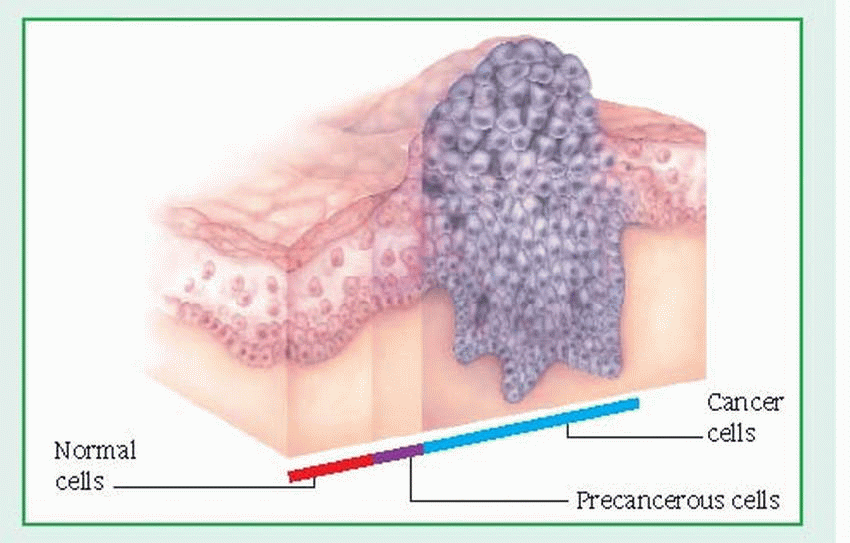
Is neoplasm the same as cancer?
While Gilbert’s cancer felt like it popped up overnight, that wasn’t the case. Pheochromocytomas are generally considered slow-growing tumors. Doctors estimate ... He encourages others to do the same. “Life is very precious,” Gilbert says.
What is the worst malignant or benign cancer?
When the cells in the tumor are normal, it is benign. Something just went wrong, and they overgrew and produced a lump. When the cells are abnormal and can grow uncontrollably, they are cancerous cells, and the tumor is malignant. To determine whether a tumor is benign or cancerous, a doctor can take a sample of the cells with a biopsy procedure.
What is the difference between a tumor and a neoplasm?
- Before surgery (to reduce the size of a tumor/usually combined with chemotherapy)
- After surgery (to clean up any cancer cells that may remain after surgery/usually combined with chemotherapy)
- As a primary treatment (with or without chemotherapy) to slow the growth of a tumor
- To treat metastases
Is a tumor the result of a neoplasm?
Some neoplasms do not form a tumor - these include leukemia and most forms of carcinoma in situ. Tumor is also not synonymous with cancer. While cancer is by definition malignant, a tumor can be benign, precancerous, or malignant . The terms mass and nodule are often used synonymously with tumor.

How serious is a malignant neoplasm?
A cancerous tumor (malignant neoplasm) can grow unchecked, invade healthy tissue and metastasize (spread), or spread from the place where it starts to other parts of the body. If it goes untreated and continues to spread, a malignant neoplasm can interfere with organ function and become life threatening.
Is malignant neoplasm the same as cancer?
Neoplasms may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign neoplasms may grow large but do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or other parts of the body. Malignant neoplasms can spread into, or invade, nearby tissues. They can also spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems.
What is an example of malignant neoplasm?
For example, lymphoma is a malignant neoplasm of lymphoid tissue, mesothelioma is a malignant neoplasm of the mesothelium, melanoma is a malignant neoplasm arising from melanocytes, and seminoma is a malignant neoplasm of the testicular epithelium.
What are the three classifications of malignant neoplasms?
These are:carcinoma – this cancer begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs. ... sarcoma – this cancer begins in the connective or supportive tissues such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle or blood vessels.leukaemia – this is cancer of the white blood cells.More items...•
What are the two categories of malignant neoplasms?
Some common types of malignant neoplasms include:Malignant neoplasm of breast/breast cancer: A malignant neoplasm may begin as a physical mass, such as a tumor in the breast.Leukemia: A neoplasm can also begin as an overproduction of a cell type.More items...•
What is the most common malignant neoplasm?
The most common type of cancer on the list is breast cancer, with 290,560 new cases expected in the United States in 2022. The next most common cancers are prostate cancer and lung cancer. Because colon and rectal cancers are often referred to as "colorectal cancers," these two cancer types are combined for the list.
What is the largest group of malignant neoplasms?
Primary and metastatic carcinomas are epithelial in origin and comprise by far the largest group of malignant tumors in humans.
What is the difference between a tumor and a neoplasm?
The difference between a tumor and a neoplasm is that a tumor refers to swelling or a lump like swollen state that would normally be associated with inflammation, whereas a neoplasm refers to any new growth, lesion, or ulcer that is abnormal.
What causes malignant neoplasm?
In general, cancerous tumor growth is triggered by DNA mutations within your cells. Your DNA contains genes that tell cells how to operate, grow, and divide. Your cells can't function normally when the DNA changes. This change is what causes cells to become cancerous.
Which characteristics are present in a malignant neoplasm?
Thus, characteristics of malignant neoplasms include: More rapid increase in size. Less differentiation (or lack of differentiation, called anaplasia) Tendency to invade surrounding tissues.
What does screening for malignant neoplasm mean?
The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation — such as during a colonoscopy — but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign (not cancerous).
What neoplasm means?
•Any growth that develops inside or on the body. •Tumors comes in two major categories: benign and malignant. •Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and immunotherapy.
What is malignant neoplasm?
The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation — such as during a colonoscopy — but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign (not cancerous).
What does it mean when a doctor says you have a malignant neoplasm?
Shutterstock. The term "malignant neoplasm" means that a tumor is cancerous.
What is the name of the test that a doctor takes to see if a polyp is cancerous?
When a polyp or other area of suspicious tissue is seen during a cancer screening test, the doctor may take a tissue sample — called a biopsy — right away, depending on the bodily location being examined, or at a later date, if doing so requires a second procedure.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Therapy: Treatment Options for Cancer Vary. Treatment options depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation . Surgery may involve removing a small tumor or polyp only, or removing a tumor and a portion of the surrounding tissue, if the tumor is larger or has spread into nearby tissue.
Does colon cancer reduce survival?
However, your chances of survival are generally decreased if a cancer has spread beyond its primary location.
Can a cancer oncologist predict how quickly a tumor will grow?
Malignant tumors can vary in their aggressiveness, so it is difficult to predict how rapidly they will grow. A medical oncologist can recommend appropriate testing and treatment to give you the best chance of survival. NEWSLETTERS. Sign up for our Cancer Care Newsletter!
What is malignant neoplasm?
Simply explained, malignant neoplasm or cancer is the uncontrollable, abnormal growth of cells within the human body. Such cells are commonly known as tumor cells, malignant cells or cancer cells. These cells are quite different in characteristics as compared to normal cells and can attack different body parts, organs, vessels, etc.
How is malignant neoplasm graded?
Grading of malignant neoplasms is done on the basis of how they appear on H&E staining. The higher the grader, the lower is the degree of tissue differentiation and vice-versa. Lesser the degree of tissue different, worse is the behavior of the tumor. Little or no tissue differentiation makes it difficult to determine the where the malignancy actually originated. Though different grading systems exist, each system usually consists of 3-4 grades depending upon the degree of differentiation. A commonly used grading system works as follows:
How to remove a tumor from a neoplasm?
Surgery – As the name suggests, the tumor or the neoplasm is cut out and eliminated via surgical means. Since the method helps complete removal of the tumor, it is often regarded as the best treatment procedure that exists. However, it must be noted that surgery cannot be performed for all types of neoplasm, especially if the tumor isn’t easily available or is located very close to the vital part of the organ. Moreover, in the later stages of cancer, when metastases have already occurred, surgery at the primary site will not be enough to remove cancer as the malignant cells have already spread to other body parts.
Why is it important to determine the stage of a malignant neoplasm?
Once a malignant neoplasm has been detected, it is important to determine its stage so that proper treatment can be started immediately. Though different staging methods exist, the TNM classification is most commonly and widely used to categorize the level of the malignant tumor.
How many grades are there in a tumor grade?
Though different grading systems exist, each system usually consists of 3-4 grades depending upon the degree of differentiation. A commonly used grading system works as follows: GX- the grade of the tumor cannot be determined. G1: the neoplasm is well differentiated. G2: the mass of tissue is moderately differentiated.
What happens when you visit a doctor with a tumor?
Upon visiting a doctor with symptoms that may be caused due to a growing tumor, the physician will carry out a series of checkups and tests which will finally reveal a malignant neoplasm, if present. The general course of action that is taken for the diagnosis of cancer is as follows:
What tests are used to determine if a tumor is cancerous?
These tests may include x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, ultrasonography, mammography, etc. depending on the body part where the cancerous lump may be present. The techniques find out the presence of the tumor, if at all and help determine the cancer stage as well as the most suitable treatment procedure.
What is a neoplasm?
A neoplasm is an abnormal growth of cells in the body, also described as a tumor. A neoplasm can be a small growth, such as a mole, or a cancerous or pre-cancerous tumor. Most of the time, neoplasms are not dangerous to your health, but they can be.
What is metastatic neoplasm?
A metastatic neoplasm is defined as cancer. It is most often associated with damage to a cell's DNA. 4 This damage results in genetic mutations that cause abnormal cells to lose their normal function, multiply faster, live longer, and invade other cells and tissue.
What is a benign tumor called?
Benign neoplasms are often called birthmarks, and they may develop during late childhood or in adulthood. Benign tumors usually grow slowly, if at all, and they are generally not life-threatening. These are caused by a limited overgrowth of cells, usually without a known cause.
How to tell if you have a neoplasm?
A visible neoplasm may look exactly like your skin, or it may be a different color or texture. They are usually painless, but they can hurt or bleed —a main point that differentiates them from warts. Neoplasms may grow very slowly, and it is rare for a neoplasm to grow rapidly.
What is a pre-cancerous tumor?
A pre-cancerous tumor has features of a malignant tumor, but has not yet become cancer, and has not spread. 1
What are the causes of cancer mutations?
Certain factors can trigger these mutations, including genetics, sun exposure, and toxic substances. 5 Smoking, for instance, can increase a person's risk of lung cancer, while excessive alcohol use may lead to liver cancer.
What to do if you have a tumor on your body?
If you ever do find an unusual growth on your body, contact your primary care provider as soon as possible . Depending on where the growth is, you may need a physical exam, blood tests, imaging tests, or a tissue biopsy. After that, if anything looks suspicious, you'll at least have the opportunity to get it diagnosed and treated early when success rates are highest.
What is the most common type of heart tumor?
Tumors of the Heart. Most malignant heart tumors are angiosarcomas, although other types include rhabdomyosarcomas, mesotheliomas, or fibrosarcomas. As mentioned earlier, sarcomas are cancers formed in the soft tissue of the body, normally in connective tissue and muscle.
What is the most common thyroid cancer?
They represent only 1.8 percent of all cancer diagnoses, but this does not mean they should be dismissed. The most frequent cause is lymphoma, which often follows a history of goiters and the disease Hashimoto thyroiditis. This condition causes the immune system to attack the thyroid and can lead to an underactive thyroid gland followed by other problems such as tumors.
How rare are sarcomas?
Sarcomas are rare but often malignant. They originate in the soft tissues of the body, generally connecting tissues such as muscle, ligaments, tendons, fat, and cartilage. Only about 8,000 soft tissue tumors occur in the U.S. each year. Luckily, over 90 percent of people diagnosed with a soft tissue tumor do not see the tumor spread, and surgeons can generally remove it before it causes further problems. If it has spread, however, it is much more difficult to treat and may require more than just surgical treatment.
Where do adenocarcinomas appear?
It also appears as a part of the digestive system and the lining of the hollow parts of organs. Adenocarcinomas are often to blame for a diagnosis of breast, colon, and lung cancer. They can also appear in the bile duct, vagina, stomach, and prostate.
Does lung cancer spread quickly?
Sometimes, malignant lung tumors may appear even in people exposed to second-hand smoke, who personally never smoked. This cancer affects the air sacks in the lungs and can spread alarmingly quickly. Early treatment is a necessity.
Is a heart tumor a sarcoma?
Most malignant heart tumors are angiosarcomas, although other types include rhabdomyosarcomas, mesotheliomas, or fibrosarcomas. As mentioned earlier, sarcomas are cancers formed in the soft tissue of the body, normally in connective tissue and muscle. This type of tumor presents with symptoms that can be mistaken for other heart conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis. Echocardiography is the best way to diagnose a heart tumor, though other heart tests can identify the growths, as well.
How rare are tumors?
They are rare. Only about 8,000 tumors of this type occur each year in the United States, representing only about 1% of all malignant tumors. They are technically different from the much more common cancers or "carcinomas," which are malignant tumors that arise from organs or gland tissue (e.g.
What age do you get a malignant soft tissue tumor?
Malignant soft tissue tumors can occur at almost any age, but are most common in individuals between 50 and 70 years of age. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH), liposarcoma, and synovial sarcoma, neurosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, hemangiopericytoma, and angiosarcoma are among the most common of these tumors, but many other types exist.
What are the sites of metastasis?
Other bones can also become sites of metastasis. Malignant soft tissue tumors are classified as "sarcomas.". These tumors are thought to arise from "connective tissues" other than bone, such as muscle, tendon, ligament, fat, and cartilage. They are rare.
How do malignant soft tissue tumors spread?
These cells can spread by travel through the blood stream or by travel through lymph vessels.
Why do tumors grow so big?
Because soft tissue is very elastic, the tumors can grow quite large before they are felt. The first symptom is usually a painless lump. As the tumor grows and begins to press against nearby nerves and muscles, pain or soreness can occur.Any growing tumor should be recognized and evaluated promptly.
How many chances of a tumor spreading?
Pathologists are now able to examine many tumors under the microscope and divide tumors into high-grade tumors, which have a 70-90% chance of having spread, and low-grade tumors, where the chance of spread is low (less than 15%).
Does radiation therapy help with high grade tumors?
The addition of chemotherapy for the highest-grade tumors reduces the rate at which high-grade tumors return and may improve the rate of cure. The use of specialized radiation therapy techniques has significantly reduced the likelihood of tumors coming back at the site where they have been removed. Often, depending on the type of tumor, preoperative radiation therapy or chemotherapy (or a combination of the two) may be used to make some of these tumors more easily resected with adequate margins.
What is plasma cell neoplasm?
Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which the body makes too many plasma cells. Plasma cell neoplasms can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). There are several types of plasma cell neoplasms. Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms may cause a condition called amyloidosis.
What is the most common type of neoplasm in middle aged people?
Plasma cell neoplasms are most common in people who are middle aged or older. For multiple myeloma and plasmacytoma, other risk factors include the following:
What is the disease that causes a tumor in the bones?
Multiple myeloma cells also damage and weaken the bone. Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which abnormal plasma cells or myeloma cells form tumors in the bones or soft tissues of the body.
Where is plasmacytoma found?
Extramedullary plasmacytomas commonly form in tissues of the throat, tonsil, and paranasal sinuses.
Can age affect plasma cell neoplasms?
Multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms may cause a condition called amyloidosis. Age can affect the risk of plasma cell neoplasms. Tests that examine the blood, bone marrow, and urine are used to diagnose multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms.
Can MGUS cause cancer?
In some patients, MGUS may later become a more serious condition, such as amyloidosis, or cause problems with the kidneys, heart, or nerves. MGUS can also become cancer, such as multiple myeloma, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, or chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
What is the second most common type of spine cancer in teens?
Ewing’s Sarcoma: Ewing’s Sarcoma is the second most common type of spine cancer in teens, with men being marginally more affected than women. Although researchers don’t 100% understand the cause of Ewing’s Sarcoma, it is thought to result from a chromosomal mutation. Unlike osteosarcomas, this type of malignant spine tumor does lead to spine fractures. Other defining symptoms include fever and warmth to the touch at the site of the tumor.
What is an intramedullary tumor?
Doctors classify other types of spinal tumors as Intramedullary Tumors (ITMs) if they grow within the matter, or medulla, of the spinal cord; or as Intradural-Extramedullary Tumors (if they grow on the dura of the spinal meninges). ITMs, like astrocytomas, arise from mutations in glial cells. Glial aptly sounds like “glue.”.
What is the most aggressive form of astrocytoma?
Astrocytoma: Astrocytomas arise from astrocytes, a form of glial or supportive cell. These abnormal cells can also multiply in the brain, but spinal astrocytomas wind around the nerves that exit from the spinal cord. The most aggressive form of astrocytomas are known as glioblastomas; the least aggressive are termed pilocytic. Because these tumors warp around the nerve sheath, your doctor may need to use radiation therapy to treat them.
Why is the spinal column more prone to secondary tumors?
Because your vertebrae are the most exposed part of your spine, your spinal column is more prone to developing secondary tumors. Secondary means that the growth itself did not begin in your spine. For example, in women, cancers of the breast often “metastasize,” or spread, to the thoracic spine.
What does it feel like to have a spinal tumor?
Pain that erupts first thing in the morning or late at night. Symptoms of pinched nerve pain, like tingling or numbness in your arms and hands. Muscle fatigue, weakness, or loss of ...
What are the symptoms of a tumor on the spine?
Unsteadiness on your feet. Blunted sense of touch, hot, cold, or pain. Loss of bowel or bladder control. Loss of reflexes or paralysis. Fractured vertebrae. However, the location of the tumor on your spine will determine most of the symptoms that will arise.
Is osteosarcoma rare in teens?
Despite this, fractured bones are rare with osteosarcomas. The most common form of all malignant spinal tumor, spinal osteosarcomas affect young adults (age 20-30) more often than all other age groups. Ewing’s Sarcoma: Ewing’s Sarcoma is the second most common type of spine cancer in teens, with men being marginally more affected than women.