemistry, which means that they have nutritional requirements beyond carbon dioxide and Continue reading >>
How does glucose help plants?
Plants use glucose in a variety of ways that are essential to their growth and survival. Glucose aids in overall growth , allows for respiration through the cell walls and is also stored for future use in the roots, as well as in the form of seeds. Glucose is essentially energy for the plant in a carbohydrate form that can be used immediately or stored in the form of starches for later use. It is crucial to the growth and survival of the plant as it directly effects the production of cellulose, the material plants use to construct cellular walls. Glucose is initially formed through the act of photosynthesis, which is how plants use water and carbon dioxide to produce energy. From this combination of carbon dioxide and water,a carbohydrate is formed which is initially used in the leaf structure for a variety of purposes. Under the right conditions, plants can create an excessive amount of glucose, and it is then stored in various ways throughout the plant structure. It is through this process that the plant produces oxygen, as well, and the glucose present in the cell walls of the leaves aids in expelling this gas by acting as an immediate form of energy. Any glucose that isnt immediately used by the plant for cell function, such as the building of cellular walls, is either stored or converted. Glucose is the primary building block of cellulose in the plant and is vital for cell production. The construction of additional cellular walls drives the growth of the plant and the larger it becomes, the more efficient the plant becomes at photosynthesis. Leftover glucose reacts with nitrates found in the leaves and produces amino acids, which are also essential to growth. Every bit of glucose is either used or stored, from the very point of production through photosynthesis, to Continue reading >>
How do plants use light energy?
The glucose is used in respiration, or converted into starch and stored. Oxygen is produced as a by-product. This process is called photosynthesis. Temperature, carbon dioxide concentration and light intensity are factors that can limit the rate of photosynthesis. Plants also need mineral ions, including nitrate and magnesium, for healthy growth. They suffer from poor growth in conditions where mineral ions are deficient. Photosynthesis [photosynthesis: The chemical change that occurs in the leaves of green plants. It uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. ] is the chemical change which happens in the leaves of green plants. It is the first step towards making food - not just for plants but ultimately every animal on the planet. During this reaction, carbon dioxidecarbon dioxide: A gaseous compound of carbon and oxygen, which is a by-product of respiration, and which is needed by plants for photosynthesis. and water are converted into glucose and oxygenoxygen: Gaseous element making up about 20 per cent of the air, which is needed by living organisms for respiration. The reaction requires light energylight energy: Visible electromagnetic radiation., which is absorbed by a green substance called chlorophyll. Photosynthesis takes place in leaf cells. These contain chloroplasts, which are tiny objects containing chlorophyll. carbon dioxide + water (+ light energy) glucose + oxygen 'Light energy' is shown in brackets because it is not a substance. You will also see the equation written like this: Plants absorb water through their roots, and carbon Continue reading >>
How does light interception work in photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis Light interception by leaves powers photos ynthesis All organisms, animals and plants, must obtain energy to maintain basic biological functions for survival and reproduction. Plants convert energy from sunlight into sugar in a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis uses energy from light to convert water and carbon dioxide molecules into glucose (sugar molecule) and oxygen (Figure 2). The oxygen is released, or “exhaled”, from leaves while the energy contained within glucose molecules is used throughout the plant for growth, flower formation, and fruit development. There are several structures within a leaf that have important roles in the movement of nutrients and water throughout a plant. Each plant contains a branched system of tubes called xylem, which is responsible for water transport from the roots (where it is taken up) to the leaves (where it is used in photosynthesis). Water flows up from the roots, through the trunk and branches, to the leaves, where it is used in photosynthesis. Alongside xylem is another system of tubes called phloem, which transports the glucose formed in photosynthesis into the branches, fruit, trunk and roots of the tree. The ends of both the xylem and phloem transport systems can be seen within each leaf vein (Figure 3). The structure of xylem and phloem in a plant is analogous to arteries and veins in humans, which move blood to and from the heart and lungs. For more information regarding the structure and function of xylem and phloem, review the Irrigation and Rootstock sections. Leaves contain water which is necessary to convert light energy into glucose through photosynthesis. Leaves have two structures that minimize water loss, the cuticle and stomata. The cuticle is a waxy coating on the top and bottom of Continue reading >>
