What is the behavior of gases?
Behavior of Gases 1 Behavior of Gases. There are 5 main states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma and the Bose-Einstein condensate. ... 2 Standard Gas Equation. Gases which obey all gas laws under all conditions of pressure and temperature are called perfect gases or the ideal gases. 3 Solved Examples For You. ...
What is the kinetic theory of gas molecules?
The kinetic theory of gas molecules explains the behavior of gas molecules. We can study the gas molecules at a microscopic level. A gas is composed of the collaboration of a large number of molecules. The larger number of distances among the gas molecules make the volume of the gas almost negligible.
Why do gases follow the gas laws?
Although the gas laws describe relationships that have been verified by many experiments, they do not tell us why gases follow these relationships. The kinetic molecular theory (KMT) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this chapter.
What are the main assumptions of the gas theory?
The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion, colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their absolute temperatures.

What theory is used to explain the behavior of particles in gases?
The experimental observations about the behavior of gases discussed so far can be explained with a simple theoretical model known as the kinetic molecular theory.
What are the theory of gases?
Kinetic theory of gases is a theoretical model that describes the molecular composition of the gas in terms of a large number of submicroscopic particles which include atoms and molecules. Further, the theory explains that gas pressure arises due to particles colliding with each other and the walls of the container.
What theory describes the properties of gases?
kinetic theory of gases, a theory based on a simplified molecular or particle description of a gas, from which many gross properties of the gas can be derived.
What does kinetic theory of gases?
The model, called the kinetic theory of gases, assumes that the molecules are very small relative to the distance between molecules. The molecules are in constant, random motion and frequently collide with each other and with the walls of any container.
What is kinetic theory of gases in physics?
The kinetic theory of gases attempts to explain the microscopic properties of a gas in terms of the motion of its molecules. The gas is assumed to consist of a large number of identical, discrete particles called molecules, a molecule being the smallest unit having the same chemical properties as the substance.
Which theory explains the different behavior of gases and liquid under pressure?
The physical behaviour of gases is explained by the kinetic molecular theory of gases. The number of collisions that gas particles make with the walls of their container and the force at which they collide determine the magnitude of the gas pressure. Temperature is proportional to average kinetic energy.
What is the kinetic theory in chemistry?
The kinetic-molecular theory explains the states of matter, and is based on the idea that matter is composed of tiny particles that are always in motion. This theory helps explain observable properties and behaviors of solids, liquids, and gases.
Who gave kinetic theory of gases?
The kinetic theory relates the independent motion of molecules to the mechanical and thermal properties of gases—namely, their pressure, volume, temperature, viscosity, and heat conductivity. Three men—Daniel Bernoulli in 1738, John Herapath in 1820, and John James Waterston in 1845—independently developed the theory.
Q1. Calculate the total volume occupied by the carbon dioxide gas having a mass of 2.34 grams at STP...
Ans: We need to consider the formula for the ideal gas law for calculating the volume.The formula is:V = nRT/PBy putting all the values from the ab...
Q2. What are the assumptions made for the ideal Gas Law?
Ans: Here are the assumptions for the ideal gas law:The volume of the particles is negligible, as they are very small.There is no interaction betwe...
Q3. State and explain the fourth state of Matter.
Ans: The fourth state of matter is known as plasma. It has its recognition along with solid, liquid, and gas. It is generated from the heating of g...
Q4. Who discovered the Plasma state? What type of Matter is it?
Ans: Plasma was discovered by the physicist Sir William Crookes. He identified the plasma in a Crookes tube. Also, he named it as a radiant matter.
How do gas laws work?
The gas laws deal with how gases behave with respect to pressure, volume, temperature, and amount. Gases are the only state of matter that can be compressed very tightly or expanded to fill a very large space. Pressure is force per unit area, calculated by dividing the force by the area on which the force acts.
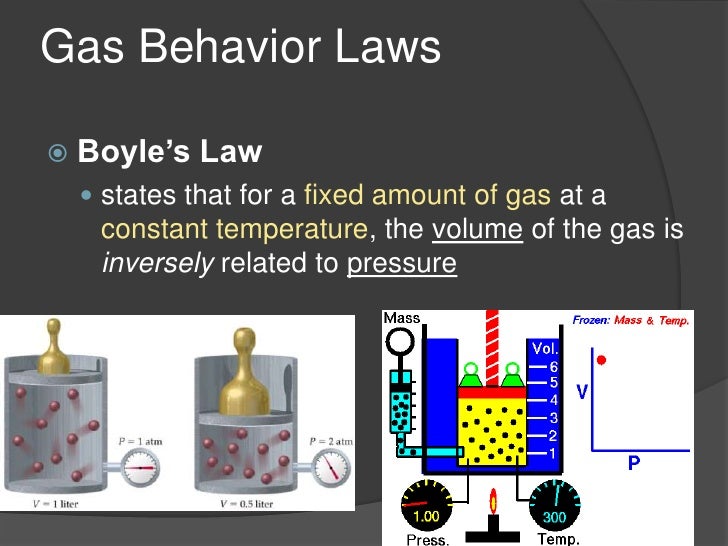
Which law states that the volume of a certain mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure and directly
The Combined Gas Law (Combination of Boyle’s Law and Charles Law) states that the volume of a certain mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure and directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
Why do gases have a greater kinetic energy than liquids?
The greater kinetic energy is due to gases existing at higher temperatures than liquids or solids. As temperature increases, particles move faster and, thus, have greater kinetic energy.
What is ideal gas?
An ideal gas is one which follows the gas law perfectly. Such a gas is non-existent, for no known gas obeys the gas laws at all possible temperatures. There are two principal reasons why real gases do not behave as ideal gases;
What does gas do for med tech?
As a med tech student learning about the theories of gases, gives a lot of knowledge. GAS helps humans to live on earth, the oxygen we breath makes our heart pumps, and the carbon dioxide helps the plants to grow. Gas is one of the states of matter, it also forms by small atoms.
How many milliliters is a gas?
A gas has a volume of 500 milliliters when a pressure equivalent to 760 millimeters of mercury is exerted upon it. Calculate the volume if the pressure is reduced to 730 millimeters. The volume and pressure of a gas are 850 milliliters and 70.0 mm respectively.
Which law states that the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its temperature?
Charles's law states that the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its temperature on the absolute temperature scale (in Kelvin) if pressure and the amount of gas remain constant. Gay-Lussac's Law shows the relationship between the temperature and pressure of a gas.
What is the behaviour of a gas?
Behaviour of Gas Molecules. The behaviour of gas molecules is dependent on the properties and laws obeyed by the molecules of the gas. The distribution of molecules in a gas is very different from the distribution of molecules in liquids and solids.
What happens to the volume of gas as the temperature increases?
As the temperature increases, the volume of the gas also increases due to an expansion of gas molecules. As the temperature decreases, the volume of the gas also decreases due to the contraction of gas molecules. As the temperature increases, the pressure of the gas also increases due to an expansion of gas molecules.
What is the ideal gas law?
According to ideal gas law, the product of pressure and volume of one gram molecule of an ideal gas is equal to the product of a number of moles of the gas, universal gas constant and the absolute temperature. Mathematical representation of the law is given in the table: PV = nRT = NkT. Where,
What happens to the pressure of gas as the quantity decreases?
As the quantity decreases, the pressure will also decrease and with an increase in the quantity, the pressure also increases. For pressure to decrease, the volume and quantity of the gas should be less. For pressure to increase, the volume and quantity of the gas should be more.
What is the classification of gas?
The classification of gases are: Ideal gas. Non-ideal gas or real gas.
When the volume of a gas is constant, the pressure of a given mass of gas varies directly with the
According to Gay-Lussac’s law, when the volume of the gas is constant, the pressure of a given mass of gas varies directly with the absolute temperature of the gas . Mathematical representation of the law is given in the table:
Is intermolecular interaction negligible?
The intermolecular interactions are also negligible. The collision of molecules with each other and with the walls of the container is always elastic. The average kinetic energy of all the molecules is dependent on the temperature.
What dictates the behavior of a gas?
The properties and laws obeyed by the molecules of the gas dictate the behavior of gas molecules. Physicists have encountered many differences among the molecular distribution of a gas and a liquid or a solid substance.
What is the ideal gas law?
The formula for an ideal gas is given above: We can derive ideal gas laws from the following laws: Boyle’s law. Boyle states that the pressure (P) of the gas is inversely proportional to its volume (V) at a constant temperature. P ∝.
How to find the ideal gas constant?
The formula for an ideal gas is the product of pressure and volume of a one-gram molecule of an ideal gas is the same as the product of a universal gas constant, absolute temperature, and the number of moles of the gas. To know what is the ideal gas constant, the mathematical expression is: PV = nRT = NkT. Here,
Why does the volume of a gas increase?
Some of these factors are given below: The volume of the gas increases due to an expansion of gas molecules due to a rise in temperature. The volume of the gas drops due to the contraction of gas molecules and the decline in temperature. The pressure of the gas rises due to an expansion of gas molecules because of the rise in temperature.
Why does gas pressure drop?
The gas pressure drops because of the contraction of gas molecules because of the decrease in temperature. The temperature of the gas molecule should be low enough, or the pressure of the gas must be very high when we convert the gas either into solid or liquid.
What is flue gas?
Flue gas is a gas that exists in the atmosphere as a result of a flue. The flue gases are formed into the atmosphere due to the release of the gas from the furnace, oven, broiler, fireplace, etc. through a channel.
What is the fourth state of matter?
State and explain the fourth state of Matter. Ans: The fourth state of matter is known as plasma. It has its recognition along with solid, liquid, and gas. It is generated from the heating of gas and contains a mixture of ions and electrons.
What is the kinetic molecular theory of gases?
A Model of Gases as Moving Particles. The kinetic molecular theory of gases assumes gas particles act as hard, completely elastic spheres. Andrew Zimmerman Jones is a science writer, educator, and researcher. He is the co-author of "String Theory for Dummies.". The kinetic theory of gases is a scientific model that explains the physical behavior ...
What happens when gas particles collide with the side of the container?
When particles of the gas collide with the side of the container, they bounce off the side of the container in a perfectly elastic collision, which means that if they strike at a 30-degree angle, they'll bounce off at a 30-degree angle.
What is the motion of a tiny particle suspended in a liquid?
One of the lynchpins in experimentally confirming the kinetic theory, and atomism is general, was related to Brownian motion . This is the motion of a tiny particle suspended in a liquid, which under a microscope appears to randomly jerk about. In an acclaimed 1905 paper, Albert Einstein explained Brownian motion in terms ...
What did Einstein explain about Brownian motion?
In an acclaimed 1905 paper, Albert Einstein explained Brownian motion in terms of random collisions with the particles that composed the liquid. This paper was the result of Einstein's doctoral thesis work, where he created a diffusion formula by applying statistical methods to the problem.
What are the assumptions of kinetic theory?
Assumptions of the Kinetic Molecular Theory. The kinetic theory involves a number of assumptions that focus on being able to talk about an ideal gas . Molecules are treated as point particles. Specifically, one implication of this is that their size is extremely small in comparison to the average distance between particles.
Who developed the kinetic theory?
The work of Daniel Bernoulli presented the kinetic theory to a European audience, with his 1738 publication of Hydrodynamica. At the time, even principles like the conservation of energy had not been established, and so a lot of his approaches were not widely adopted.
Who discovered that liquids are composed of tiny particles?
A similar result was independently performed by the Polish physicist Marian Smoluchowski, who published his work in 1906. Together, these applications of kinetic theory went a long way to support the idea that liquids and gases (and, likely, also solids) are composed of tiny particles.
What are the learning objectives of gas laws?
The gas laws that we have seen to this point, as well as the ideal gas equation, are empirical, that is, they have been derived from experimental observations. The mathematical forms of these laws closely describe the macroscopic behavior of most gases at pressures less than about 1 or 2 atm.
What happens to the temperature of a gas when the volume of the gas increases?
Charles’s law. If the temperature of a gas is increased, a constant pressure may be maintained only if the volume occupied by the gas increases. This will result in greater average distances traveled by the molecules to reach the container walls, as well as increased wall surface area.
Why do molecules have varying speeds?
In a gas sample, individual molecules have widely varying speeds; however, because of the vast number of molecules and collisions involved, the molecular speed distribution and average speed are constant.
What is the kinetic molecular theory?
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory Explains the Behavior of Gases, Part II. According to Graham’s law, the molecules of a gas are in rapid motion and the molecules themselves are small. The average distance between the molecules of a gas is large compared to the size of the molecules.
Why do gases bombard the container walls with the same frequency?
Because of the large distances between them , the molecules of one gas in a mixture bombard the container walls with the same frequency whether other gases are present or not, and the total pressure of a gas mixture equals the sum of the (partial) pressures of the individual gases.
What is the molecule theory?
(Note: The term “molecule” will be used to refer to the individual chemical species that compose the gas, although some gases are composed of atomic species, for example, the noble gases.)
Do gas laws explain relationships?
Although the gas laws describe relationships that have been verified by many experiments, they do not tell us why gases follow these relationships. The kinetic molecular theory (KMT) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this chapter.
