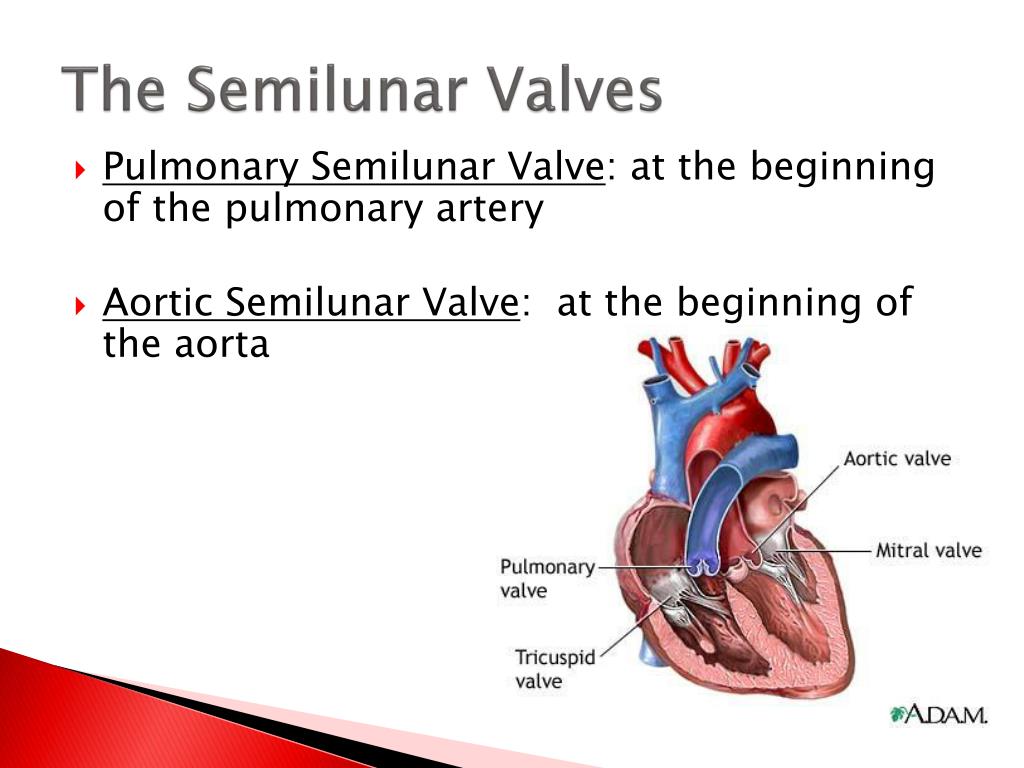
What is the function of Sasa node and AV node?
Sinoatrial (SA) Node . The sinoatrial node, also referred to as the pacemaker of the heart, coordinates heart contractions. Located in the upper wall of the right atrium, it generates nerve impulses that travel throughout the heart wall causing both atria to contract. The SA node is regulated by the autonomic nerves of the peripheral nervous system. Parasympathetic and …
Where does the AV node receive its blood supply?
The right coronary artery supplies blood to the right ventricle, the right atrium, and the SA (sinoatrial) and AV (atrioventricular) nodes, which regulate the heart rhythm. The right coronary artery divides into smaller branches, including the right posterior descending artery and the acute marginal artery.
What is an AV node block?
Feb 28, 2022 · The sinuatrial node is one of several structures of the cardiac conduction system. This intrinsic conduction system generates impulses for the contractions of the heart and ensures the coordinated flow of blood through the chambers of the heart. The components of this system include: Sinuatrial (SA) node; Atrioventricular (AV) node
What happens when the SA node sends impulses to the AV?
Jul 25, 2011 · The AV node receives its blood supply from the AV nodal artery; in 90% of people this artery branches from the right coronary artery. So AV nodal block due to a heart attack is most commonly seen with right coronary artery heart attacks.

Who supplies AV node?
The blood supply of the AV node is from the atrioventricular nodal branch. The origin of this artery is most commonly (80-90% of hearts) a branch of the right coronary artery, with the remainder originating from the left circumflex artery. This is associated with the dominance of the coronary artery circulation.
Which coronary artery supplies the SA and AV node in most of the population?
the RCAThe sinoatrial nodal artery is a branch of the RCA that supplies the SA node. The RCA also supplies the AV node via a septal perforating branch in 90% of people.Jul 28, 2021
Does the RCA supply the SA node?
The RCA gives the following branches: conus branch (anterior course supplying the right ventricular outflow tract), sinus node branch (posterior course supplying the sinoatrial node, acute marginal branches to the free wall of the right ventricle, an atrioventricular nodal branch (from the distal RCA), the posterior ...
What initiates the SA node?
SA node (sinoatrial node) – known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The impulse starts in a small bundle of specialized cells located in the right atrium, called the SA node. The electrical activity spreads through the walls of the atria and causes them to contract. This forces blood into the ventricles.May 1, 2019
Does the circumflex artery supply the SA node?
From the left coronary system, the left anteromedial artery is the one responsible with the sinoatrial node supply; the source is the circumflex artery and its origin is the medial third of the left anterior quadrant.
What coronary artery supplies the lateral wall?
Circumflex artery, which passes behind the heart between the left atrium and left ventricle and supplies blood to the side (lateral wall) of the left ventricle.
Is the SA node posterior?
The CS arises in the SA node, which is found in the upper anterior right atrium (Figure 1). The AV node is found in a lower, posterior position in the atrium.
What artery supplies the interventricular septum?
The posterior interventricular artery (in 90% of individuals), which supplies the posterior one-third of the interventricular septum, the inferior surface of the right ventricle and a portion of the inferior surface of the left ventricle.
Where are the SA and AV nodes located?
An electrical stimulus is generated by the sinus node (also called the sinoatrial node, or SA node). This is a small mass of specialized tissue located in the right upper chamber (atria) of the heart.
What cells are the SA node made of?
It is made up of specialized cardiomyocytes, also known as nodal cardiac muscle cells or 'pacemaker' cells which are grouped together into an elongated ellipsoid bundle with a length of 8 to 25 mm. Nodal cardiac muscle cells are smaller than typical cardiomyocytes and lack intercalated discs.
What is the difference between SA node and AV node?
SA node is the primary element of the heart that produces cardiac impulses. Therefore, it is called the pacemaker of the heart. On the other hand, AV node is the secondary element of the heart, which relays on the signals of the SA node, intensifying them and transmitting them to the ventricles.Aug 27, 2018
What do Purkinje fibers stimulate?
Purkinje fibers are networks of fibers that receive conductive signals originating at the atrioventricular node (AVN), and simultaneously activate the left and right ventricles by directly stimulating the ventricular myocardium.
Which artery supplies blood to the right ventricle?
This artery supplies blood to the outer side and back of the heart. Right coronary artery (RCA). The right coronary artery supplies blood to the right ventricle, the right atrium, and the SA (sinoatrial) and AV (atrioventricular) nodes, which regulate the heart rhythm.
Which artery divides into smaller branches?
The right coronary artery divides into smaller branches, including the right posterior descending artery and the acute marginal artery. Together with the left anterior descending artery, the right coronary artery helps supply blood to the middle or septum of the heart.
Which artery supplies blood to the left side of the heart muscle?
The left main coronary artery supplies blood to the left side of the heart muscle (the left ventricle and left atrium). The left main coronary divides into branches: The left anterior descending artery branches off the left coronary artery and supplies blood to the front of the left side of the heart. The circumflex artery branches ...
What is the function of the heart muscle?
Like all other tissues in the body, the heart muscle needs oxygen-rich blood to function. Also, oxygen-depleted blood must be carried away. The coronary arteries wrap around the outside of the heart. Small branches dive into the heart muscle to bring it blood.
What is the function of the AV node?
The AV node controls the passage of the heart’s electrical signal from the atria to the ventricles. After an electrical impulse is generated by the sinus node (located at the top of the right atrium), it spreads across both atria, causing these chambers to beat. The AV node then "gathers" that electrical impulse and, after a brief delay, ...
What is the AV node?
Updated on April 28, 2021. The atrioventricular (AV) node is a key part of the heart's electrical system, controlling the transmission of the heart’s electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles.
Why is decremental conduction important?
The decremental conduction prevents most of those impulses from reaching the ventricles and keeps the heart rate from becoming dangerously elevated.
What is the role of the AV node in the heart?
It transmits the heart’s electrical signal from the atrium to the ventricle, optimizes the coordination of each heartbeat, and, if atrial fibrillation occurs, protects the ventricles from being bombarded with a dangerous number of electrical signals.
What is the difference between second degree and third degree AV block?
2. With second degree AV block, some impulses from the atria are blocked from reaching the ventricles. With third-degree AV block, all of the impulses are blocked. 3.
What is the delay in conduction through the AV node?
A delay in conduction through the AV node is seen on the ECG as an increased PR interval.
Where is the AV node located?
What Is the AV Node? The AV node is a tiny "button" of specialized cells (roughly 3 by 5 millimeters in diameter) located near the center of the heart. It is on the right side of the atrial septum at the junction of the atria and the ventricles. 1. Its job is to help coordinate the contraction of the atria and the ventricles in response to ...
Where are the SA and AV nodes located?
SA node and AV node are two elements of the contractile system of the heart. They are located in the wall of the right atrium. Both are involved in maintaining the heart rate by inducing contraction.
What is the difference between AV and SA node?
The main difference between SA node and AV node is that the SA node generates cardiac impulses whereas the AV node relays and intensifies cardiac impulses. Furthermore, SA node is located in the right atrium, close to the point of entry of the superior vena cava while AV node is located in the right atrium, close to the opening ...
What is the AV node?
AV ( atrioventricular) node is the group of cells located in the border between the right atrium and the right ventricle, which serves as the secondary contractile system of the heart. It is primarily induced by SA node. It relays on signals of the SA node and holds them for 0.09 seconds, which is the time required by ...
Which node transmits cardiac impulses directly to the right and left atrium?
SA node transmits cardiac impulses directly to the right and left atrium while AV node transmits cardiac impulses the right and left ventricles through the branches and the terminal strands of the bundle of His.
Which node sets the rhythm of the heartbeat?
Then the cardiac impulses from the SA node are transmitted to the ventricles, contracting them. This chiefly means SA node sets the rhythm of the heartbeat while AV node sets the rhythm of the heart contraction.
Which two elements of the cardiac conduction system control the heart rate?
SA node and AV node are two elements of the cardiac conduction system that controls the heart rate.
Which system slows down the rate of impulses?
The cells of the SA node are smaller than the cells that make up the atrium. Also, they encompass fewer mitochondria. Sympathetic nervous system slows down the rate of the impulses while parasympathetic nervous system accelerates the rate of impulses.
Which artery supplies the AV node?
The atrioventricular nodal artery supplies the AV node and comes of the RCA. The sino-atrial nodal blood supply in 60% of cases is from the proximal RCA, but variants can be seen with blood supply from proximal LCx. [7] In most cases, epicardial fat surrounds the coronary arteries.
Which branch of the RCA is responsible for blood supply to the posterior one-third of the interventricular septum?
The RCA then classically descends into smaller branches including the right posterior descending artery (PDA) and acute marginal artery. The posterior descending artery is responsible for blood supply to the posterior one-third of the interventricular septum.
What is the RCA and LMCA?
The RCA gives rise to the sinoatrial nodal branch of the right coronary artery, posterior descending artery branch of the RCA, and the marginal branch. The LMCA branches into the circumflex and LAD.
What is the LAD?
The left anterior descending artery (LAD) supplies the anterior two-thirds of the septum.[2] . The LAD is one of two major branches of the LMCA, with the other being the left circumflex (LCx) coronary arteries. Combined, these two supply blood to the left atrium and left ventricle.
Which artery gives rise to the left marginal artery and posterior descending artery?
The LMCA branches into the circumflex and LAD. The circumflex artery gives rise to the left marginal artery and posterior descending artery (in a left-dominant heart). The left anterior descending artery gives off the diagonal branches. The RCA supplies blood to the right side of the heart.
Where does the LCX supply blood?
The LCx supplies blood to the lateral wall of the left ventricle and sometimes to the posterior inferior aspect of the heart when there is left heart dominance. The heart has a lymphatic system (lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid organs) just like every other organ in the body.
Which artery supplies blood to the left ventricle?
Combined, these two supply blood to the left atrium and left ventricle. The circumflex artery is responsible for blood supply to the left atrium and the posterior-lateral aspect of the left ventricle while the LAD supplies blood to the anterior portion of the left ventricle.
What is the difference between the AV and the SA node?
The SA node generates cardiac action potential due to spontaneous depolarization by the pacemaker cells whereas, the AV node involves in the reception of the action potential from the SA node and pass it to the AV bundle.
What is the role of the SA node?
The main role of the SA node is to generate an action potential which causes the contraction of the atriums. This is regulated by the nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system slows down the rate of induction of action potential, and para sympathetic nervous system speeds up the rate respectively.
How is the AV node activated?
The AV node is activated by the sino atrial node (SA node) after it is excited. A wave of excitation is spread through the atria for the activation of SA node. After the AV node is activated, a 0.12s delay of impulses is taken place.
How many chambers does the heart have?
The human heart is composed of four chambers; two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). The rate of the heartbeat and the two circulatory mechanisms; pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation are regulated by nodes present in the heart. The Sino atrial (SA) node and Atrio ventricular ...
What is the function of paranodal cells?
The main function of the paranodal cells is to insulate the SA node with the help of the connective tissue.
What are the components of the pacemaker cells in the SA node?
The pacemaker cells of SA node are present within a connective tissue that comprises of different components such as blood vessels, nerves, fat and collagen fibers. In the SA node, the pacemaker cells are surrounded by another group of cells known as paranodal cells.
Where is the AV node located?
The AV node is found at the lower posterior portion of the interatrial septum closer to the coroner sinus. Precisely, the AV node lies in the middle of a triangular area known as the Koch’s triangle, which is comprised of the tricuspid valve, the coronary sinus, and the interatrial septum membrane.