Can HCC cancer be cured?
If caught early, it can sometimes be cured with surgery or transplant. In more advanced cases it can't be cured, but treatment and support can help you live longer and better.
Is HCC an aggressive cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy, resulting as the third cause of death by cancer each year. The management of patients with HCC is complex, as both the tumour stage and any underlying liver disease must be considered conjointly.
Is HCC a fast growing cancer?
In the beginning, hepatocellular carcinoma grows very slowly. It can take years before you notice any symptoms.
What is the most common cause of HCC?
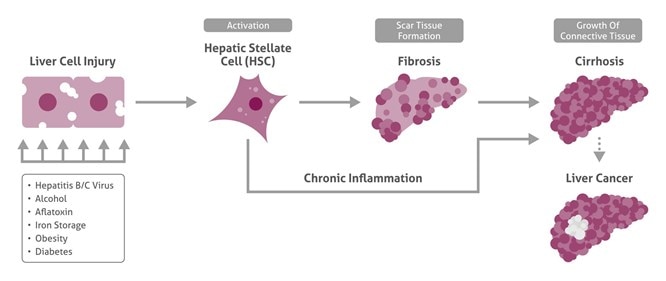
Chronic viral hepatitis In the US, infection with hepatitis C is the more common cause of HCC, while in Asia and developing countries, hepatitis B is more common. People infected with both viruses have a high risk of developing chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
What is the survival rate of HCC?
Unfortunately, HCC is typically diagnosed late in its course, with a median survival following diagnosis of approximately 6 to 20 months. In the United States, 2 years survival is less than 50% and 5-year survival is only 10%.
How quickly does HCC progress?
It takes 10 years to develop chronic hepatitis, 20 years to develop cirrhosis and 30 years to develop HCC which explains why it usually affects patients in the 50–70-year age group [12]. Macroscopically, HCC can be solitary or multifocal, nodular or diffuse.
Does HCC liver cancer spread?
Liver cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. When cancer does this, it is called metastasis. But even if a liver cancer spreads to your bones, it is still called and treated like a liver cancer, not bone cancer.
Can chemo get rid of liver cancer?
Chemotherapy (chemo) is treatment with drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemo may be an option for people whose liver cancer cannot be treated with surgery, has not responded to local therapies such as ablation or embolization, or when targeted therapy is no longer helpful.
What does HCC mean after a diagnosis?
Hierarchical Condition CategoriesHCCs, or Hierarchical Condition Categories, are sets of medical codes that are linked to specific clinical diagnoses.
What is the best treatment for HCC?
Orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) is an effective treatment for both HCC and underlying cirrhosis, and is considered the best therapeutic option.
What is end stage HCC?
Patients with end stage or terminal HCC are those presenting with tumors leading to a very poor Performance Status (ECOG 3–4) or Child–Pugh C patients with tumors beyond the transplantation threshold. Among HCC patients, 15–20% present with end stage or terminal stage HCC. Their median survival is less than 3–4 months.
How long can you live with Stage 4 HCC?
In one small study of people with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma, those whose liver cancer had spread to their lymph nodes or distant organs had an average survival rate of 4 and 11 months, depending on the severity of their liver damage and whether they received treatment.
What are the stages of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Based on these variables, patients are classified into three stages (I: not advanced; II: moderately advanced; III: very advanced) with different outcomes [Table 2]. Okuda staging system was accepted and widely used as an improved classification system for HCC.
Does HCC spread?
HCC is the most common primary liver malignancy with a high risk of metastasis. HCC hematogenous spread occurs via the lymphatic route or by direct invasion resulting in intrahepatic as well as extrahepatic metastasis [2].
What causes HCC liver cancer?
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the major form of liver cancer. Risk factors for HCC include chronic HBV (hepatitis B virus) and HCV (hepatitis C virus) infections, autoimmune hepatitis, chronic alcohol use, obesity and diabetes mellitus etc [2].
Is hepatocellular carcinoma slow growing?
Growth speed of small HCC is significantly related to histological differentiation of tumors: a slow-growing HCC tends to be well-differentiated and a rapid-growing HCC moderately- or poorly-differentiated.
What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is cancer in your liver. Although it is a life-threatening illness, catching it early can mean successful treatment with surgery or a liver transplant. Other treatments focus on easing your symptoms and helping you to live longer. People at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma should have regular checks for signs of cancer.
What age is more likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma?
Men ages 60 and older are more likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma than women and younger men.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of liver cancer. It is a serious illness that can be life-threatening. If it diagnosed early, hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated with surgery to remove the cancerous tumor or with a liver transplant. Other treatments can shrink the tumor or slow its growth and relieve your symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma is linked to cirrhosis of the liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD ). People who have cirrhosis or NAFLD should be regularly checked for signs of hepatocellular carcinoma.
How long does it take for hepatocellular carcinoma to grow?
In the beginning, hepatocellular carcinoma grows very slowly. It can take years before you notice any symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma growth speeds up as it progresses.
How to cure a tumor in the liver?
Surgery to remove your tumor or a liver transplant are the best options for a cure. If surgery is not an option, there are other treatments to ease your symptoms, slow the tumor’s growth and help you to live longer.
When were you born with hepatitis C?
You were born from 1945 through 1965. Most people in the United State who have hepatitis C were born in these years.
Can you get hepatocellular cancer if you smoke?
If you have or have had any of these illnesses, talk to your healthcare provider about being screened for hepatocellular cancer. If you smoke, have obesity or drink a lot of alcohol, your provider can help you improve your health and decrease your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
How to treat HCC?
Nonsurgical treatments are the most common way to ease symptoms and slow down disease progression in people with HCC. Your doctor may recommend ablation (destruction) of liver tumors. Ablation can be done via: an ethanol injection. burning the cancer cells.
What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a type of liver cancer that begins in the hepatocytes, the main type of liver cell. worldwide every year. It often occurs in people with a history of chronic liver diseases, like cirrhosis. Symptoms often don’t appear until the later stages of the cancer. Here are some common symptoms of HCC, ...
How do you know if you have HCC?
Symptoms of HCC include: jaundice. pain. weight loss. swelling in the abdomen. However, signs of the disease often don’t become noticeable until the disease has reached an advanced state. If you think you may have HCC, talk to your doctor right away. They can order tests to make a diagnosis.
How long does it take to live with HCC?
The median survival rate is typically between 6 and 20 months after diagnosis. The 2-year survival rate is below 50 percent for people with HCC in the United States. The 5-year survival rate is 10 percent.
When do symptoms of cancer appear?
Symptoms often don’t appear until the later stages of the cancer.
Can HCC cause nausea?
Nausea. Nausea or feelings of queasiness is a common symptom of HCC. A number of other conditions can also cause nausea, though, so it’s difficult to tell if it’s your liver causing trouble from this symptom alone.
Can liver cancer show up sooner?
Most of the time, people with liver cancer don’t notice symptoms until the disease progresses into later stages. However, it’s possible for signs to show up sooner. Here are some of the most common symptoms of HCC.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma – The most common form of primary liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma develops in liver tissues and occurs primarily in individuals with a chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis B or C.
What is the name of the cancer that moves bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine?
Cholangiocarcinoma – Also known as bile duct cancer, cholangiocarcinoma is a relatively uncommon and aggressive malignancy that forms in the thin tubes that move bile from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine.
What is the name of the cancer that affects infants and young children?
Hepatoblastoma – A rare cancer that primarily affects infants and young children, hepatoblastoma cells are similar to fetal liver cells and usually bind together to form a large and painful liver mass. Sometimes, the cancer promotes the release of hormones that result in early puberty.
What are the two main types of liver cancer?
There are two main types of liver cancer: primary liver cancer, which originates in the liver , and secondary liver cancer , which spreads to the liver after developing in another area of the body.
Where does hepatic angiosarcoma originate?
Hepatic angiosarcoma – An uncommon and aggressive malignancy, hepatic angiosarcoma originates in the blood vessels of the liver.
Is liver cancer metastatic?
For instance, if colorectal cancer spreads to the liver, the liver tumor is classified as metastatic colorectal cancer, not liver cancer. In addition to metastatic colorectal cancer, some common types of secondary liver cancer include:
What are the signs and symptoms of HCC?
The most common and earliest symptom of hepatocellular carcinoma is hepatosplenomegaly, which is associated with pain in the abdomen. Jaundice is a late sign of hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma depends on whether the cancer is localized or advanced.
What is the HCC cell?
HCC starts in the main type of liver cells, called hepatocellular cells. Most cases of HCC are the result of infection with hepatitis B or C, or cirrhosis of the liver caused by alcoholism. Fibrolamellar HCC is a rare type of HCC that is typically more responsive to treatment than other types of liver cancer.
How many cases of liver cancer are caused by HCC?
HCC is thought to account for about three-fourths of all liver cancer cases.
What are the different types of liver cancer?
Liver cancer has several types, each based on the type of cells that becomes cancerous. They include: 1 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), also called hepatoma, is the most common type of liver cancer, accounting for approximately 75 percent of all liver cancers. HCC starts in the main type of liver cells, called hepatocellular cells. Most cases of HCC are the result of infection with hepatitis B or C, or cirrhosis of the liver caused by alcoholism. 2 Fibrolamellar HCC is a rare type of HCC that is typically more responsive to treatment than other types of liver cancer. 3 Cholangiocarcinoma ( bile duct cancer) occurs in the small, tube-like bile ducts within the liver that carry bile to the gallbladder. Cholangiocarcinomas account for 10-20 percent of all liver cancers. Intrahepatic bile duct cancer begins in ducts located in the liver. Extrahepatic bile duct cancer develops in ducts outside the liver. 4 Angiosarcoma, also called hemangiocarcinoma, accounts for about 1 percent of all liver cancers. Angiosarcomas begin in the blood vessels of the liver and grow quickly. They are typically diagnosed at an advanced stage. 5 Secondary liver cancer, also known as a liver metastasis, develops when primary cancer from another part of the body spreads to the liver. Most liver metastases originate from colon or colorectal cancer. More than half of patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer develop secondary liver cancer.
How many people get bile duct cancer each year?
About 8,000 patients are diagnosed with bile duct cancer each year in the United States, according to the ACS .
Where does bile duct cancer begin?
Intrahepatic bile duct cancer begins in ducts located in the liver. Extrahepatic bile duct cancer develops in ducts outside the liver. Angiosarcoma, also called hemangiocarcinoma, accounts for about 1 percent of all liver cancers. Angiosarcomas begin in the blood vessels of the liver and grow quickly. They are typically diagnosed ...
What is the term for a liver cancer that is spread to the liver?
They are typically diagnosed at an advanced stage. Secondary liver cancer, also known as a liver metastasis , develops when primary cancer from another part of the body spreads to the liver. Most liver metastases originate from colon or colorectal cancer.
What percentage of hepatocellular carcinomas are fibrolamellar?
About 1 percent of all hepatocellular carcinomas are fibrolamellar HCC, according to the American Cancer Society (ACS) .