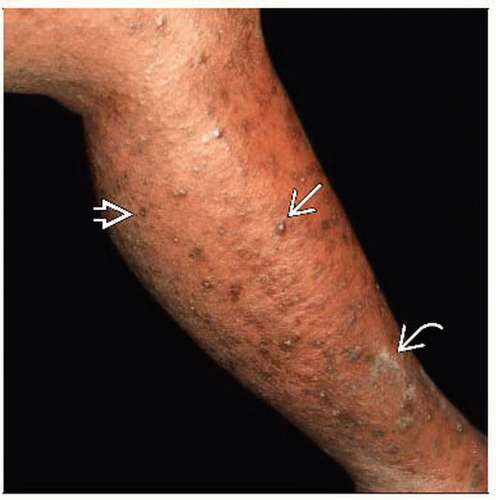
What are the three functions of lymph nodes?
The lymphatic system has three functions:
- The removal of excess fluids from body tissues.
- Absorption of fatty acids and subsequent transport of fat, chyle, to the circulatory system.
- Production of immune cells (such as lymphocytes, monocytes, and antibody producing cells called plasma cells).
Is a lymph node considered to be an organ?
Organs of the Immune System: Lymph Nodes. Among the organs that contribute to our immune response, there are two categories: primary lymphoid organs and secondary lymphoid organs. Lymph nodes are considered secondary lymphoid organs, along with the spleen. Shaped like beans, they contain lymphocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells.
What size should lymph nodes be?
They are always changing size. A lymph node in the neck can be anywhere from 1-2cm and still that would be quite normal in size. If you are concerned about the current size of the lymph nodes in your neck and worried about a particular disease it would be better to have an experienced clinician feel them.
What structure carries lymph into a lymph node?
structure. bean-shaped; less than 2.5cm long. afferent. lymphatic vessels- more of these "going toward" brings lymph into lymph node. efferent. Lymphatic vessels - only two of these; quotation going away; carries filtered lymph out of lymph node; exit at hilum. hilum.

Are lymph nodes epithelial tissue?
Most of the lymphocytes enter the lymph nodes via blood vessels, and about 10% enter through the lymph. The structure of the post-capillary venule, in the deep cortex (paracortex) is unusual in that it is not lined by simple squamous epithelium, but by a simple cuboidal epithelium.
What is the lymph connective tissue?
It consists of connective tissue formed of reticular fibers, with various types of leukocytes (white blood cells), mostly lymphocytes enmeshed in it, through which the lymph passes. Regions of the lymphoid tissue that are densely packed with lymphocytes are known as lymphoid follicles.
Is lymph tissue a connective tissue?
Lymph is a clear fluid that is similar to plasma but contains less protein. It flows through lymphatic vessels throughout the body and includes chemicals and cells whose composition varies according to location within the body. Despite being a fluid, lymph is classified as a connective tissue.
What are components of lymph?
Lymph contains water, proteins, salts, lipids, white blood cells, and other substances that must be returned to the blood.
What type of connective tissue is blood and lymph?
Fluid Connective TissueFluid Connective Tissue Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues. Cells circulate in a liquid extracellular matrix.
What are the 4 main types of connective tissues?
The extracellular matrix between the cells usually includes fibers of one or more types embedded in an amorphous ground substance. Connective tissues are classified into four classes: BLOOD, BONE, CARTILAGE, CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER.
What is the most common cell type in the lymphoid tissue?
Subscribe Now. The most common cell type in the lymphoid tissue is the lymphocyte. Like macrophages, lymphocytes are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and then circulated in the blood to the lymphoid tissue. T lymphocytes mature in the thymus before proceeding to the other lymphoid organs, such as the spleen.
What is the lymphoid tissue?
In the spleen (a soft, purplish organ lying high in the abdomen), the lymphoid tissue is a cylinder of loosely organized cells surrounding small arteries. In the bone marrow this tissue is mixed with the blood-forming cells, and no organization is apparent.
What is the role of lymphoid tissue in cancer?
Lymphoid tissue has a central role in metastasis, the process by which cancer cells spread to tissues distant from the site of tumour origin. This is due largely to the proximity of lymph vessels to tumour masses in organs or other tissues of the body.
What type of cells are included in the lymphoid system?
Most nodules appear and disappear in response to local needs. Several types of cells are included in the lymphoid system—for example, reticular cells and white blood cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes.
Where do T lymphocytes mature?
T lymphocytes mature in the thymus before proceeding to the other lymphoid organs, such as the spleen. B lymphocytes mature in the bone marrow and proceed directly to the lymphoid organs. Both kinds play a key role in immune responses to infectious microorganisms.
What is the lymphatic system?
lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body by collecting excess fluid and particulate matter from tissues and depositing them in the bloodstream. It also…
How do macrophages help?
Macrophages help eliminate invaders by engulfing foreign materials and initiating the immune response. These cells may be fixed in one place, such as lymph nodes, or they may wander in the loose connective-tissue spaces. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
What is the connective tissue capsule in the lymph node?
Additionally, there is a pericapsular adipose tissue layer that surrounds the connective tissue capsule. This layer contains arterioles and venules that supply the lymph node. The lymph node is divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Histological staining of the node reveals that the cortex stains darker than the medulla with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) due to its higher cell content. The cortex contains lymphoid nodules, which are non-encapsulated, spherical collections of lymphocytes. Beneath the fibrous capsule is the subcapsular sinus. The subcapsular sinus receives afferent lymphatic ducts at intervals that deposit lymphatic fluid in the space. The subcapsular sinus communicates with the cortical sinuses that travel parallel to the capsular trabeculation. They carry lymph to the medullary sinus.
How do efferent lymphatic vessels enter the lymph node?
Afferent lymphatic vessels enter the lymph node through the capsule peripherally and efferent lymphatic vessels leave the node via the hilum. The former takes lymph from peripheral sites to the node, while the latter takes processed lymph from the nodes back to the venous circulation. Lymphatic system Explore study unit.
What is the indentation on the surface of a lymph node?
The node is enclosed in a capsule and has an indentation on one surface (along one of its long axes) known as the hilum. The hilum is the point at which arteries carrying nutrients and lymphocytes enter the lymph node and veins leave it.
What is lymph node tissue?
Introduction to lymph nodes. Lymphoid tissues are collections of lymphocytes strategically located at potential sites of infection. They can be classified as either primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow and thymus) where de novo synthesis and maturation of lymphocytes occur; or secondary lymphoid organs where activation of lymphocytes occur. ...
How many lymph nodes are there in the body?
The average young adult has about 450 lymph nodes throughout the body; most of which are in the abdominopelvic region, then the thorax and the remainder in the head and neck. This article will focus on the anatomy and histology of lymph nodes, their various locations and clinically relevant points.
Why do sentinel lymph nodes biopsy?
As a result, clinicians are more inclined to perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy in order to help diagnose and stage individuals suspected to have cancer.
How many groups are there in the axillary lymph nodes?
Subsequently, axillary nodes have been divided into five groups: apical.
What is the lymphatic system?
lymphatic system: Lymph nodes. The lymph nodes, or lymph glands, are small, encapsulated bean-shaped structures composed of lymphatic tissue. Thousands of lymph nodes... Each lymph node is divided into two general regions, the capsule and the cortex. The capsule is an outer layer of connective tissue. Underlying the capsule is the cortex, ...
What are the structural divisions of lymph nodes?
Most of the lymphocytes within a node are “naive”—i.e., they have yet to encounter antigen—and therefore must migrate to regions where they will be most effective in recognizing foreign agents.
What are the HEVs?
HEVs contain a single layer of large endothelial cells that possess surface receptors specific for B and T lymphocytes. As these cells pass through the HEVs, they bind to the receptors and are carried into the paracortex of the lymph node. The structural divisions within a lymph node serve different purposes.
How do cells enter lymph nodes?
Cells enter the lymph node through two primary routes. Lymph and its associated cells enter through the afferent lymphatic vessels, which drain into each node through its convex surface. These vessels may drain directly from the lymphatic capillaries, or they may be connected to a previous node.
What is the name of the small, bean-shaped masses of lymphoid tissue enclosed by a capsule of?
Alternative Title: lymph gland. Lymph node, any of the small, bean-shaped masses of lymphoid tissue enclosed by a capsule of connective tissue that occur in association with the lymphatic vessels. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph nodes serve as filters for the blood, providing specialized tissues where foreign antigens can be trapped ...
Where do activated lymphocytes enter the lymphatic system?
All activated lymphocytes migrate through the medulla and enter the lymphatic circulation through the efferent lymphatic vessel, which drains either into adjacent lymph nodes or ultimately into the thoracic duct, a major vessel of the lymphatic system.
Where do B cells enter the paracortex?
B cells enter the paracortex through the HEVs and then migrate into the outer cortex and join specialized dendritic cells and macrophages to form follicles. Primary follicles consist of a resting B cell surrounded by a loose network of dendritic cells.
When should I call my doctor about an issue with my lymphatic system?
Call your doctor if you experience fatigue (extreme tiredness) or have unexplained swelling that lasts more than a few weeks or interferes with your daily activities .
What is the lymphatic system?
Overview. The lymphatic system is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work together to move lymph back into your your bloodstream. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system.
What system collects excess fluid from cells and tissue throughout the body?
Maintains fluid levels in your body: As just described, the lymphatic system collects excess fluid that drains from cells and tissue throughout your body and returns it to your bloodstream, which is then recirculated through your body.
How to check if lymphatic system is working?
To see if your lymphatic system is working as it should, your doctor may use imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI. These tests allow your doctor to see blockages in your lymphatic system.
Which ducts are used to collect lymph?
Collecting ducts: Lymphatic vessels empty the lymph into the right lymphatic duct and left lymphatic duct (also called the thoracic duct). These ducts connect to the subclavian vein, which returns lymph to your bloodstream. The subclavian vein runs below your collarbone.
How much plasma does the body use?
Some 20 liters of plasma flow through your body’s arteries and smaller arteriole blood vessels and capillaries every day. After delivering nutrients to the body’s cells and tissues and receiving their waste products, about 17 liters are returned to the circulation by way of veins. The remaining three liters seep through the capillaries and into your body’s tissues. The lymphatic system collects this excess fluid, now called lymph, from tissues in your body and moves it along until it's ultimately returned to your bloodstream.
Where are lymph nodes located?
A few of the more familiar locations of lymph nodes are in your armpit, groin and neck. Lymph nodes are connected to others by the lymphatic vessels.·.
Spreading to lymph nodes helps cancer metastasize
The researchers first asked whether cancer in the lymph nodes of mice helps tumors metastasize to the lungs, one of the most common places cancer spreads to.
Cancer cells dodge attack on the way to lymph nodes
Next, the researchers asked what gives some melanoma cells the ability to spread to the lymph nodes.
Cancer highjacks the immune system
The researchers also explored what happens once cancer gets to the lymph nodes. Similar to what other studies have found, it appears that when cancer cells arrive, they shift the amounts and types of immune cells in the lymph nodes.
A new view of cancer metastasis
In the lymph nodes, immune cells learn what to attack (such as infected cells) and what to protect (such as healthy cells).
What is the function of OSSEOUS TISSUE?
OSSEOUS TISSUE; the hard outer layer of the bone. Function: provides support to the body and protects the organs.
Which tissue is often well vascularized and contains an extracellular matrix?
Epithelial tissues are often well vascularized and contain an extracellular matrix.
Where is the dense connected tissue located?
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE; found in the valves of the heart, dermis of the skin, periosteum. Function: provides strength to resist forces applied from many directions; helps prevent overexpansion of organs such as the bladder.
Where is muscle tissue located?
Muscle tissue is located in the brain, spinal cord and nerves.
Where are small lymphoid aggregates?
Small lymphoid aggregates in the esophagus. Lymphoid tissue accumulating with age in the stomach. Peyer's patches in the small intestine. Diffusely distributed lymphoid cells and plasma cells in the lamina propria of the gut. Intraepithelial lymphocytes ( IELs) interspersed into epithelial layer of mucosal surfaces.
Where is the underlying layer of loose connective tissue located?
These are located at the bottom of the crypts and release a number of antibacterial substances, among them lysozyme, and are thought to be involved in the control of infections. Underneath them, there is an underlying layer of loose connective tissue called lamina propria.
What is the role of gut-associated lymphoid cells?
They are of different origins and follow different maturation processes but share the same GALT role – to rapidly respond to pathogens and secrete effector cytokines. Such multi-layered protection systems highlights the susceptibility of mucosal sites to invading agents. The mucosal route is the most frequent way for entering of pathogenic infections into the host. Robust engagement of a variety of lymphoid cells patrolling the epithelial layer also reflects evolutionary pressure and arms race between immune systems and pathogens escaping its control.
What is the structure of the intestinal mucosa?
In order to increase the surface area for absorption, the intestinal mucosa is made up of finger-like projections ( villi ), covered by a monolayer of epithelial cells, which separates the GALT from ...
Which tissue acts as an interface between the immune system and incoming antigens?
The following examples comprise lymphoid tissues that act as interfaces between immune system and incoming antigens either as food antigens or as pathogenic or commensal microbiota´s antigens: Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. Small lymphoid aggregates in the esophagus. Lymphoid tissue accumulating with age in the stomach.
Where is lymphatic circulation?
There is also lymphatic circulation through the tissue connected to the mesenteric lymph nodes . Both GALT and mesenteric lymph nodes are sites where the immune response is started due to the presence of immune cells through the epithelial cells and the lamina propria .
Where are antigen presenting cells found?
Majority of antigen presenting cells (APCs) in intestine is derived from macrophages , which have very quick turnover. Macrophages are prevalent in lamina propria and submucosal deeper layers like muscularis layer. Macrophages can use their trans-epithelial dendrites (long cytoplasmic extensions) and directly contact epithelial layer and sample luminal bacteria. Under healthy conditions macrophages engulf commensal bacteria and surrounding cellular debris, secrete IL-10, drive maturation of Treg and contribute to tissue homeostasis. Because of low expression of innate response receptors and co-stimulatory surface molecules, intestinal macrophages do not initiate inflammation. But upon infection or inflammation, the profile of macrophages changes and they start to secrete large amounts of TNF- α and become proinflammatory effector cells.
What are the three types of tissue?
Three types of this tissue include skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
What type of tissue attaches bones to bones?
Cord-like tissues that attach bones to bones
Does connective tissue have blood vessels?
This tissue contains no blood vessels and depends upon underlying connective tissue to supply its need for oxygen and nutrients
Which organs have epithelium?
Epithelium that lines the ducts and tubules of many organs, including the kidneys
Where is the symlink found?
This tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
