
Examples of Polygenic Traits
- Height. Human height is controlled by many genes; in fact, there are over 400 genes related to height, and all of these genes interact to make up a person’s phenotype.
- Skin Color. In humans, skin color is influenced by many things, but the pigment melanin influences most of a person’s phenotype.
- Eye Color. There are 2 major human eye color genes, OCA2 and HERC2, but at least 13 other genes also play a role.
Which traits are polygenic select three options?
What are the 3 types of natural selection quizlet?
- Stabilizing Selection. average form of a trait is favored.
- Directional Selection. one extreme form of a trait is favored.
- Diversifying Selection. both extremes of a trait are favored over an average form of a trait.
What is polygenic characteristics?
Polygenic characteristics are both: Polygenic traits are quantitative, meaning they have continuous variation. This results in a spread of traits that looks like a bell curve on a graph. For example, height, eye color, and skin color are all polygenic traits.
What are the characteristics of traits?
What Are Character Traits?
- Core Values vs. Character Traits. Note: For more on this topic, see this ultimate guide to core values. ...
- Personality Traits vs. Character Traits. ...
- Internal vs. External Character Traits. ...
- Character Traits Definition (Recap) Character traits are ALL the micro-habits of thought and action that define “what” you do. ...
What is polygenic phenotype?
While a polygenic phenotype can occur without epistasis, if you have epistasis you must be dealing with a polygenic phenotype. Polygenic just means that there are multiple genes involved in a phenotype. Epistasis refers to situations where one allele masks the phenotypic effect of one or more alleles of another gene. (10 votes)
Which is an example of polygenic inheritance in humans?
Some examples of polygenic inheritance are: human skin and eye color; height, weight and inteligence in people; and kernel color of wheat.
Why are most human traits polygenic?
Human features like height, eye color, and hair color come in lots of slightly different forms because they are controlled by many genes, each of which contributes some amount to the overall phenotype.
How many polygenic traits make up humans?
We leveraged genome-wide summary statistics for 870 polygenic traits and attempted to quantify signals of selection on traits of different forms in European ancestry across four periods in human history and evolution. We found that 88% of these traits underwent polygenic change in the past 2,000–3,000 years.
What are three examples of polygenic?
Three examples of polygenic traits in humans are height, skin colour and eye colour. These traits are governed by multiple genes.
Which trait is polygenic in humans quizlet?
Human height, eye and hair color are examples of polygenic traits. Skin color is another polygenic trait for humans and a variety of other animals.
Which of the following human traits is not a polygenic trait?
Blood type AB in humans, for instance, is not a polygenic trait.
Is skin tone a polygenic trait?
Skin color is also a polygenic trait, as are hair and eye color. Polygenic inheritance often results in a bell shaped curve when you analyze the population (Figure below).
Is hair color a polygenic trait?
The term polygenic means “many genes.” Therefore, a polygenic trait is influenced by many genes that work together to produce the phenotype. Human phenotypes such as hair color, eye color, height, and weight are examples of polygenic traits.
Is weight a polygenic trait?
Although often attributed to unhealthy lifestyle choices or environmental factors, obesity is known to be heritable and highly polygenic – the majority of inherited susceptibility is related to the cumulative impact of many common DNA variants.
Is intelligence a polygenic trait?
Intelligence Is a Polygenic Trait These findings show that intelligence is a highly polygenic trait where many different genes would exert extremely small, if any, influence, most probably at different stages of development.
How do you identify a polygenic trait?
Usually, traits are polygenic when there is wide variation in the trait. For example, humans can be many different sizes. Height is a polygenic trait, controlled by at least three genes with six alleles. If you are dominant for all of the alleles for height, then you will be very tall.
What is a polygenic trait quizlet?
a trait that is controlled by several pairs of genes; different combinations of all the genes contribute to the trait in varying degrees.
Why might polygenic traits vary more in phenotype than do single gene traits?
Why might polygenic traits vary more in phenotype than do single gene traits? Polygenic traits are controlled by two or more genes, so there are more combination of alleles leading to multiple phenotypes.
How are polygenic traits different from traits that only require 2 genes?
8) How are polygenic traits different from traits that only require 2 genes? The polygenic traits have a wide variation in each trait. 9) Why do you think that some children are taller than their parents? The children can have more tall genes than either parent.
What is a polygenic trait quizlet?
a trait that is controlled by several pairs of genes; different combinations of all the genes contribute to the trait in varying degrees.
What does polygenic mean in psychology?
an attribute that is determined by numerous genes rather than only one. An example is a person's height.
What are examples of polygenic traits?
Two example of polygenic traits and height and skin color. Each are controlled by multiple genes, each with multiple alleles and produce a wide co...
What is meant by polygenic inheritance?
Polygenic inheritance occurs when more than one gene, and thus multiple alleles, control expression of a trait. Polygenic inheritance produces tra...
What are characteristics of polygenic traits?
Some characteristics of polygenetic traits are that they are quantitative and appear on a spectrum, such as height. They are also multifactorial a...
What is a polygenic pattern?
A polygenic pattern is a type of inheritance pattern where one trait is controlled by multiple genes. Each gene has multiple alleles and creates a...
What is polygenic traits?
Polygenic Traits Definition. Polygenic traits are traits that are controlled by multiple genes instead of just one. The genes that control them may be located near each other or even on separate chromosomes. Because multiple genes are involved, polygenic traits do not follow Mendel’s pattern of inheritance. Instead of being measured discretely, ...
Why are polygenic traits not inherited?
Because multiple genes are involved, polygenic traits do not follow Mendel’s pattern of inheritance. Instead of being measured discretely, they are often represented as a range of continuous variation. Some examples of polygenic traits are height, skin color, eye color, and hair color.
What are the two traits that are represented by only one gene?
This is because each trait was represented by only one gene which had two alleles: dominant and recessive. If a plant had two dominant alleles, or one dominant and one recessive allele, the flowers were purple, while if it had two recessive alleles, the flowers were white. Polygenic traits also have dominant and recessive alleles, ...
What is the basic unit of heredity?
Gene – The basic unit of heredity; made up of DNA, it is transferred by parent to offspring and codes for a specific part of the offspring’s phenotype. Allele – A certain variant of a gene . Melanin – A pigment in skin, hair, and eyes that affects its color. Phenotype – Any part of an organism’s physical appearance.
How many genes are involved in height?
Height. Human height is controlled by many genes; in fact, there are over 400 genes related to height, and all of these genes interact to make up a person’s phenotype. This is a very large number, but it makes sense because height is a compilation of the lengths of many different body parts, such as leg bones, the torso, and even the neck. ...
Why do people have green eyes?
Green eyes are caused by multiple factors; they are the result of a light brown iris combined with a blue tone given by light scattering.
How does the eye color of a person determine the color of their eyes?
A person’s eye color is determined by the pigmentation of their irises, but also by the way the cells in their irises scatter light.
What are some examples of polygenic traits?
Examples of polygenic traits include skin color, eye color, hair color, body shape, height, and weight.
What is the distribution of polygenic traits?
Polygenic Traits Distribution. Polygenic traits tend to result in a distribution that resembles a bell-shaped curve, with few at the extremes and most in the middle. In polygenic inheritance, the genes contributing to a trait have equal influence and the alleles for the gene have an additive effect.
What is polygenic inheritance?
Polygenic traits may express several different phenotypes, or displayed characteristics. Polygenic inheritance is a type of incomplete dominance inheritance, where the expressed phenotypes are a mixture of inherited traits.
What is polygenic distribution?
Polygenic traits tend to have a bell-shaped distribution in a population. Most individuals inherit various combinations of dominant and recessive alleles. These individuals fall in the middle range of the curve, which represents the average range for a particular trait.
What color does a dominant allele produce?
Having all dominant alleles results in black eye color. The presence of at least two dominant alleles produces the black or brown color. The presence of one dominant allele produces the green color, while having no dominant alleles results in blue eye color.
How many genes are involved in skin color?
This trait is determined by at least three genes and other genes are also thought to influence skin color. Skin color is determined by the amount of the dark color pigment melanin in the skin. The genes that determine skin color have two alleles each and are found on different chromosomes .
What color is dominant in gene 1?
In this example, the allele for black color (B) is dominant to the recessive blue color (b) for gene 1. For gene 2, the dark hue (G) is dominant and produces a green color. The lighter hue (g) is recessive and produces a light color. This cross would result in five basic phenotypes and nine genotypes .
What is a Polygenic Trait?
A polygenic trait is a trait in which the phenotype is controlled by more than one gene. Phenotype is the physical or behavioral traits of an organism, whereas their genotype is the genetic makeup and specific combination of genes and alleles present. Polygenic characteristics are both:
Genetic Inheritance
Genetic inheritance is the way that people inherit their traits. All diploid organisms inherit two sets of chromosomes, one set from the maternal parent and one set from the paternal parent. In humans, each person gets 23 chromosomes from their mom and 23 chromosomes from their dad.
Monogenic Traits and Mendelian Inheritance
Monogenetic traits are traits that are controlled by a single gene. These genes are typically inherited with two alleles, one which is dominant and masks the other, called the recessive allele. This type of inheritance pattern is called Mendelian Inheritance after the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel.
What is a Polygenic Trait?
A polygenic trait is one in which a number of non-allelic genes play a role. These sorts of genes are referred to as polygenes. They are a collection of genes that, when activated, express as a single unit. Each of these has an influence on the characteristics as a whole.
Polygenic Trait Etymology
The phrase polygenic derives from the words poly, which means “many,” and genic, which means “of genes.”
How are polygenic traits determined?
Polygenic traits are determined by the interactions between several different genes, which display incomplete dominance. 2. How many different allele combinations can possibly be produced from two parents that are heterozygous for a polygenic trait controlled by three different genes with two allele pairs? A. 5. B. 7.
What are the physical traits that are controlled by polygenic inheritance?
Because of the inheritance mode patterns, the physical traits that are controlled by polygenic inheritance, such as hair color, height and skin color, as well as the non-visible traits such as blood pressure, intelligence, autism and longevity, occur on a continuous gradient, with many variations of quantifiable increments.
What is the probability of the second lightest skin tones?
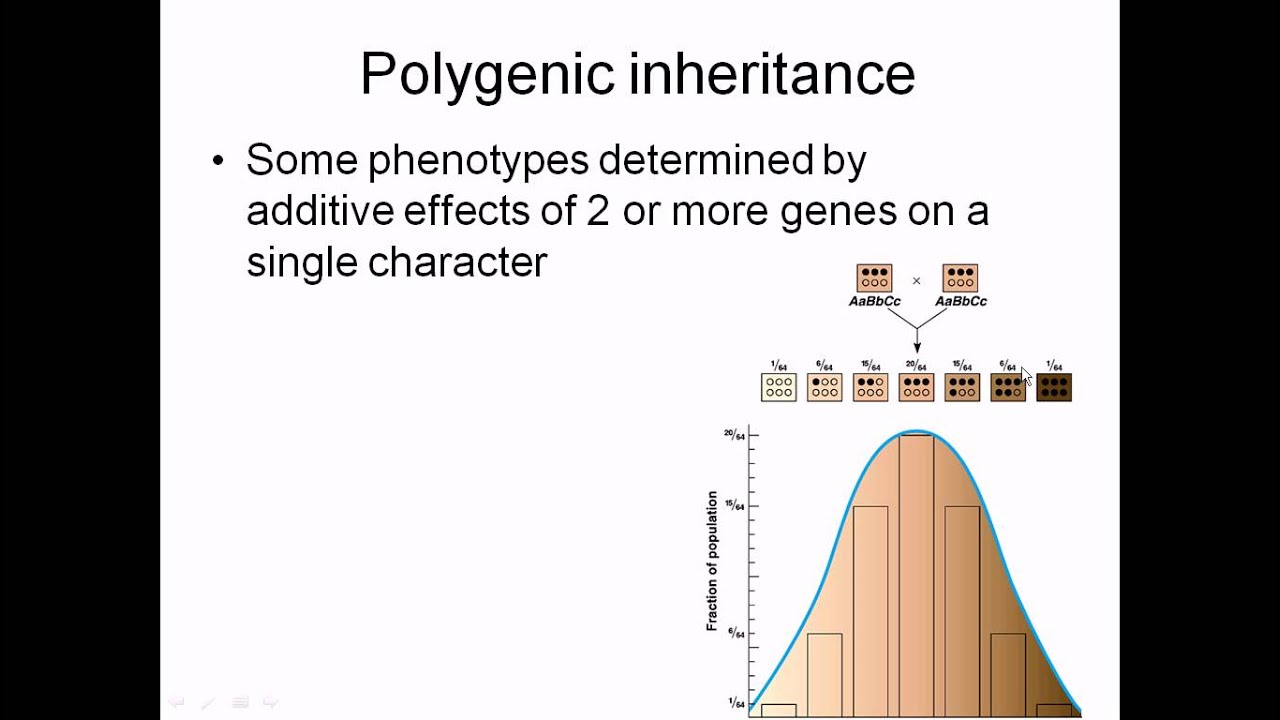
As the number of contributing alleles changes within the allele combinations, the units of melanin pigment increases and decreases; the probability of the second lightest or darkest skin tones (1 or 5) is 6/64, the third lightest or darkest skin tones (2 or 4), is 15/64 and an entirely intermediate skin tone (3) is the most common at 20/64.
What is additive effect in polygenic inheritance?
It is important to remember here that in polygenic inheritance, alleles do not display dominance over others, rather, each contributing allele gives an additive effect rather than a masking effect, and so the way that the alleles interact is different to those in Mendelian genetics. The additive effect means that each contributing allele produces ...
What is polygenic inheritance?
Polygenic inheritance, also known as quantitative inheritance, refers to a single inherited phenotypic trait that is controlled by two or more different genes. In a system which differs from Mendelian Genetics, where monogenic traits are determined by the different alleles of a single gene, ...
What is the pigment that controls skin color?
The pigment melanin is responsible for dark coloration in the skin and there are at least three genes, which control for human skin color. Using a hypothetical example where the production of melanin is controlled by contributing alleles (denoted here as A, B and C), resulting in dark skin color, and therefore light skin color is produced by non contributing alleles (denoted here as a, b and c), it is possible to see how the spectrum of different skin colors can result in the offspring.
What is the lightest skin tone?
The lightest skin tone, 0 (aabbcc), which lacks any alleles contribu ting melanin pigment , or the darkest skin tone, 6 (AABBCC), which contains all possible contributing alleles; each of these phenotypes occurs at a probability of 1/64.
