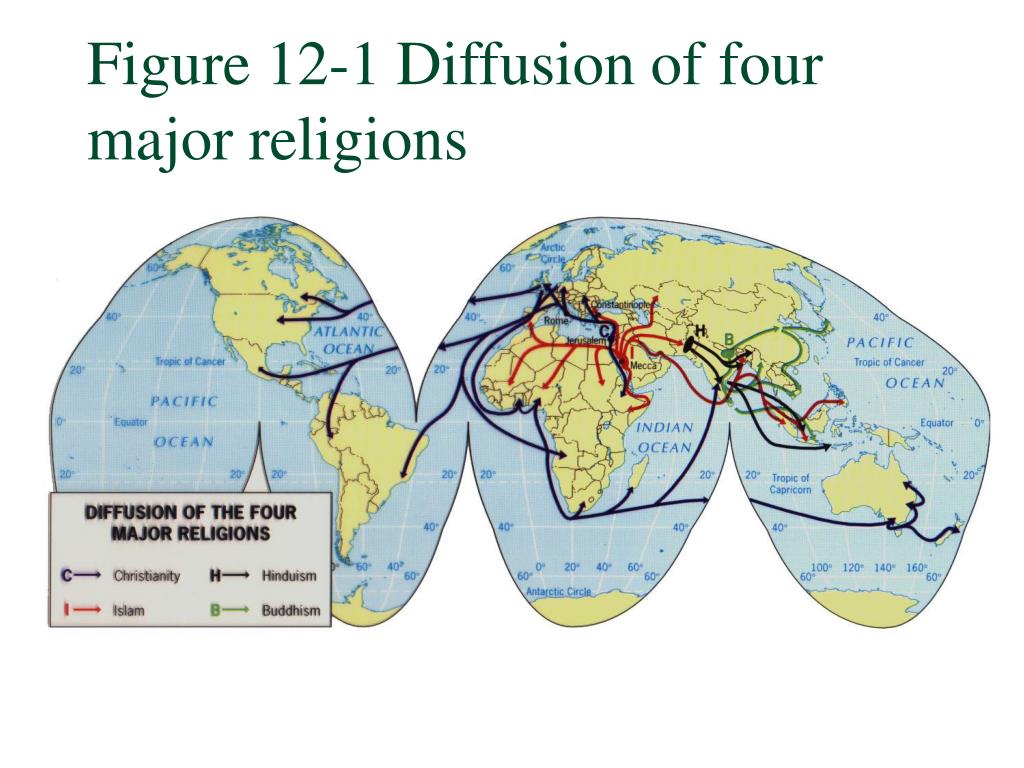
What has been the pattern of diffusion of Judaism?
The world’s two major ethnic religions - Hinduism and Judaism - are ancient religions. The diffusion of these ethnic religions has been limited, but still substantial, and is largely due to relocation diffusion, as neither religion has actively sought to recruit new believers. In your own words, compare Universalizing and Ethnic Religions.
What are the four different types of diffusion?
Types of Diffusion:
- Self-Diffusion: Self-diffusion is the migration of atoms in pure materials. ...
- Inter-Diffusion: It occurs in binary metallic alloys. Observed in binary metal alloys such as Cu-Ni system.
- Volume Diffusion: Volume diffusion means atomic migration through the bulk of the material.
What type of diffusion was used to spread Islam?
Ummah, or Muslim communities, were formed throughout this vast territory. Two major types of diffusion were used during the spread of Islam: contagious ( contact) and hierarchal (through force). Reasons for the success of Islam have been debated, but there are generally two on which scholars generally agree.
What made Judaism different from other religions?
how did judaism influence the development of islam
- A Jew, a Christian, a Muslim and a Jim – The Jim Jefferies Show
- Jews Under Islam
- History of Jews in 5 Minutes – Animation
- The Birth of Islam: Muhammad and the Jews | The Jewish Story | Unpacked
See more
Is Judaism contagious or relocation diffusion?
Ethnic religions, including Hinduism and Judaism, are generally found near the hearth or spread through relocation diffusion.
How did Judaism diffuse?
Jews scattered outside of Palestine after the Babylonian exile (the diaspora). Many Jews became merchants, and their religion was spread through trade—a monotheistic religion based on the fundamentals of Judaism founded in 33 C.E. by Jesus.
What type of diffusion is religion?
Religion uses nearly all forms of diffusion to reproduce itself across space. Hierarchical diffusion generally involves the conversion of a king, emperor, or other leader who then influences others to convert.
Why is Judaism relocation diffusion?
Buddhism spread primarily through relocation diffusion by missionaries and was slow to diffuse outside the area of origin. By its definition, ethnic religions are found near the hearth but spread through relocation diffusion.
Is Judaism monotheistic or polytheistic?
monotheisticJudaism, monotheistic religion developed among the ancient Hebrews. Judaism is characterized by a belief in one transcendent God who revealed himself to Abraham, Moses, and the Hebrew prophets and by a religious life in accordance with Scriptures and rabbinic traditions.
Where did Judaism start spreading?
The origins of Judaism date back more than 3500 years. This religion is rooted in the ancient near eastern region of Canaan (which today constitutes Israel and the Palestinian territories). Judaism emerged from the beliefs and practices of the people known as “Israel”.
What type of diffusion is Islam?
Islam has diffused through both expansion diffusion and relocation diffusion to become the second most followed religion in the world. Since the death of Muhammad, Islam has divided into a number of different factions.
What type of diffusion is Hinduism?
contagious diffusionHinduism spread by contagious diffusion (person to person contact) from its hearth in the Punjab (Northern India/Pakistan) southward throughout the Indian subcontinent and into SE Asia.
What type of diffusion is Shintoism?
Shintoism spread through Japan and into parts of China. Shintoism did not diffuse far, and only spread by people and heritage on where they lived through Japan and the into China.
What is contagious diffusion of religion?
Contagious Diffusion religions when people are in contact with belief systems especially universalizing religions such as Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam. Missionaries spread christianity.
What is hierarchical diffusion?
Hierarchical Diffusion. The spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places. Examples- Birkenstocks, Christianity, styles of clothing, music.
What is an example of relocation diffusion?
One example of relocation diffusion could be when Italians first came to America they taught us how to make pizza. Stimulus diffusion is the spread of an underlying principle even though a characteristic itself fails to diffuse.
The Spectrum of Judaism
Judaism is comprised of several “branches,” also called denominations or streams, that exist on a spectrum from traditionally religious to liberal. Yet the Jews are a people, not a religion; Jewishness and Judaism are not necessarily the same thing.
Beliefs and Behavior
It should also be noted that, while each branch of Judaism has its own more or less “official” take on the Jewish faith, simply attending a particular synagogue doesn’t necessarily mean a person believes (or even understands) those official beliefs.
The Branch of Orthodox Judaism
Until the late 18th century, there was only one kind of Judaism. What is now called “Orthodox” Judaism was normative and did not need to be distinguished as a branch until other, less traditional, varieties of Judaism began to develop.
The Branch of Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism is the product of modernity. The 18th-century Enlightenment in Europe brought, among other things, an overturning of traditional religious convictions. Reason, not revelation, was seen as the path to truth. In this new climate, Reform Judaism was birthed in 19th-century Germany.
The Branch of Conservative Judaism
Also known as Masorti (“traditional”) Judaism outside North America, Conservative Judaism developed from roots in 19th-century Germany, but has become a largely American branch. It occupies a middle ground between Orthodoxy and Reform.
Culture Region (Region)
Location and number of adherents: They are major located in Israel, Europe, USA and have 15 million followers. Teachings and Principles/Beliefs: Judaism does not have a formal mandatory beliefs. The most common and accepted of Jewish beliefs are Rambam's 13 principles of faith, but even those are debated.
Diffusion (Mobility)
History: It was founded in 1800 BC, during Abraham's pact with Yahweh. Types of Diffusion, including Barriers: Abraham started to preach the religion and his children brought the religion to Egypt.
Religious Ecology (Nature-Culture)
Relationship with Nature: They believe that creator shaped nature after his image, he construct the image after the ability to discern and reason.
Culture Integration (Globalization)
Economic Impacts and Relationship: "The Torah is replete with precepts dealing with business, and the Talmud, the source of Jewish oral law, elaborates and expands Torah law. The process is ongoing and rabbinical authorities today build on the decisions of their predecessors to apply Jewish law to modern problems.
Cultural Landscapes (Cultural Landscapes)
Structures: In Judaism is no "formal" structure, it has no centralized leadership strucure at all, because the various traditions like orthodox, conservative, or reform have all their own leader, no one, who governs over them all as in the Catholic Church or in other religions. Sacred Places: Are cities like Jerusalem, Safed,Hebron and Tiberias, even Israel itself. Sacred Space: Jews worship in synagogues, but their also used for education and community..
What do Jews believe?
Judaism Beliefs. Jewish people believe there’s only one God who has established a covenant—or special agreement—with them. Their God communicates to believers through prophets and rewards good deeds while also punishing evil.
What is the Talmud?
Talmud. Later, the Talmud, a collection of teachings and commentaries on Jewish law, was created . The Talmud contains the Mishnah and another text known as the Gemara (which examines the Mishnah). It includes the interpretations of thousands of rabbis and outlines the importance of 613 commandments of Jewish law.
What are the different sects of Judaism?
There are several sects in Judaism, which include: Orthodox Judaism : Orthodox Jews are typically known for their strict observance of traditional Jewish law and rituals. For instance, most believe Shabbat shouldn’t involve working, driving or handling money.
What is the Jewish sacred text called?
The Jewish sacred text is called the Tanakh or the “Hebrew Bible.” It includes the same books as the Old Testament in the Christian Bible, but they’re placed in a slightly different order.
What happened to the Jewish people in 1066?
Judaism and Persecution. Throughout history, Jewish people have been persecuted for their religious beliefs. Some well-known events include: 1066 Granada Massacre: On December 30, 1066, a Muslim mob stormed the royal palace in Granada and killed more than 1,000 Jewish families.
What is the sacred text of Judaism?
Jewish Holy Books. While the Tanakh (which includes the Torah) is considered the sacred text of Judaism, many other important manuscripts were composed in later years. These offered insights into how the Tanakh should be interpreted and documented oral laws that were previously not written down.
Where did Chabad originate?
This form started in the 18th century in Eastern Europe and holds different values than traditional or ultra-Orthodox Judaism. Hasidic Jews emphasize a mystical experience with God that involves direct communion through prayer and worship. Chabad is a well-known Orthodox Jewish, Hasidic movement.
