What is the van der Waals equation for bonds?
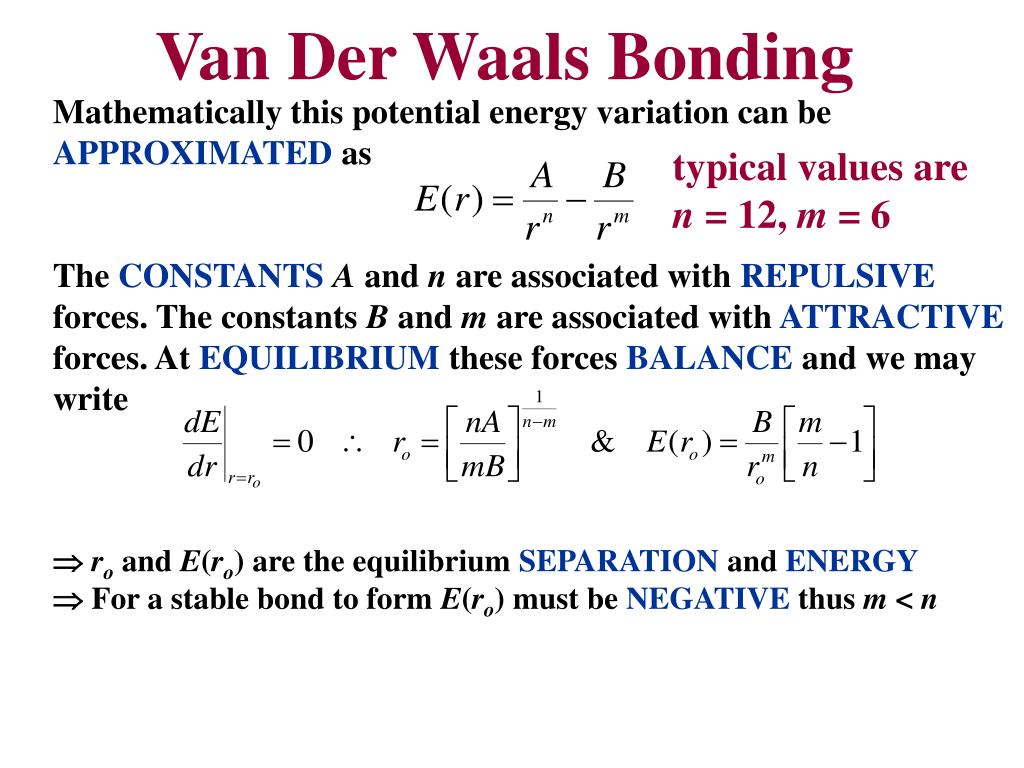
Equation of Van Der Waal Bonds The Van Der Waals equation is a state that shows two properties of gases, such as the excluded volume of real gases and its attractive forces. It gets expressed as: (P+n2a/V2) (V-nb)= nRT
Is a van der Waals bond found in minerals?
The van der Waals’ weak bond ties neutral molecules into a lattice and is the weakest of the chemical bonds. This type of bond is not often found in minerals. An example is the mineral graphite, which consists of covalent bonded sheets of carbon atoms linked only by van der Waals’ bonds.
What is the difference between covalent and Van der Waals bonding?
They differ from covalent and ionic bonding in that they are caused by correlations in the fluctuating polarizations of nearby particles (a consequence of quantum dynamics). Click to see full answer. Keeping this in consideration, is Van der Waals a chemical bond?
Is H-bond a van der Waals force?
I'm a physics grad student. From my understanding, H-bond is not what people typically mean by van der waals force. H-bond is just basic dipole-dipole interaction with essentially fixed dipole moments (the dipoles are simple result of difference of electronegativity within each molecule).
Is van der Waals an ionic bond?
Definition. Van der Waals forces include attraction and repulsions between atoms, molecules, and surfaces, as well as other intermolecular forces. They differ from covalent and ionic bonding in that they are caused by correlations in the fluctuating polarizations of nearby particles (a consequence of quantum dynamics).
Is van der Waals a chemical bond?
Van der Waals forces are distance-dependent forces between atoms and molecules not associated with covalent or ionic chemical bonds. Sometimes the term is used to encompass all intermolecular forces, although some scientists only include among them the London dispersion force, Debye force, and Keesom force.
Is van der Waals a secondary bond?
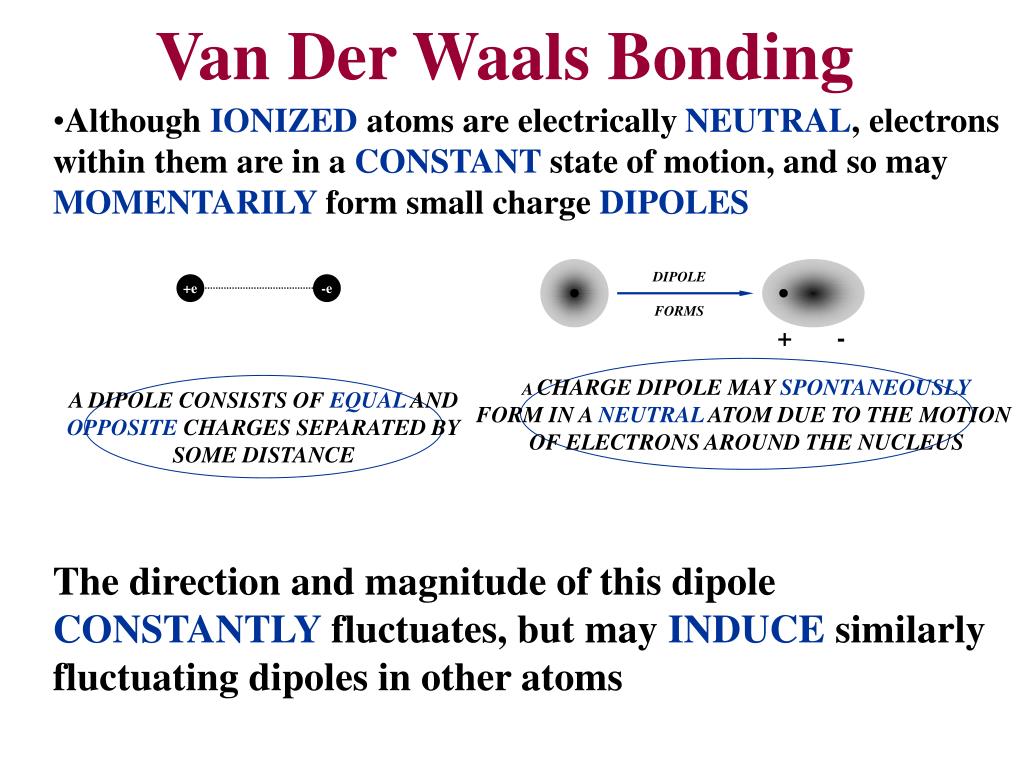
This is the type of bonding present in N2 molecules, and is known as Van Der Waals Bonding. Secondary bonding may also exist when there is a permanent dipole in a molecule due to an asymmetrical arrangement of positive and negative regions.
Is van der Waals a polar covalent bond?
Some molecules form areas of positive and negative charge formed through an uneven sharing of electrons (polar covalent bonding).
Are van der Waals forces intermolecular or intramolecular?
Van der Waals forces are a category of intermolecular forces that includes London dispersion and dipole-dipole interactions. Some sources also consider hydrogen bonding to be a Van der Waals force.
Are van der Waals and hydrogen bonds the same?
Hydrogen bonding is the third type of van der Waals' forces. It is exactly the same as dipole-dipole interaction, it just gets a special name. A hydrogen bond is a dipole dipole interaction that occurs between any molecule with a bond between a hydrogen atom and any of oxygen/fluorine/nitrogen.
What are the secondary types of bonding?
The three types of secondary bonding are van der Waals forces, permanent dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Bonding influences a molecule or compound's shape, structure and properties.
What are primary bonds What are secondary bonds?
Primary bonds are formed when the bonding process involves a transfer or sharing of electrons. Secondary bonds are formed from the subtle attraction forces between positive and negative charges. There is no transfer or sharing of electrons involved in a secondary bond.
What are the types of primary bonds?
There are three primary types of bonding: ionic, covalent, and metallic.Ionic bonding.Covalent bonding.Metallic bonding.
What are considered van der Waals?
What are Van der Waals Forces? Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that are dependent on the distance between atoms or molecules. These forces arise from the interactions between uncharged atoms/molecules.
Do polar molecules have van der Waals forces?
Van der Waals forces are weak interactions between molecules that involve dipoles. Polar molecules have permanent dipole-dipole interactions. Nonpolar molecules can interact by way of London dispersion forces.
How do you describe van der Waals?
3:3510:38Van Der Waals Forces - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo these two they will feel a force of attraction that accelerates them and so these forces thatMoreSo these two they will feel a force of attraction that accelerates them and so these forces that attracts these atoms together they're known collectively as the Vander Waal forces also known as the
1. How Do You Define Hydrogen Bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of dipole interaction and are unique. When a hydrogen atom binds to an atom of a strongly electronegative element such as...
2. What are the Types of Van Der Waals Forces?
There are three types of Van Der Waal forces- Dispersion Forces or London Dispersion forces Dipole-Dipole ForcesHydrogen Bond
3. What Kind of Force is there Between Nonpolar Molecules?
Between nonpolar molecules, you will find dispersion forces.
4. Write the Relative Strengths of the Intermolecular Forces.
Intermolecular Force Relative Strength Dipole-Dipole forceMedium London Dispersion forceWeakest Hydrogen Bond Strongest
5. What Factors Can Affect the Van Der Waals Forces?
There are 3 factors that can have an effect on Van Der Waals forces such as - Number of electrons present in an atomSize and shape of the atom Natu...
What type of interaction is Van der Waals?
Van der Waals forces can develop due to the following types of interactions: Interaction between two permanent dipoles (as in hydrochloric acid, for example) Interaction between a permanent dipole and an uncharged atom/molecule (causes the formation of an induced dipole)
What are Van der Waals forces?
Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that are dependent on the distance between atoms or molecules. These forces arise from the interactions between uncharged atoms/molecules. For example, Van der Waals forces can arise from the fluctuation in the polarizations of two particles that are close to each other.
What is the weakest intermolecular force?
Induced electrical interactions between two or more atoms or molecules that are very near to each other produce Van der Waals forces. The Van der Waals interaction is the weakest of all the intermolecular forces that hold molecules together.
What causes debye forces?
Debye forces are caused by the interactions between permanent dipoles and other atoms/molecules, which results in the formation of induced dipoles. For example, an induced dipole can be formed from the repulsive forces between electrons (belonging to a molecule) and a permanent dipole.
Why do dispersion forces occur?
London dispersion forces arise due to the interactions between an instantaneous dipole and an atom/molecule. These forces are named after the German physicist Fritz London and are also known as instantaneous dipole – induced dipole forces.
Which molecules tend to have stronger dispersion forces?
2. Shape of the Molecule. Long, unbranched molecules tend to feature stronger dispersion forces than branched, short-chain molecules. For example, the structural isomers butane and isobutane (2-methyl propane) have different boiling points despite having the same chemical formulae.
What are the factors that affect Van der Waals forces?
Factors Affecting Van der Waals Forces. 1. Number of Electrons Held by the Atoms/Molecules. While traversing down a group in the modern periodic table, the atomic radii of the elements increase along with the number of electrons held by their respective nuclei.
Who discovered the Van der Waals bond?
As a segment of molecular physics, these forces came into existence from the name of a Dutch Scientist, Johannes Diderik Van Der Waals. In 1873, he first discovered the Van Der Waals bond while working on a theory on real gases. Let us explore to study more about them!
What are Van der Waals forces?
In simple words, Van Der Waals Forces are those bonds that play the role of attracting both molecules and atoms. These interactions include weak electrostatic forces lying in a close range within molecules lacking charges. Moreover, they are the weakest intermolecular forces, comprising of dipole-dipole and dispersion forces.
What is Van der Waals dispersion force?
Van Der Waals dispersion forces are close-knit interactions depending on distance resulting in intermolecular attractions or repulsions. These bonds get stronger when they lie in a range of 0.4 kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) and 4 kJ/mol. Moreover, they are active within a distance of fewer than 0.6 nanometers (nm).
What is London dispersion force?
London Dispersion Forces: These bonds are weakest attractive bonds, resulting from temporary and induced dipoles present in various atoms and molecules. They form when electrons present in two adjacent atoms occupy temporary positions. They are also known as dipole-induced dipole attraction.
What are the factors that affect Van der Waals forces?
The factors affecting Van Der Waals forces are as follows: Number of Electrons Present In An Atom: The amount of electrons present is responsible for the creation of temporary dipoles. The strength of the Waals forces depends on the number of dipoles. Therefore, an increase in the number of dipoles increases the bonds of Van Der Waals.
How strong is hydrogen bond?
The strength of a hydrogen bond ranges within 4 kJ/mol and 50 kJ/mol. A hydrogen atom in a molecule gets attracted to other N, F and O atoms. However, only N, O and F atoms in one molecule can form hydrogen bonds. A Vanderwaal Force example of hydrogen bonds is the interaction of water molecules.
Do Van der Waal forces arise from electronic bonds?
In comparison to most of the ionic and covalent bonds, these interactions do not arise from an electronic bond. The Van Der Waal forces include attractions within various atoms, resulting from influenced dipoles.
What is van der Waals force?
In molecular physics, the Van der Waals force, named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance.
What are dispersion forces?
London dispersion forces, named after the German-American physicist Fritz London, are weak intermolecular forces that arise from the interactive forces between instantaneous multipoles in molecules without permanent multipole moments. In and between organic molecules the multitude of contacts can lead to larger contribution of dispersive attraction, particularly in the presence of heteroatoms. London dispersion forces are also known as ' dispersion forces', 'London forces', or 'instantaneous dipole–induced dipole forces'. The strength of London dispersion forces is proportional to the polarizability of the molecule, which in turn depends on the total number of electrons and the area over which they are spread. Hydrocarbons display small dispersive contributions, the presence of heteroatoms lead to increased LD forces as function of their polarizability, e.g. in the sequence RI>RBr>RCl>RF. In absence of solvents weakly polarizable hydrocarbons form crystals due to dispersive forces; their sublimation heat is a measure of the dispersive interaction.
Is Van der Waals attraction greater than temperature?
Van der Waals attraction is greater if the molecules are closer. Van der Waals forces are independent of temperature except for dipole – dipole interactions.
What type of bonding does Van der Waals use?
Types of Van Der Waals Bonding. The Waals’s interactions depend on three types of forces, such as London forces, dipole-dipole and hydrogen bonding. They are based on the type of bonding they share within molecules or atoms. These include:
What are Van der Waals forces?
Van Der Waals forces are the interactions between atoms and molecules that result in a pull between them. These forces comprise of weak intermolecular interacting with each the nearest possible distance. The molecules do not contain any charge. These interactions or bonds comprise of three types, such as dipole-dipole, ...
What is the Waals force?
Ans. The Waals forces are the interactions occurring between two or more molecules or atoms due to their attraction. These weak forces attract neutral molecules with the other ones in gases.
What is London dispersion force?
London dispersion force form a vital component of the Waals bond. It arises due to the interaction between non-polar or polar molecules. Debye force also acts as a key contributor in the Waals forces. It is accountable for the occurrence of attractions between molecules containing an induced and permanent polarity.
What forces are responsible for dipole bonds?
The dispersion forces are also responsible for creating dipole-induced dipole bonds. These bonds occur when electrons available within two adjoining atoms take interim positions. They are also accountable for condensation of non-polar materials into liquids, and freezing of solid when the temperature drops.
What are the three types of bonds that form in Waals?
The molecules do not contain any charge. These interactions or bonds comprise of three types, such as dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonds and London dispersion forces. Their formation depends on the type of bonding between molecules. The concept of Waals’ interactions is vast.
How far away do Van der Waals repel?
However, their pull tend to repel when situated at a distance less or within 0.4 nanometers (nm). Mostly, they appear to be highly active when they get situated at a space of less than 0.6 nanometers. Try reading the below pointers to gain knowledge about the components of Van Der Waals bonding. They are as follows:

What Are Van Der Waals Forces?
Characteristics of Van Der Waals Forces
- Covalent bondsand ionic bonds are significantly stronger than Van der Waals forces
- These forces are additive in nature, they are made up of several individual interactions
- These forces cannot be saturated
- No directional characteristic can be attributed to these forces
Types of Van Der Waals Forces
- 1. Keesom Interactions
Keesom interactions can arise due to the following interactions (all of which are electrostatic in nature): 1. The electrostatic interaction between the charges in ionic molecules. 2. Interaction between dipoles in polar molecules. 3. Quadrupole interactions in the molecules whose symmet… - 2. Debye Forces
Debye forces are caused by the interactions between permanent dipoles and other atoms/molecules, which results in the formation of induced dipoles. For example, an induced dipole can be formed from the repulsive forces between electrons (belonging to a molecule) an…
Factors Affecting Van Der Waals Forces
- 1. Number of Electrons Held by the Atoms/Molecules
While traversing down a group in the modern periodic table, the atomic radii of the elements increase along with the number of electrons held by their respective nuclei. The presence of a relatively large number of electrons (along with the additional space for these electrons to dispe… - 2. Shape of the Molecule
Long, unbranched molecules tend to feature stronger dispersion forces than branched, short-chain molecules. For example, the structural isomers butane and isobutane (2-methyl propane) have different boiling points despite having the same chemical formulae. The boiling point of bu…
Applications of Van Der Waals Forces
- It is widely believed that Geckos exploit Van der Waals forces hanging on to smooth surfaces with only their toes.
- The attractive forces that arise between the spatulae of the Gecko’s footpads and the smooth surface enable the lizard to effectively climb these surfaces. Similar biological designs can be observe...