
How many people died in the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake?
San Francisco earthquake of 1989, also called Loma Prieta earthquake, major earthquake that struck the San Francisco Bay Area, California, U.S., on October 17, 1989, and caused 63 deaths, nearly 3,800 injuries, and an estimated $6 billion in property damage.
What magnitude was the 89 earthquake?
What magnitude was the 89 earthquake? 6.9 Its epicentre was in the Forest of Nisene Marks State Park, near Loma Prieta peak in the Santa Cruz mountains, northeast of Santa Cruz and approximately 60 miles (100 km) south of San Francisco.
Who won the 89 World Series?
The Oakland Athletics won the AL West division by seven games over the Kansas City Royals, then defeated the Toronto Blue Jays four games to one in the American League Championship Series . It was the Giants' first World Series appearance since 1962, while the Athletics were playing in their second straight Fall Classic following the 1988 Series.
Why did the Bay Bridge collapse?
Why did the Bay Bridge collapse? The Bay Bridge collapsed in 1989 because of an earthquake in San Francisco. Is the Golden Gate Bridge earthquake resistant? The Golden Gate Bridge is regarded as one of the most beautiful bridges in the world. It is also supposed to be known as one of the most photographed bridge in the world.
What time was the earthquake on October 17 1989?
Its epicentre was in the Forest of Nisene Marks State Park, near Loma Prieta peak in the Santa Cruz mountains, northeast of Santa Cruz and approximately 60 miles (100 km) south of San Francisco. It struck just after 5:00 pm local time and lasted approximately 15 seconds, with a moment magnitude of 6.9.
What time did the San Francisco earthquake happen 1906?
5:12 AMOrigin Time and Epicenter At 5:12 AM local time, on April 18, 1906, a foreshock occurred with sufficient force to be felt widely throughout the San Francisco Bay area. The great earthquake broke loose some 20 to 25 seconds later, with an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean just 2 miles west of San Francisco.
When did San Francisco get an 8.0 earthquake?
On April 18, 1906, at 5:13 a.m., an earthquake estimated at close to 8.0 on the Richter scale strikes San Francisco, California, killing an estimated 3,000 people as it topples numerous buildings.
How many seconds did the San Francisco earthquake last?
The great earthquake broke loose some 20 to 25 seconds later, with an epicenter near San Francisco. Violent shocks punctuated the strong shaking which lasted some 45 to 60 seconds.
What was the worst earthquake in California?
California's Largest Recorded Earthquakes Since 1800, Ranked by MagnitudeMagnitudeDateLocation7.9Jan. 9, 1857Fort Tejon7.8April 18, 1906San Francisco7.4Mar. 26, 1872Owens Valley7.4Nov. 8, 1980W. of Eureka*12 more rows
What is the biggest earthquake ever recorded?
Mw 9.5 earthquakeOn May 22, 1960 a great Mw 9.5 earthquake, the largest earthquake ever instrumentally recorded, occurred off the coast of southern Chile. This earthquake generated a tsunami that was destructive not only along the coast of Chile, but also across the Pacific in Hawaii, Japan, and the Philippines.
Did the Golden Gate Bridge collapse in 1989?
Loma Prieta Earthquake, October 17, 1989 Although the Golden Gate Bridge suffered no observed damage from the Loma Prieta quake, since the epicenter was located some 60 miles to the south, the earthquake became a catalyst for the extensive seismic retrofit program that the historic structure is undergoing today.
What magnitude was the 89 earthquake?
magnitude 6.9On October 17, 1989, the San Francisco Bay area was jolted by the Loma Prieta earthquake. The quake's epicenter was near Loma Prieta Peak in the Santa Cruz Mountains. The magnitude 6.9 quake was the most powerful the state had experienced in several years.
How long was the Bay Bridge closed in 1989?
about a monthThe Bay Bridge had lost one section of the upper deck during the quake and was closed for about a month while the California Department of Transportation made repairs.
How far away was the 1989 San Francisco earthquake felt?
Magnitude established at 6.9 after consultation with monitoring stations around the world. The Loma Prieta quake was felt as far away as San Diego and western Nevada.
When did SF burn down?
Shows the aftermath of the San Francisco earthquake of April 18, 1906, and the devastation resulting from the subsequent three-day fire. The earthquake struck at 5:12 a.m. San Francisco, with thousands of unreinforced brick buildings, and closely-spaced wooden Victorian dwellings, was poorly prepared for a major fire.
Did the 1989 San Francisco earthquake cause a tsunami?
Abstract. We investigated the tsunami recorded at Monterey, California, during the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake (MW=6.9). The first arrival of the tsunami was about 10 min after the origin time of the earthquake.
Where was the 1989 World Series earthquake?
Remarkably, the earthquake struck just before the start of the third game of the 1989 World Series, which was to be played in San Francisco’s Candlestick Park between the two Bay Area baseball teams, the San Francisco Giants and the Oakland Athletics. The disaster’s occurrence during a major live television broadcast meant that news ...
When was the San Francisco earthquake?
( A Britannica Publishing Partner) See all videos for this article. San Francisco earthquake of 1989, also called Loma Prieta earthquake, major earthquake that struck the San Francisco Bay Area, California, U.S., on October 17, 1989, and caused 63 deaths, ...
What did the Loma Prieta earthquake teach us?
Listen to what the Loma Prieta earthquake of 1989 taught about seismology, early warning system, earthquake preparedness and the role of the Berkeley seismology lab. A discussion of the lessons learned from the Loma Prieta (San Francisco–Oakland) earthquake of 1989. Displayed by permission of The Regents of the University of California.
How many people died in the 1989 earthquake?
The quake struck with a moment magnitude of 6.9 on October 17, just before the start of the third game of the World Series, which was being held at San Francisco's Candlestick Park. Sixty-three people died, and nearly 3,800 were injured.
What happened to Santa Cruz in 1989?
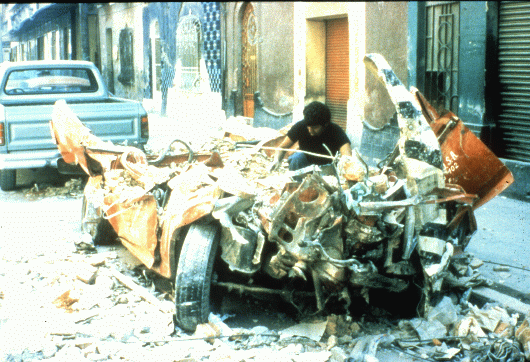
Damaged buildings in Santa Cruz, California, following the San Francisco-Oakland earthquake of 1989. C.E. Meyer/U.S. Geological Survey. The earthquake significantly damaged the transportation system of the Bay Area. The collapse of the Cypress Street Viaduct (Nimitz Freeway) caused most of the earthquake-related deaths.
What was the hardest hit area in San Francisco?
San Francisco’s Marina district was particularly hard hit because it had been built on filled land (comprising loose, sandy soil), and the unreinforced masonry buildings in Santa Cruz (many of which were 50 to 100 years old) failed completely. San Francisco-Oakland earthquake of 1989.
What causes earthquakes?
Earthquake, any sudden shaking of the ground caused by the passage of seismic waves through Earth’s rocks. Seismic waves are produced when some form of energy stored in Earth’s crust is suddenly released, usually when masses of rock straining against one another suddenly fracture and “slip.” Earthquakes occur most often…
When did the San Andreas earthquake occur?
The Loma Prieta segment of the San Andreas Fault System had been relatively inactive since the 1906 San Francisco earthquake (to the degree that it was designated a seismic gap) until two moderate foreshocks occurred in June 1988 and again in August 1989.
How many buildings were destroyed in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake?
In Santa Cruz, the Pacific Garden Mall was severely damaged, with falling debris killing three people, half of the six earthquake deaths in Santa Cruz and Monterey Counties. Some 31 buildings were damaged enough to warrant demolition, seven of which had been listed in the Santa Cruz Historic Building Survey. The four oldest were built in 1894, the five oldest withstood the 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
How many people died in the Loma Prieta earthquake?
63 killed, 3,757 injured. The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake occurred on California's Central Coast on October 17 at 5:04 p.m. local time. The shock was centered in The Forest of Nisene Marks State Park in Santa Cruz County, approximately 10 mi (16 km) northeast of Santa Cruz on a section of the San Andreas Fault System and was named for ...
How did the earthquake affect the Bay Area?
Not only did the quake force seismic retrofitting of all Bay Area bridges, it caused enough damage that some parts of the region's freeway system had to be demolished. Damage to the region's transportation system was estimated at $1.8 billion (equivalent to $3.8 billion today).
What station was on the air after the earthquake?
About an hour and 40 minutes after the quake, Fox affiliate KTVU resumed broadcasting, with their news anchors, Dennis Richmond and Elaine Corral reporting from the station's parking lot. KCBS-AM ( CBS News Radio) switched immediately to backup power and managed to stay on air despite a subsequent generator failure.
How many people lost power in the San Francisco earthquake?
An estimated 1.4 million people lost power following the quake, mainly due to damaged electrical substations. Many San Francisco radio and television stations were temporarily knocked off the air. KGO-TV, the local ABC station in San Francisco, was off the air for about 15 minutes, while KRON-TV (at the time the region's NBC affiliate) was off the air for about half an hour, and KGO-AM ( ABC News Radio) was off the air for about 40 minutes. About an hour and 40 minutes after the quake, Fox affiliate KTVU resumed broadcasting, with their news anchors, Dennis Richmond and Elaine Corral reporting from the station's parking lot. KCBS-AM ( CBS News Radio) switched immediately to backup power and managed to stay on air despite a subsequent generator failure. KCBS later won a Peabody Award for their news coverage, as did KGO-TV.
Where did the ML 5.3 earthquake occur?
The ML 5.3 June 1988 and the M L 5.4 August 1989 events also occurred on previously unknown oblique reverse faults and were within 3 mi (4.8 km) of the M6.9 Loma Prieta mainshock epicenter, near the intersection of the San Andreas and Sargent faults. Total displacement for these shocks was relatively small (approximately 4 in (100 mm) of strike-slip and substantially less reverse-slip) and although they occurred on separate faults and well before the mainshock, a group of seismologists considered these to be foreshocks due to their location in space and time relative to the main event. Each event's aftershock sequence and effect on stress drop was closely examined, and their study indicated that the shocks affected the mainshock's rupture process. Following the August 8, 1989 shock, in anticipation of an upcoming large earthquake, staff at the University of California, Santa Cruz deployed four accelerometers in the area, which were positioned at the UCSC campus, two residences in Santa Cruz, and a home in Los Gatos. Unlike other nearby (high gain) seismographs that were overwhelmed (driven off scale) by the large magnitude mainshock, the four accelerometers captured a useful record of the main event and more than half an hour of the early aftershock activity.
What happened in 1989 in San Francisco?
San Francisco Earthquake: History and Facts About the 1989 Loma Prieta Quake. Discover interesting facts about the 1989 Loma Prieta San Francisco Earthquake, also known as the World Series Quake. Loma Prieta is one of two famous quakes in SF. The other one is the 1906 earthquake.
How many people died in the San Francisco earthquake?
Overall there were 63 deaths from this San Francisco earthquake. In addition, there were over 3,500 injuries and over 8,000 people became homeless. Significant structural damage also occurred. It is estimated that around 1,300 buildings were destroyed, and 20,000 buildings were damaged.
What was the second most devastating earthquake in San Francisco?
They have first-hand accounts of what it was like during the shaking and what it took to rebuild after each one. The 1989 Loma Prieta San Francisco earthquake was the second most devastating earthquake in SF's history. Visit the SF 1906 Earthquake page to learn more about the other famous San Francisco earthquake or visit the What Causes Quakes?
When did the Loma Prieta earthquake happen?
The Loma Prieta quake hit the bay area on the evening of October 17, 1989 at 5:04pm. It measured a 6.9 on the Richter Scale. This one originated on the San Andreas fault in the Santa Cruz mountains. It got its name from the mountain where the shaking started, Loma Prieta.
What happened after the 1906 earthquake?
After the Shock. As with the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, fires began to break out in the city after it hit. The main area that was impacted was the Marina District . This district in the city is built on landfill, not hard stone or rock.
What time was the 1989 World Series?
Game three of the 1989 World Series was just getting started in SF that night. It was scheduled to begin at 5:15pm and the live broadcast had just begun. This one was caught on film and is the only major quake to be broadcast live on TV. It's also interesting to note that the World Series that year was between the two bay area teams: The Giants ...
Why was the freeway torn down in the city of San Francisco?
After this one, the only freeway running through the city had to be torn down due to damage from the quake. The freeway ran along the waterfront on the eastern side of the city.
How many people died in the San Francisco earthquake?
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake hit the San Francisco Bay Area, killing 67 people, injuring 3,757, leaving more than 12,000 homeless, and causing more than $5 billion in damages. Despite the fact it was one of the most powerful and destructive quakes ever to hit a populated area of the United States, the death toll was fortunately relatively small. At least 27 fires broke out across the City, including a major blaze in the Marina District where apartment buildings sank into a lagoon filled with bay mud in preparation for the Panama-Pacific International Exposition of 1915. Dozens of people were rescued by firefighters from fallen buildings in the area that were imperiled by the flames. As they also had done in 1906, SF citizens formed a bucket brigade to help firefighters who were without water because of broken mains.
What was the crisis of the earthquake?
What the crisis of the earthquake engendered was a shared urgency in which the usual cultural divisions, including racial alienation, were sometimes temporarily upended. This breif experience of unusual solidarity was rooted in our shared experience of surviving a disaster together. In my situation it happened to be most striking via the momentary erasure of prevailing racial alienation. But such strong (and transient) bonds of solidarity happened in literally thousands of different little ways throughout San Francisco among people from all walks of life. It was one of the unexpected benefits to arise from a time of crisis. A week later it was all gone. But that was one glorious week to live in San Francisco.
Who wrote the essay on the aftermath of the 1906 earthquake?
I had long forgotten that memory until I recently read William James account of the aftermath of SF's 1906 earthquake. He wrote an essay entitled: "On Some Mental Effects of the Earthquake", that was published on June 7, 1906 in the journal Youth's Companion. One passage by James, in particular, spoke directly to what I experienced some 83 years later at the intersection of 18th and Dolores:

Overview
The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake occurred on California's Central Coast on October 17 at 5:04 p.m. local time. The shock was centered in The Forest of Nisene Marks State Park in Santa Cruz County, approximately 10 mi (16 km) northeast of Santa Cruz on a section of the San Andreas Fault System and was named for the nearby Loma Prieta Peak in the Santa Cruz Mountains. With an Mw magnitude …
Background
The history of earthquake investigations in California has been largely focused on the San Andreas Fault system because of its strong influence in the state as the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate; it is the most studied fault on Earth. Andrew Lawson, a geologist from the University of California, Berkeley, had named the fault after the San Andreas Lake (prior to th…
Earthquake
The Loma Prieta earthquake was named for Loma Prieta Peak in the Santa Cruz Mountains, which lies just to the east of the mainshock epicenter. The duration of the heaviest shaking in the Santa Cruz Mountains was about 15 seconds, but strong ground motion recordings revealed that the duration of shaking was not uniform throughout the affected area (because of different types and thicknes…
Damage
The earthquake caused severe damage in some very specific locations in the Bay Area, most notably on unstable soil in San Francisco and Oakland. Oakland City Hall was evacuated after the earthquake until a US$80 million (equivalent to US$175 million today) seismic retrofit and hazard abatement work was completed in 1995. Many other communities sustained severe damage throug…
1989 World Series and television coverage of earthquake
The 1989 World Series featured the Oakland Athletics and the San Francisco Giants in the first cross-town World Series since 1956. Game 3 of the series was scheduled to begin at San Francisco's Candlestick Park on October 17 at 5:35 PDT, and American TV network ABC began its pre-game show at 5:00 PDT. When the quake struck at approximately 5:04 PDT, sportscaster Tim McCarver was narrating taped highlights of Game 2, which had been played two days prior acros…
In popular culture
The earthquake is featured in films and television shows:
• The events in the TV sitcom Full House episode "Aftershocks" (December 8, 1989) take place following the Loma Prieta earthquake; it centers on 7-year-old Stephanie Tanner having a hard time telling her father Danny about how she fears another aftershock might happen and kill him (since he is a widowed sin…
See also
• 1906 San Francisco earthquake
• 1992 Landers earthquake
• 1994 Northridge earthquake
• 1999 Hector Mine earthquake
External links
• The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.
• A film clip "Loma Prieta Earthquake, ca. 1989" is available at the Internet Archive
• "October 17, 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake – United States Geological Survey".