
Even objects that we think of as being very cold, such as an ice cube, emit infrared. When an object is not quite hot enough to radiate visible light, it will emit most of its energy in the infrared. For example, hot charcoal may not give off light but it does emit infrared radiation which we feel as heat.
What emits infrared light?
Many things besides people and animals emit infrared light - the Earth, the Sun, and far away things like stars and galaxies do also! For a view from Earth orbit, whether we are looking out into space or down at Earth, we can use instruments on board satellites. What does the Infrared show us? We know that many things emit infrared light.
What does the infrared show us in space?
Other satellites, like the Infrared Astronomy Satellite (IRAS) look up into space and measure the infrared light coming from things like large clouds of dust and gas, stars, and galaxies! What does the Infrared show us? We know that many things emit infrared light. But many things also reflect infrared light, particularly near infrared light.
How does infrared radiation affect the Earth?
MONITORING THE EARTH. Earth scientists study infrared as the thermal emission (or heat) from our planet. As incident solar radiation hits Earth, some of this energy is absorbed by the atmosphere and the surface, thereby warming the planet. This heat is emitted from Earth in the form of infrared radiation.
How is infrared used in everyday life?
In infrared light, hot things look bright yellow and orange. Items that are colder, such as an ice cube, are purple or blue. We use infrared cameras to help us see things. NASA scientists use infrared to help predict weather. Rescue workers use them to find people who need help. How can we "see" using the Infrared?
What is infrared light?
Infrared waves, or infrared light, are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. People encounter Infrared waves every day; the human eye cannot see it, but humans can detect it as heat. A remote control uses light waves just beyond the visible spectrum of light—infrared light waves—to change channels on your TV.
Why use infrared light to see the Earth?
Why use the infrared to image the Earth? While it is easier to distinguish clouds from land in the visible range, there is more detail in the clouds in the infrared. This is great for studying cloud structure. For instance, note that darker clouds are warmer, while lighter clouds are cooler. Southeast of the Galapagos, just west of the coast of South America, there is a place where you can distinctly see multiple layers of clouds, with the warmer clouds at lower altitudes, closer to the ocean that's warming them.
How does infrared energy work?
To astrophysicists studying the universe, infrared sources such as planets are relatively cool compared to the energy emitted from hot stars and other celestial objects. Earth scientists study infrared as the thermal emission (or heat) from our planet. As incident solar radiation hits Earth, some of this energy is absorbed by the atmosphere and the surface, thereby warming the planet. This heat is emitted from Earth in the form of infrared radiation. Instruments onboard Earth observing satellites can sense this emitted infrared radiation and use the resulting measurements to study changes in land and sea surface temperatures.
Why can't we see new stars in visible light?
Most of the new stars cannot be seen in the visible-light image (left) because dense gas clouds block their light. However, when the pillar is viewed using the infrared portion of the spectrum (right), it practically disappears, revealing the baby stars behind the column of gas and dust.
What are the sources of heat on Earth's surface?
There are other sources of heat on the Earth's surface, such as lava flows and forest fires.
What wavelength is thermal infrared?
LEFT: A typical television remote control uses infrared energy at a wavelength around940 nanometers.
Can you see cool objects in the infrared?
Many objects in the universe are too cool and faint to be detected in visible light but can be detected in the infrared. Scientists are beginning to unlock the mysteries of cooler objects across the universe such as planets, cool stars, nebulae, and many more, by studying the infrared waves they emit.
What are some things that emit infrared light?
Many things besides people and animals emit infrared light – the Earth, the Sun, and far away things like stars and galaxies do also! For a view from Earth orbit, whether we are looking out into space or down at Earth, we can use instruments on board satellites.
Why do we use infrared to see the Earth?
This is an infrared image of the Earth taken by the GOES 6 satellite in 1986. A scientist used temperatures to determine which parts of the image were from clouds and which were land and sea. Based on these temperature differences, he colored each separately using 256 colors, giving the image a realistic appearance.Why use the infrared to image the Earth? While it is easier to distinguish clouds from land in the visible range, there is more detail in the clouds in the infrared. This is great for studying cloud structure. For instance, note that darker clouds are warmer, while lighter clouds are cooler. Southeast of the Galapagos, just west of the coast of South America, there is a place where you can distinctly see multiple layers of clouds, with the warmer clouds at lower altitudes, closer to the ocean that’s warming them.
What satellites are used to measure infrared light?
Other satellites, like the Infrared Astronomy Satellite (IRAS) look up into space and measure the infrared light coming from things like large clouds of dust and gas, stars, and galaxies!Satellites like GOES 6 and Landsat 7 look at the Earth. Special sensors, like those aboard the Landsat 7 satellite, record data about the amount of infrared light reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface.
What is thermal infrared?
Far infrared waves are thermal. In other words, we experience this type of infrared radiation every day in the form of heat! The heat that we feel from sunlight, a fire, a radiator or a warm sidewalk is infrared. The temperature-sensitive nerve endings in our skin can detect the difference between inside body temperature and outside skin temperature. Infrared light is even used to heat food sometimes – special lamps that emit thermal infrared waves are often used in fast food restaurants!
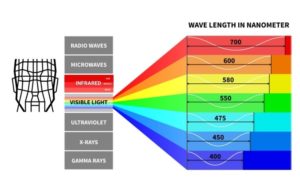
What is the wavelength of infrared light?
Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range from red light to violet. “Near infrared” light is closest in wavelength to visible light and “far infrared” is closer to the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The longer, far infrared wavelengths are about the size of a pin head and the shorter, near infrared ones are the size of cells, or are microscopic.
What wavelength do humans radiate?
Humans, at normal body temperature, radiate most strongly in the infrared at a wavelength of about 10 microns. (A micron is the term commonly used in astronomy for a micrometer or one millionth of a meter.) This image ( which is courtesy of the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center at CalTech), shows a man holding up a lighted match! Which parts of this image do you think have the warmest temperature? How does the temperature of this man’s glasses compare to the temperature of his hand?
What can be taken on board a satellite?
Instruments on board satellites can also take pictures of things in space. The image below of the center region of our galaxy was taken by IRAS. The hazy, horizontal S-shaped feature that crosses the image is faint heat emitted by dust in the plane of the Solar System.
Why does infrared film see the object?
Infrared film 'sees' the object because the Sun (or some other light source) shines infrared light on it and it is reflected or absorbed by the object.
What is the color of the infrared waves?
False-color infrared images of the Earth frequently use a color scheme like the one shown here, where infrared light is mapped to the visible color of red. This means that everything in this image that appears red is giving off or reflecting infrared light. This makes vegetation like grass and trees appear to be red. The visible light waves drawn on this picture are green, and the infrared ones are darker red.
What is the term for the heat waves that are felt from sunlight?
Far infrared waves are thermal. In other words, we experience this type of infrared radiation every day in the form of heat! The heat that we feel from sunlight, a fire, a radiator or a warm sidewalk is infrared.
What does it mean when an object is not hot enough to emit visible light?
When an object is not quite hot enough to radiate visible light, it will emit most of its energy in the infrared. For example, hot charcoal may not give off light but it does emit infrared radiation which we feel as heat. The warmer the object, the more infrared radiation it emits.
What is the wavelength of infrared light?
Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range from red light to violet. "Near infrared" light is closest in wavelength to visible light and "far infrared" is closer to the microwave region ...
What satellites look up into space?
Other satellites, like the Infrared Astronomy Satellite (IRAS) look up into space and measure the infrared light coming from things like large clouds of dust and gas, stars, and galaxies!
What can be taken on board a satellite?
Instruments on board satellites can also take pictures of things in space. The image below of the center region of our galaxy was taken by IRAS. The hazy, horizontal S-shaped feature that crosses the image is faint heat emitted by dust in the plane of the Solar System.
What materials reflect infrared light?
Gold, silver, aluminum, Plexiglas and hybrid pigments are materials that reflect infrared light. The atomic makeup of materials is what renders them transparent, opaque or reflective to infrared radiation.
Why is gold foil used in spaceflight?
Many components used in spaceflight are coated in gold foil for this reason. Gold also blocks other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, including ultraviolet radiation, which has a wavelength shorter than the shortest visible light.
Is aluminum foil good for infrared?
However, aluminum is much more abundant than gold, making it ideal for conventional infrared radiation-shielding applications. Using aluminum foil to bake goods in an oven shows the ability of this material to internally reflect infrared radiation and trap heat. ADVERTISEMENT.
Is gold foil good for heat shields?
This reflectivity also extends into the infrared range, making gold foil an ideal material for high-performance heat shields.
Does aluminum reflect infrared radiation?
This ability to selectively filter out radiation on both sides of the visible spectrum enables gold as a visor material for astronaut helmets. Aluminum also reflects infrared radiation, although thin sheets of it are not as transparent in the visible light range as gold.
Why does the body emit infrared energy?
The answer is kinect energy. Our body will emit infrared since it is burning glicose into energy and electrons are disturbed on the process. Electrons will return into their original state emiting infrared.
How many times does the Earth emit infrared light?
The Earth re-radiates the same heat into space (if it didn't, we'd all boil in short order) in the form of infrared light, but to do so, it emits approx. ten times as many (infrared) photons than the number of (visible light) photons it receives.
How much radiation does the Sun emit?
In total, the Sun radiates gravitational radiation at a measly 79 megawatts.
What happens when atoms wiggle?
Now atoms are made of positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons. When these charged particle wiggle they are in fact accelerating and decelerating in the electric field which surrounds them caused by the neighboring atoms’ electrons . If you accelerate a charged particle in an electric field it emits electromagnetic radiation. It so happens that the frequency of their wiggles matches
What would happen if we could make an object from particles that do not interact with light?
If we could somehow make an object from particles (e.g., neutrinos) that do not interact with light at all, the resulting object would not emit any light at all, no matter how hot. And it would be completely transparent to all light. And here is another thing... objects emit not just light when they are hot.
How does low frequency light affect life?
Low frequency light (like radio waves) has so little energy that its impact on living organisms is negligible to non-existent. Life forms receive no survival advantages from an ability to detect very low frequency light. As a result, humans are free to use this part of the spectrum to communicate invisibly over large distances.
Why can't we see high frequency light?
The reason we don’t see high frequency light is because the nitrogen and oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere are opaque to high frequencies. These high frequencies are absorbed or deflected, which makes adapting human vision to detect them unnecessary.
What is the radioactive isotope used in smoke detectors?
Smoke detectors. According to experts, some household smoke detectors use small amounts of radioactive isotope, americium-241, to alert you when there is smoke in the air. The detector does not pose any health risks because the material is surrounded by ceramic and foil.
What is the biggest radiation?
According to the EPA, the largest radiation dose received by the public (after radon) is from smoking cigarettes. Cigarette smoke contains small amounts of radioactive materials, which smokers bring into their lungs as they inhale.
Is ionization smoke detector dangerous?
The EPA reports that there is no health risk from ionization smoke detectors, as long as the detector is not tampered with and is used as directed.
Is RF energy ionizing radiation?
RF energy is one type of non-ionizing radiation. Government agencies set safety guidelines that limit RF exposure from wireless devices. Scientists are continuing to study the effects of long-term exposure to low levels of RF. Don't Edit.
Do smart meters emit radiation?
The frequency and power of the RF waves given off from a smart meter are similar to that of a cell phone, cordless phone or Wi-Fi router. The meters emit less radiation than an individual can get from using a cell phone, according to Bob McGee, a spokesman for Con Edison. Don't Edit. PRNewsFoto/Linksys.
