
Why are earthquakes so devastating in Haiti?
Jan 12, 2010 · 2010 Haiti earthquake, large-scale earthquake that occurred January 12, 2010, on the West Indian island of Hispaniola, comprising the countries of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Most severely affected was Haiti, occupying the western third of the island. An exact death toll proved elusive in the ensuing chaos. The Haitian government’s official count was …
What was the worst earthquake in Haiti?
On 12 January 2010, a magnitude 7 earthquake hit Haiti at 16:53 local time. Click to see full answer. People also ask, what type of fault was the 2010 Haiti earthquake? The strike-slip fault system in the region has two branches in Haiti, the Septentrional-Oriente fault in the north and the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault in the south; both its location and focal mechanism suggested …
When was the last earthquake in Haiti?
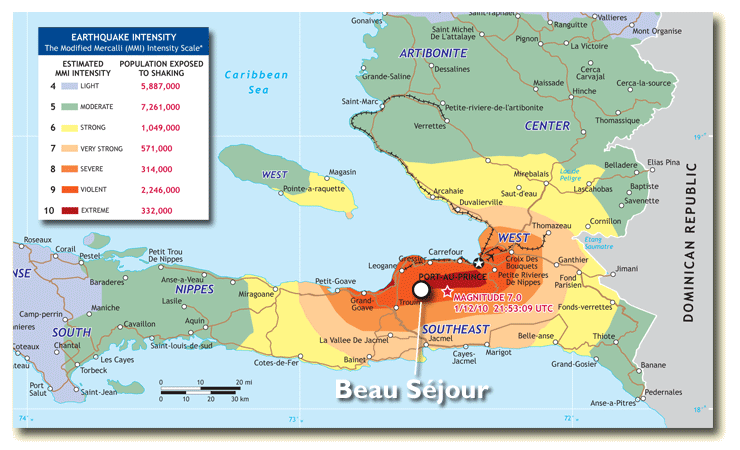
Jan 11, 2010 · A 7.0 magnitude earthquake. When? Jan. 12 2010 at 16.53 local time (21.53 GMT). Where? The earthquake occurred 18.457°N, 72.533°W. The focus of the earthquake was 13km (8.1 miles) below the surface of the earth. Why? Al Jazeera explains science behind Haiti's earthquake Watch on
What are facts about Haiti earthquake?
On 12 January 2010, at 4:53 p.m. local time, a magnitude 7.0 earthquake struck the Republic of Haiti, with an epicenter located approximately 25 km south and west of the cap- …
See more
Sep 28, 2018 · The January 12, 2010, Haiti Earthquake (Mw = 7.0) along the strike-slip Enriquillo-Plantain Garden Fault, which bounds the Caribbean Plate and Gonâve Microplate, caused liquefaction and failure of the coastal sediments of the Bay of Grand Goâve with an alongshore length of 400 m and a shore-normal distance of 100 m (Hornbach et al., 2010; Fritz et al., 2013).
What type of earthquake was the Haiti earthquake?
...
2021 Haiti earthquake.
| Destruction from the earthquake | |
|---|---|
| Port-au-Prince Léogâne Les Cayes class=notpageimage| Interactive map | |
| Epicenter | 18.417°N 73.480°W |
| Fault | Enriquillo–Plantain Garden fault zone |
| Type | Oblique-reverse |
What type of earthquake was Haiti 2010?
What plate boundary caused Haiti earthquake?
Haiti lies right on the boundary of the Caribbean and North American plates. There was slippage along a conservative plate boundary that runs through Haiti. On 12 January 2010, a magnitude 7 earthquake hit Haiti at 16:53 local time.
What caused Haiti earthquake 2010?
What causes earthquakes in Haiti?
What type of plate is the Caribbean plate?
What type of boundary is the Caribbean plate?
Is Haiti on a destructive plate boundary?
What year did the Haiti earthquake happen?
A magnitude 8.0 earthquake struck the Dominican Republic and shook Haiti on 4 August 1946, producing a tsunami that killed 1,790 people and injured many others. Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere and is ranked 149th of 182 countries on the Human Development Index.
How many people died in the Haiti earthquake?
An estimated three million people were affected by the quake. Death toll estimates range from 100,000 to about 160,000 to Haitian government figures from 220,000 to 316,000, although these latter figures are a matter of some dispute.
How much money did Hope for Haiti raise?
The most-watched telethon in history aired on 22 January, called " Hope for Haiti Now ," raising US$58 million by the next day.
How many aftershocks were there after the earthquake?
The U.S. Geological Survey recorded eight aftershocks in the two hours after the main earthquake, with magnitudes between 4.3 and 5.9. Within the first nine hours, 32 aftershocks of magnitude 4.2 or greater were recorded, 12 of which measured magnitude 5.0 or greater; in addition, on 24 January, the US Geological Survey reported that there had been 52 aftershocks measuring 4.5 or greater since the main quake.
Who was Haiti's ambassador to the United States?
Raymond Joseph, Haiti's ambassador to the United States, and his nephew, singer Wyclef Jean, who was called upon by Préval to become a "roving ambassador" for Haiti, also pleaded for aid and donations. Images and testimonials circulating after the earthquake across the internet and through social media helped to intensify the reaction of global engagement.
How much did Canada contribute to the Haiti earthquake?
After a United Nations call for help for the people affected by the earthquake, Canada pledged an additional C$60 million in aid on 19 January 2010, bringing Canada's total contribution to C$135 million.
What happened to the beach in Petit Paradis?
The Pacific Tsunami Warning Center issued a tsunami warning immediately after the initial quake, but quickly cancelled it. Nearly two weeks later it was reported that the beach of the small fishing town of Petit Paradis was hit by a localised tsunami shortly after the earthquake, probably as a result of an underwater landslide, and this was later confirmed by researchers. At least three people were swept out to sea by the wave and were reported dead. Witnesses told reporters that the sea first retreated and a "very big wave" followed rapidly, crashing ashore and sweeping boats and debris into the ocean.
When did the Haiti earthquake happen?
Massive earthquake strikes Haiti - HISTORY. On January 12, 2010, Haiti is devastated by a massive earthquake. It drew an outpouring of support from around the globe but the small nation has yet to fully. On January 12, 2010, Haiti is devastated by a massive earthquake.
What happened in Haiti in 2010?
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images. On January 12, 2010, Haiti is devastated by a massive earthquake. It drew an outpouring of support from around the globe but the small nation has yet to fully recover. Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, due largely to its history of colonization, occupation and exploitation by Spain, ...
When was Haiti devastated?
On January 12, 2010, Haiti is devastated by a massive earthquake. It drew an outpouring of support from around the globe but the small nation has yet to fully. On January 12, 2010, Haiti is devastated by a massive earthquake.
Why is Haiti the poorest country in the world?
Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, due largely to its history of colonization, occupation and exploitation by Spain, France and the United States. It also has a history of seismic activity—devastating earthquakes were recorded there in 1751, 1770, 1842 and 1946.
How many people died in Haiti?
The human toll was horrific and remains incalculable. Some estimates put the number of deaths around 40-50,000, while the Haitian government estimated that over 316,000 died, but all authorities acknowledge that the death toll is impossible to truly count. Something approaching 1 million people were displaced.
How much money did Hope for Haiti raise?
The "Hope for Haiti" telethon on January 22nd broke records by raising $58 million in one day. Though the humanitarian response was immediate and overwhelming, Haiti's crippled infrastructure made the delivery of aid difficult. The situation was still classified as an emergency six months after the earthquake.
Who was the first woman to be elected to the Senate?
Hattie Ophelia Wyatt Caraway, a Democrat from Arkansas, becomes the first woman to be elected to the U.S. Senate. Caraway, born near Bakerville, Tennessee, had been appointed to the Senate two months earlier to fill the vacancy left by her late husband, Thaddeus Horatio Caraway. ...read more.
Is Haiti a North American or Caribbean plate?
Haiti is situated to the north of the Caribbean Plate, on a transform (slip/conservative) plate boundary with the North American Plate. The North American plate is moving west. This movement is not smooth and there is friction between the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate.
Where was the epicenter of the earthquake?
The epicenter of the earthquake was 16km south west of Port-Au-Prince. The earthquake was caused by a slip along an existing fault in this area (Enriquillo-Plaintain Garden fault). A map to show the location of the epicentre of the earthquake.
Which is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere?
Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere. The buildings in Port-Au-Prince and other areas of Haiti were in very poor condition in general and were not designed or constructed to be earthquake resistant.

Overview
A catastrophic magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest department, approximately 25 kilometres (16 mi) west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's capital.
By 24 January, at least 52 aftershocksmeasuring 4.5 or greater had been recor…
Background
The island of Hispaniola, shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic, is seismically active and has a history of destructive earthquakes. During Haiti's time as a French colony, earthquakes were recorded by French historian Moreau de Saint-Méry (1750–1819). He described damage done by an earthquake in 1751, writing that "only one masonry building had not collapsed" in Port-au-Prince; he also wrote that the "whole city collapsed" in the 1770 Port-au-Prince earthquake. Cap-Haïtien, …
Geology
The magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake occurred inland, on 12 January 2010 at 16:53 (UTC−05:00), approximately 25 km (16 mi) WSW from Port-au-Prince at a depth of 13 km (8.1 mi) on blind thrust faults associated with the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault systemand lasted less than 30 seconds. There is no evidence of surface rupture; based on seismological, geological and ground deformation d…
Damage to infrastructure
Amongst the widespread devastation and damage throughout Port-au-Prince and elsewhere, vital infrastructure necessary to respond to the disaster was severely damaged or destroyed. This included all hospitals in the capital; air, sea, and land transport facilities; and communication systems.
The quake affected the three Médecins Sans Frontières(Doctors Without Borde…
Conditions in the aftermath
In the nights following the earthquake, many people in Haiti slept in the streets, on pavements, in their cars, or in makeshift shanty towns either because their houses had been destroyed, or they feared standing structures would not withstand aftershocks. Construction standards are low in Haiti; the country has no building codes. Engineers have stated that it is unlikely many buildings woul…
Casualties
The earthquake struck in the most populated area of the country. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societiesestimated that as many as 3 million people had been affected by the quake. In mid February 2010, the Haitian government reported the death toll to have reached 230,000. However, an investigation by Radio Netherlands has questioned the official de…
Early response
Appeals for humanitarian aid were issued by many aid organizations, the United Nations and president René Préval. Raymond Joseph, Haiti's ambassador to the United States, and his nephew, singer Wyclef Jean, who was called upon by Préval to become a "roving ambassador" for Haiti, also pleaded for aid and donations. Images and testimonials circulating after the earthquake across th…
Rescue and relief efforts
Rescue efforts began in the immediate aftermath of the earthquake, with able-bodied survivors extricating the living and the dead from the rubble of the many buildings that had collapsed. Treatment of the injured was hampered by the lack of hospital and morgue facilities: the Argentine military field hospital, which had been serving MINUSTAH, was the only one available until 13 January. Rescue …