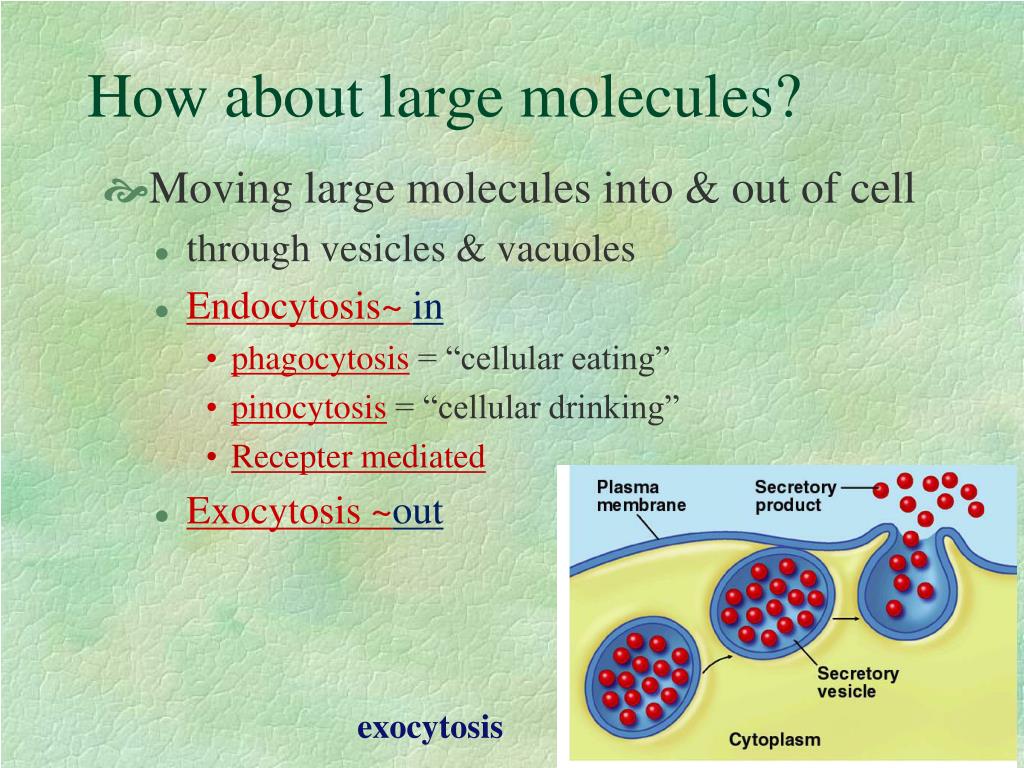
What is the transporter of simple diffusion?
Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes.
What is the transport of diffusion?
Diffusion is a passive process of transport. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. You are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air.
Where is diffusion transported by?
In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into (or out of) the cell by moving down it.
What are the 3 types of transports?
The different modes of transport are air, water, and land transport, which includes rails or railways, road and off-road transport.
What is an example of diffusion transport?
Examples of Diffusion: Examples of diffusion include perfume filling a whole room and the movement of small molecules across a cell membrane. One of the simplest demonstrations of diffusion is adding a drop of food coloring to water. Although other transport processes do occur, diffusion is the key player.
What is the diffusion short answer?
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration . Diffusion occurs in liquids and gases when their particles collide randomly and spread out. Diffusion is an important process for living things - it is how substances move in and out of cells.
What are the 4 types of transport?
Air, Road, Sea and Rail. These are the four major modes of transport (or types) in the logistics industry.
What are 4 examples of diffusion?
Some examples of diffusion that occurs in our daily life are given below.The smell of perfumes/Incense Sticks.Opening the Soda/Cold Drinks bottle and the CO2 diffuses in the air.Dipping the tea bags in hot water will diffuse the tea in hot water.Small dust particles or smoke diffuse into the air and cause air pollution.More items...
What is simple diffusion?
Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules through a cell membrane without using the channels formed by integral membrane protein. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules through those channels. Comment on Sarah King's post “Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules thro...”. Button opens signup modal.
What is facilitated diffusion?
In facilitated diffusion, molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. A concentration gradient exists for these molecules, so they have the potential to diffuse into (or out of) the cell by moving down it.
How do molecules move through the cell?
Molecules can move through the cell’s cytosol by diffusion, and some molecules also diffuse across the plasma membrane (as shown in the picture above). Each individual substance in a solution or space has its own concentration gradient, independent of the concentration gradients of other materials, and will diffuse according to that gradient. Other factors being equal, a stronger concentration gradient (larger concentration difference between regions) results in faster diffusion. Thus, in a single cell, there can be different rates and directions of diffusion for different molecules. For example, oxygen might move into the cell by diffusion, while at the same time, carbon dioxide might move out in obedience to its own concentration gradient.
How do molecules move down concentration gradients?
In cells, some molecules can move down their concentration gradients by crossing the lipid portion of the membrane directly , while others must pass through membrane proteins in a process called facilitated diffusion. Here, we’ll look in more detail at membrane permeability and different modes of passive transport.
What is the purpose of the cell membrane in airport security?
Cell membranes are selectively permeable, regulating which substances can pass through, as well as how much of each substance can enter or exit at a given time. Selective permeability is essential to cells’ ability to obtain nutrients, eliminate wastes, and maintain a stable interior environment different than that of the surroundings (maintain homeostasis).
What is the simplest form of transport?
The simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. A concentration gradient is a just a region of space over which the concentration of a substance changes, ...
What is the role of the opening and closing of the ion channels in the cell?
The opening and closing of these channels, and the resulting shifts in ion levels inside the cell, play an important role in electrical transmission along membranes (in nerve cells) and in muscle contraction (in muscle cells).
How does diffusion occur?
It is the process in which solutes are passed through the concentration gradient in a solution across a semipermeable membrane. The assistance of membrane proteins is not required in this process of diffusion wherein substances move from higher concentration to lower. The process is conducted by the actions of hydrogen bonds which form between solutes and water molecules. Molecules of water move in to surround the solute molecules that maximizes hydrogen bonding.
Why do bacteria need simple diffusion?
It may use facilitated diffusion for the transportation of most of the nutrients , it depends on simple diffusion to pass water, oxygen and small nutrients to the cytoplasm. In its cells, there are no special organelles to transport or hold substances, hence bacteria depend on simple diffusion of substances in the cell to make sure that matter is found in it for reaction to regulate its life processes.
What is the spontaneous gross diffusion or movement of solvent molecules?
It is the spontaneous gross diffusion or movement of solvent molecules via a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water potential to a region of lower water potential in the direction which has a tendency for equalizing concentrations of solute on both sides. It can be described as a physical phenomena wherein any solvent moves through a selectively permeable membrane which separates two solutions of varying concentrations.
What is facilitated diffusion?
Molecules in facilitated diffusion diffuse across the plasma membrane with aid from the membrane proteins such as the carrier and channels. A concentration gradient is seen in these molecules for it has the potential for diffusing into cells by moving down them. But, as they are polar or charged, it cannot cross the phospholipid part of the membrane with no assistance. The facilitated transport proteins protect such molecules from the hydrophobic core of the membrane rendering a path through which it can cross. Carrier proteins and channels are the two broad classes of facilitated transport proteins.
What is the process of moving molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration?
A substance tends to move from a region of high concentration in diffusion to a region of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. The total movement of molecules in and out of the more concentrated region and into the lesser concentrated one is till the concentration is equal. Such a process does not require any input of energy. A concentration gradient itself is a form of stored energy, which is utilized as concentrations tend to equalize.
What is the chief mode of water movement in and out of cells?
Osmosis renders a chief mode by which water is moved in and out of the cells. The turgor pressure of cells is majorly maintained by osmosis across the cell membrane between the interior of the cell and its comparative hypotonic ambience.
Where does active transport occur?
The process of active transportation necessitates cellular energy in order to move. Active transportation commonly occurs in root hair cells, walls of the small intestine (villi) etc.
What Is Simple Diffusion?
In a solution or gas that has an area of high numbers of particles and an area of lower numbers of particles, the particles will diffuse, or move, from the area of higher to the area of lower concentration. This is known as simple diffusion, or passive diffusion.
What molecules use simple diffusion?
Molecules in water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethanol, and urea use simple diffusion to travel in and out of cell membranes along the concentration gradient using random motion instead of energy. Learn more about the definition of simple diffusion through various examples of the process, such as the lungs removing carbon dioxide. Updated: 09/23/2021
What is the difference between a membrane and a diffusion membrane?
Therefore, a membrane is classified as permeable (which means things can pass through it), impermeable (which means things can't pass through it), or semi permeable (which means things can pass through it by diffusion). In the case of simple diffusion, the membrane is semi permeable, which means the particles or solutes can pass through it by random motion.
What is the process of solutes moving through a solution called?
So, let's put it all together. Concentration gradient is the process by which particles, which are sometimes called solutes, move through a solution or gas from an area of higher number of particles to an area of lower number of particles. The actual movement is called diffusion. Solutes moving through a solution or a gas happen by random motion along the concentration gradient until there are equal numbers of particles in the two areas.
What molecules can be used to travel through the cell membrane?
In the cell, examples of molecules that can use simple diffusion to travel in and out of the cell membrane are water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethanol and urea . They pass directly through the cell membrane without energy along the concentration gradient. With what you have learned so far, what would be the reason for these molecules to move either into or out of the cell? The answer is that the molecules either in the cell or outside the cell have higher concentration in numbers.
How many types of diffusion are there?
There are actually three types of diffusion. We've been talking about simple diffusion (also known as passive diffusion), but there's also facilitative diffusion and active transport. We will only go into detail about the focus of this lesson: simple diffusion.
How to see diffusion?
An easy way to see simple diffusion in action is to drop food coloring into a cup of water. If you have ever done this, you have likely noticed that the food coloring is concentrated when dropped into the cup of water. However, as a few seconds pass, the particles become lighter in color as they move to the lower concentration level. Again, this happens without energy, which is why it is known as passive diffusion.
How to demonstrate diffusion?
By filling a jar to the brim with ink, capping it, placing it at the bottom of a water bucket, and then carefully removing the cap, you can demonstrate diffusion . The ink molecules will spread out of the jar until the bucket and jar have a uniform concentration. This uniformity in molecular concentration is a kind of equilibrium.
How do ions diffuse across the cell membrane?
One of the simplest ways for a substance to diffuse across a cell membrane is through a channel, as ions do. Ions are solutes (substances dissolved in water) with an unequal number of protons and electrons. Those with large amounts of protons are charged positively and are called cations. Ions with more electrons are charged negatively and referred to as anions. Since they are charged, the ions interact well with polar molecules such as water but are repelled by a phospholipid bilayer's non - polar interior. Therefore, ions cannot move between the cytoplasm of a cell and the extracellular without the assistance of membrane transport proteins. Ion channels have an interior that is hydrated and spans the membrane. Ions can diffuse in either direction through the channel without coming in contact with the hydrophobic tails of the membrane phospholipids, and the transported ions do not bind or interact with the channel proteins. The ions ' net movement direction is determined by two conditions: their relative concentrations on either side of the membrane, and the voltage across the membrane. Each of the channel types is specific to a specific ion, such as calcium (Ca++) or chloride (Cl–), or in some cases to a few ion types. Ionic channels play an essential role in the nervous system signalling.
What is the transporter of glucose in red blood cells?
Another important facilitated transport carrier in red blood cells is the glucose transporter. RBC keep their internal concentration of glucose low through a chemical trick: they immediately add a phosphate group to any entering glucose molecule, converting it to a highly charged glucose phosphate that cannot pass back across the membrane. This maintains a steep concentration gradient for glucose, favouring its entry into the cell. Instead, the transmembrane protein appears to bind the glucose and then flip its shape, dragging the glucose through the bilayer and releasing it on the inside of the plasma membrane. Once it releases the glucose, the glucose transporter reverts to its original shape. Figure 1 describes the difference between simple transport and facilitated transport.
What is facilitated transport?
Facilitated Transport. Many cell - needed molecules, including glucose and other sources of energy, are polar and cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer's nonpolar interior. These molecules enter the cell in the plasma membrane through specific channels. The inside of the channel is polar and thus “friendly” to the polar molecules, ...
Why do molecules diffuse through the plasma membrane?
It tends to uniformly distribute substances. Membrane transport proteins allow diffusion through the plasma membrane only for certain molecules and ions. Diffusion occurs because of the free energy of molecules; that is, they are always in motion. The molecules in a solid move very slowly; those in a liquid move faster;
What is selective channel transport?
The characteristic of selective channel transport is that its rate is saturable. In other words, if a substance's concentration gradient is gradually increased, it will also increase its transport rate to a certain point and then level off. Further gradient increases will not result in any additional rate increases. The scientific explanation for this kind of observation is that the membrane contains a limited number of carriers.
What is the process of a substance moving in water?
This random motion causes these substances to move neatly from regions where their concentration is high to regions where their concentration is lower, a process called diffusion.Net diffusion-driven movement will continue until the concentrations are ...

Simple Diffusion Definition
Principle of Simple Diffusion
- How does simple diffusion work?
Image Source: Khan Academy 1. In free diffusion through a membrane, the solute particles move about by random Brownian motion, like that in free solution. 2. The solute flux, which is a measurable and reproducible quantity, is essentially the result of these separate motions. 3. Eve… - Diffusion of electrolytes
1. The principle for the diffusion of charged species is driven by an additional force along with the concentration gradient. 2. Charged solutes are subject to electrical forces when electrostatic potential gradients are present. 3. Accordingly, the driving force for electrolyte transport is the gr…
Factors Affecting Simple Diffusion
- Because the rate of diffusion is determined by several parameters, these parameters/factors affect the mechanism of diffusion. 1. Concentration gradient 1. The concentration gradient across a biological membrane is the driving force for the diffusion of a nonelectrolyte. 2. Therefore, the higher the concentration difference across the membrane, the higher will be the rate of diffusion…
Examples of Simple Diffusion
- Oxygen and Carbon dioxide
1. One of the classic examples of simple diffusion is the movement of gases across the membrane in animals. 2. Oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood is exchanged by the process of simple diffusion. 3. Depending on the concentration gradient of these gases in the cells, the dire… - Movement of waste materials
1. In animals, the removal of waste materials occurs via simple diffusion. 2. In the liver, waste material, urea, is excreted onto the blood by the process f simple diffusion. 3. Similarly, in kidneys, removal of waste chemicals and toxins and absorption of water occurs via simple diffusion. A se…
Application of Simple Diffusion
- The concept of simple diffusion is applied in various fields like the food, medicine, and environment 1. In beverages like tea and soda, the diffusion of gases and chemicals from tea leaves plays a vital role in the development of the particular taste. 2. The process of simple diffusion is applied in the action of medicines in the body. Once a medicine is ingested, the mole…
References
- Friedman, M. (2008). Principles and models of biological transport. Springer.
- https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-diffusion.html
- https://biologydictionary.net/simple-diffusion/
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Introductory_and_General_Biology/Book%3A_General…
Sources
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/electrochemical-potential
- 1% – https://www.quora.com/What-are-some-factors-that-affect-the-rate-of-diffusion
- 1% – https://socratic.org/questions/what-factors-affect-the-rate-of-diffusion-2
- 1% – https://sciencing.com/four-things-affect-rate-diffusion-8348637.html