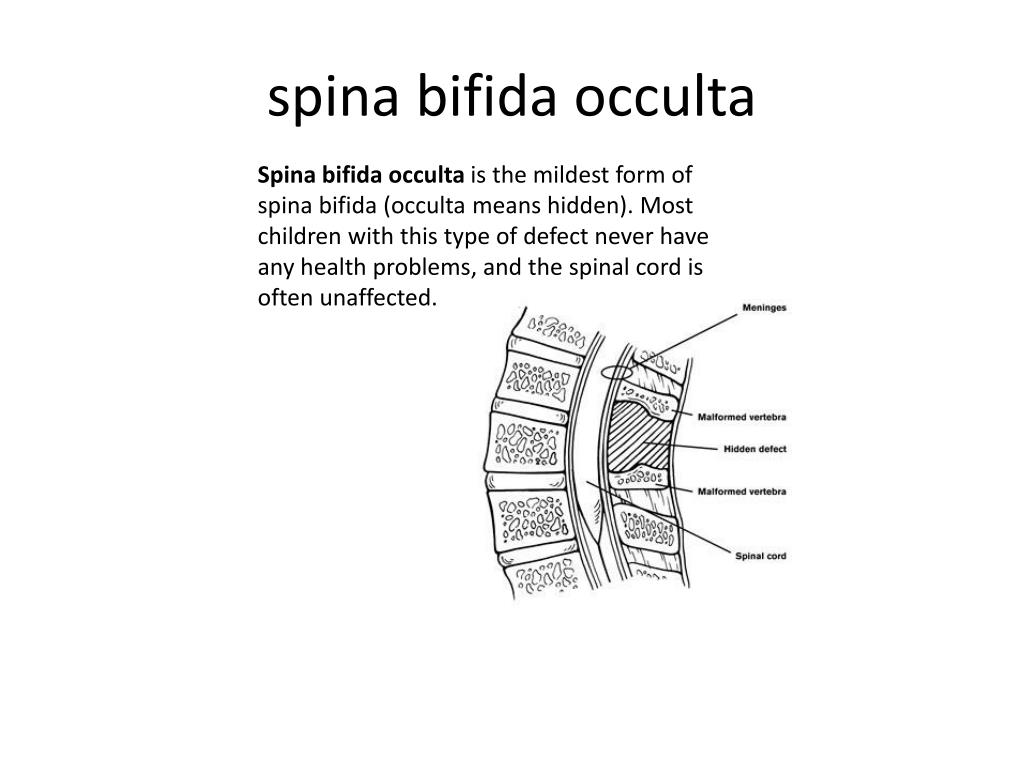
What is the membrane that covers the spinal cord and brain?
Meninges – The three membranes covering the spinal cord and brain — dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. Meningioma – A firm, often vascular, tumor arising from the coverings of the brain; the most common primary brain tumor.
What are the protective coverings of central nervous system?
The protective coverings of central nervous system • There are three coverings that protect the brain and spinal cord. • Apart from protection they carry venous blood/sinuses. • They constitute the blood brain barrier.
What is the meninges of the brain?
Updated October 01, 2018. The meninges is a layered unit of membranous connective tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. These coverings encase central nervous system structures so that they are not in direct contact with the bones of the spinal column or skull.
What layer of the meninges covers the cerebral cortex?
Pia Mater: This thin inner layer of the meninges is in direct contact with and closely covers the cerebral cortex and spinal cord. The pia mater has a rich supply of blood vessels, which provide nutrients to nervous tissue.

Which layer of the cerebrum separates the right from the left hemisphere?
5. The cranial Dura • It is double layered, periosteal layer and menningeal layer. The meningeal layer continues as the spinal dural. • The falx cerebri separates the right from the left cerebral hemisphere, the tentorium cerebelli separates the occipital lobe of the cerebrum from the underlying cerebellum, and the diaphragma sellae forms a circular partition around the stalk of the pituitary gland. • The medial edge of the tentorium cerebelli is called the tentorial incisure. • The falx cerebelli separates the two cerebellar hemisphere, and attached to the inner surface of tentorium cerebelli. Tuesday, January 07, 2014 5
Which diaphragm is the smallest dural infolding?
11. The diaphragma sellae • The sellar diaphragm is the smallest dural infolding and is a circular sheet of dura that is suspended between the clinoid processes, forming a partial roof over the hypophysial fossa. • The sellar diaphgram covers the pituitary gland in this fossa and has an aperture for passage of the infundibulum (pituitary stalk) and hypophysial veins. Tuesday, January 07, 2014 11
What is the mechanical link that connects the skull to the delicate strands of arachnoid (?
The thickness and abundant collagen of the dura make it the mechanical link that connects the skull to the delicate strands of arachnoid ( arachnoid trabeculae) that suspend the CNS in its bath of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This combination of partial flotation of the CNS in subarachnoid CSF, together with mechanical suspension by the skull-dura-arachnoid-arachnoid trabeculae-pia-CNS connections (see Fig. 4-3 ), stabilizes the fragile CNS during routine head movements.
What do the dark bars on the meninges mean?
The dark bars interconnecting the innermost arachnoid cells indicate the bands of tight junctions that form the arachnoid barrier.
What is the dura mater?
The dura mater, or dura, is a thick connective tissue membrane that also serves as the periosteum of the inside of the skull ( Fig. 4-1 ). The arachnoid and the pia mater (or pia) are much thinner collagenous membranes. The arachnoid is attached to the inside of the dura and the pia is attached to the outer surface of the CNS. Hence the only space normally present between or around the cranial meninges is subarachnoid space (not counting the venous sinuses found within the dura). The arrangement of spinal meninges is slightly different, as described later in this chapter.
Why are meninges important?
The meninges form a major part of the mechanical suspension system of the CNS, necessary to keep it from self-destructing as we move through the world. In addition, one layer of the meninges participates in the system of barriers that effectively isolates the extracellular spaces in the nervous system from the extracellular spaces in the rest of the body.
Which layer of the spinal column is composed of the meningeal layer and does not contain a perio?
The dura mater of the spinal column is composed of the meningeal layer and does not contain a periosteal layer. Arachnoid Mater: This middle layer of the meninges connects the dura mater and pia mater. The arachnoid membrane loosely covers the brain and spinal cord and gets its name from its web-like appearance.
Which layer of the brain connects the dura mater to the skull?
The outer periosteal layer firmly connects the dura mater to the skull and covers the meningeal layer. The meningeal layer is considered the actual dura mater. Located between these two layers are channels called dural venous sinuses.
What is the subarachnoid space?
The subarachnoid space provides a route for the passage of blood vessels and nerves through the brain and collects cerebrospinal fluid that flows from the fourth ventricle. Membrane projections from the arachnoid mater called arachnoid granulations extend from the subarachnoid space into the dura mater.
What are the three membranes of the meninges?
The meninges are composed of three membrane layers known as the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater . Each layer of the meninges serves a vital role in the proper maintenance and function of the central nervous system.
How does the arachnoid membrane get its name?
The arachnoid membrane loosely covers the brain and spinal cord and gets its name from its web-like appearance. The arachnoid mater is connected to the pia mater through tiny fibrous extensions that span the subarachnoid space between the two layers.
What is the role of cerebral fluid in the brain?
Cerebrospinal fluid protects and nourishes CNS tissue by acting as a shock absorber, by circulating nutrients, and by getting rid of waste products.
What is the meninges?
Updated July 02, 2019. The meninges is a layered unit of membranous connective tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord. These coverings encase central nervous system structures so that they are not in direct contact with the bones of the spinal column or skull.
What is the term for a surgical connection of nerves or blood vessels in the nervous system?
Anastomosis – A surgical connection of nerves or blood vessels in the nervous system. Anesthesiologist – Physician who administers pain-killing medications during surgery. Anencephaly – Absence of the greater part of the brain, skull and scalp.
What is the term for a tumor in the nerve that connects the ear to the brain?
A. Abscess – A circumscribed collection of pus in any part of the body, usually accompanied by swelling and inflammation. Acoustic Neuromas – A benign tumor in the nerve that connects the ear to the brain.
What is the term for a thickening of the arachnoid membrane?
Arachnoiditis – Inflammation of the arachnoid membrane. Arteriosclerosis – Thickening and calcification (buildup of calcium) of the arterial wall with loss of elasticity and contractility; also known as a hardening of the arteries. Arteriovenous – Term used when a condition relates to arteries and/or veins.
What is the term for an interruption in breathing?
Apnea – An interruption in breathing. Apoplexy – A condition in which there is bleeding into an organ or blood flow to an organ has ceased. Arachnoid Mater – One of the three meninges that cover the brain and spinal cord, it is the delicate middle layer of these three membranes.
What is the term for a dilation of an artery, formed by a circumscribed enlargement of?
Aneurysm – Dilation of an artery, formed by a circumscribed enlargement of its wall. Angiogram – A medical imaging report that depicts the blood vessels traveling to and within the brain; test usually is performed by injecting a special dye through a catheter.
What is the term for loss of sensation in a body part induced by the administration of a drug?
Anesthesia – Loss of sensation in a body part induced by the administration of a drug. Anesthesiologist – Physician who administers anesthesia prior to surgery; also monitors reactions and complications during surgery. Aneurysm – Dilation of an artery, formed by a circumscribed enlargement of its wall.
What is the name of the procedure that uses opaque material to increase visibility of the vessels?
Angiography – Radiography of blood vessels using the injection of material opaque to X-rays to increase visibility of the vessels. Anorexia – An eating disorder marked by excessive weight loss due to the restriction of food intake; spurred by distorted body image and other factors.
What part of the brain is affected by a seizure?
The entire brain is affected by the seizure.
How much does the brain weigh?
The adult brain weighs around three pounds. Its size and weight are proportional to body size, not intelligence. Which of the following statements best describes the anatomy of the brain?
Is there a relationship between low levels of oxygen in the brain and the development of CP?
There is a relationship between low levels of oxygen in the brain and the development of CP.
What is the surface of the brain called?
The surface of the brain, known as the cerebral cortex, is very uneven, characterized by a distinctive pattern of folds or bumps, known as gyri (singular: gyrus), and grooves, known as sulci (singular: sulcus), shown in [link]. These gyri and sulci form important landmarks that allow us to separate the brain into functional centers. The most prominent sulcus, known as the longitudinal fissure, is the deep groove that separates the brain into two halves or hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
Where does the spinal cord end?
In the opposite direction, the spinal cord ends just below the ribs —contrary to what we might expect, it does not extend all the way to the base of the spine.
Which part of the brain contains the cerebral cortex?
The two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex are part of the forebrain ( [link] ), which is the largest part of the brain. The forebrain contains the cerebral cortex and a number of other structures that lie beneath the cortex (called subcortical structures): thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the limbic system (collection of structures). The cerebral cortex, which is the outer surface of the brain, is associated with higher level processes such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory. Each cerebral hemisphere can be subdivided into four lobes, each associated with different functions.
Where is the reticular formation located?
The midbrain is comprised of structures located deep within the brain, between the forebrain and the hindbrain. The reticular formation is centered in the midbrain , but it actually extends up into the forebrain and down into the hindbrain. The reticular formation is important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity.
How does the spinal cord respond to sensory signals?
Withdrawal from heat and knee jerk are two examples. When a sensory message meets certain parameters, the spinal cord initiates an automatic reflex. The signal passes from the sensory nerve to a simple processing center, which initiates a motor command. Seconds are saved, because messages don’t have to go the brain, be processed, and get sent back. In matters of survival, the spinal reflexes allow the body to react extraordinarily fast.
What happens when the spinal cord is damaged?
When the spinal cord is damaged in a particular segment, all lower segments are cut off from the brain, causing paralysis. Therefore, the lower on the spine damage is, the fewer functions an injured individual loses.
How many segments are there in the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is functionally organized in 30 segments, corresponding with the vertebrae. Each segment is connected to a specific part of the body through the peripheral nervous system. Nerves branch out from the spine at each vertebra. Sensory nerves bring messages in; motor nerves send messages out to the muscles and organs. Messages travel to and from the brain through every segment.
What is the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is made up of nerves that carry information between the brain and the rest of the body. Essentially, the brain and spinal cord are a part of the nervous system. In this article, we shall explore more differences between the two: The brain can be described as having 4 major regions – cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon and brainstem.
What is the difference between Brain and Spinal Cord?
In higher organisms such as humans and other vertebrates, it is also the centre of learning. The spinal Cord is a tube-like structure that starts from the bottom of the brain and ends at the bottom of the backbone. The spinal cord is made up of nerves that carry information between the brain and the rest of the body.
What happens if you have a spinal cord injury?
Injuries to the brain can result in varying consequences – ranging from loss of consciousness to vomiting and nausea. Depending on the injury, other medical complications can also arise such as loss of smell, taste and also hamper vision.
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal Cord is a tube-like structure that starts from the bottom of the brain and ends at the bottom of the backbone. The spinal cord is made up of nerves that carry information between the brain and the rest of the body.
Where is the brain located?
Brain is housed inside the skull and it controls most of the activities of the body. In higher organisms such as humans and other vertebrates, it is the centre of learning. Spinal Cord is a tube-like structure that begins from the end of the brain and ends at the bottom of the backbone.
How many regions are there in the brain?
The brain can be described as having 4 major regions – cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon and brainstem
