The major cell type found on the alveolar surface, covering about 95% of the surface area, are thin, broad cells known as squamous Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.Epithelium
What are the three types of alveolar cells?
- Collagen appears blue
- Cytoplasm appears pink
- Nuclei are dark brown to black.
What cells make up the alveolar?
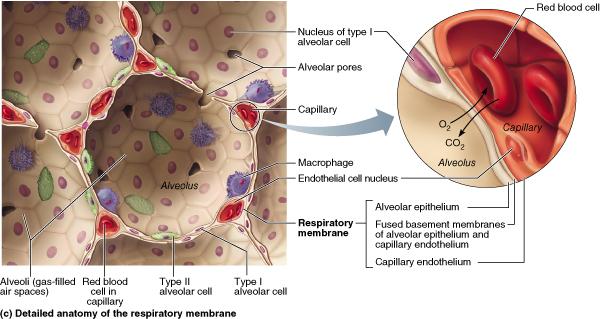
Alveolar epithelium is composed of type I pneumocytes, type II pneumocytes, and the occasional brush cells. Also present in the alveolar walls are the club cells and alveolar macrophages. The alveolar walls contain the pores of Kohn , which allow communication between adjacent alveoli. This allows air to flow from one alveolus to another, which ...
What do alveolar cells do?
Type 1 alveoli cells cover 95 percent of the alveolar surface and constitute the air-blood barrier. Type 2 alveoli cells are smaller and responsible for producing the surfactant that coats the inside surface of the alveolus and helps reduce surface tension. The surfactant helps keep the shape of each alveolus when you breathe in and out.
Which cells in the alveoli secrete surfactant?
- Identification of genetic modifiers influencing the pathogenesis of surfactant and type II cell-related disorders.
- Elucidation of the role of protein misfolding in interstitial lung disease.
- Identification of additional genes influencing surfactant homeostasis and interstitial lung disease.

How big is the alveoli?
The alveoli cover a surface that measures more than 1,076.4 square feet (100 square meters).
How many millimeters are in an alveolus?
The number of alveoli and alveolar sacs are what give your lungs a spongy consistency. Each alveolus (singular of alveoli) is about 0.2 millimeters in diameter (about 0.008 inches). Each alveolus is cup-shaped with very thin walls. It’s surrounded by networks of blood vessels called capillaries that also have thin walls.
What is the name of the small duct at the end of each bronchial duct?
The bronchi divide into smaller branches called bronchioles. And at the end of each bronchiole is a small duct (alveolar duct) that connects to a cluster of thousands of microscopic bubble-like structures, the alveoli. The word alveolus comes from the Latin word for “little cavity.”. Alveoli in cross-section.
What are the tiny air sacs in your lungs that take up oxygen?
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in your lungs that take up the oxygen you breathe in and keep your body going. Although they’re microscopic, alveoli are the workhorses of your respiratory system.
How do alveoli work?
There are three overall processes involved in your breathing: moving air in and out of your lungs (ventilation) oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange (diffusion) pumping blood through your lungs (perfusion) Although tiny, the alveoli are the center of your respiratory system’s gas exchange. The alveoli pick up the incoming energy ...
What is the center of the respiratory system?
Although tiny, the alveoli are the center of your respiratory system’s gas exchange. The alveoli pick up the incoming energy (oxygen) you breathe in and release the outgoing waste product (carbon dioxide) you exhale.
How many branches are there in the right lung?
Picture your lungs as two well-branched tree limbs, one on each side of your chest. The right lung has three sections (lobes), and the left lung has two sections (above the heart). The larger branches in each lobe are called bronchi.
