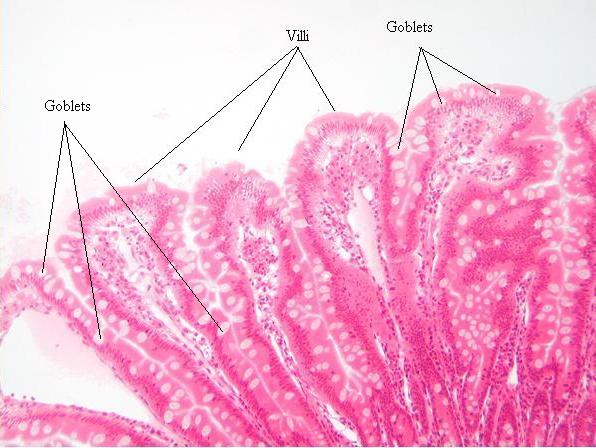
Where are goblet cells found?
Goblet cells are usually found scattered amongst the cells of the simple epithelial tissues that secrete mucus. In some areas, there are a small number of cells, but in others, goblet cells are highly abundant.
What is the function of a goblet in epithelial tissue?
Their name corresponds to their shape, as they resemble a goblet, with their narrow bases and wide apex. Their role is to protect the surface of epithelium, lubricate it, and catch harmful particles.
What is epithelial tissue made of?
Epithelial tissue is made up of epithelial cells. The cells can be different shapes and can be arranged in a single layer or multiple layers depending on where they are in your body and what kind of functions they have. In biology, a cell is the smallest unit that can live on its own. Cells make up all living organisms and the tissues of your body.
Are goblet cells harmful?
Goblet cells are protective, yet they can also be harmful. There are four types of basic tissues in the body: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle and Nervous tissue. Goblet cells can be found in the epithelial tissue of the Gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts.
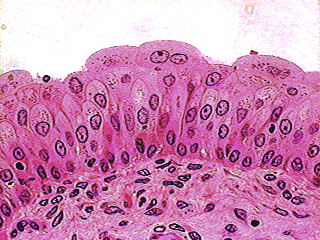
Are goblet cells found in simple squamous epithelium?
This type of epithelium is adapted for secretion and/or absorption, and can also be protective. Simple secretory columnar epithelium lines the stomach and uterine cervix. The simple columnar epithelium that lines the intestine also contains a few goblet cells.
Which two types of epithelium are goblet cells commonly found in?
Goblet cells are a specialized type of epithelial cell that secrete mucins, which are significant components of mucus. They are most often found in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, where they make up part of the surface epithelium.
Are goblet cells found in stratified squamous epithelium?
Stratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells covers most of the conjunctiva and transitions at the limbus, the palpebral margins, and the caruncle into stratified squamous epithelium. There is polarity or a normal sequence of maturation from the basal layers to the more superficial layers.
Where are goblet cells found epithelial tissue?
Goblet cells are mostly found scattered in the epithelia of the small intestines and respiratory tract. The morphology of goblet cells reflects their function, with the cell containing all the organelles necessary for the production of glycosylated proteins called mucins.
Are goblet cells found within Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
It is TRUE that goblet cells are found within the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
Where is simple squamous epithelium found?
Simple squamous epithelia are found lining the cavities of the body including the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities, or in areas where passive diffusion occurs, such as glomeruli in the kidney and alveoli in the respiratory tract.
What type of epithelium is found in the epidermis?
keratinized stratified squamous epitheliumEpidermis, the epithelial layer of skin, is primarily protective. This layer, consisting of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, is tough, relatively impermeable, and self-replacing. These functional qualities are conferred by the epidermis' principal cell type, the keratinocyte.
What is the location of Pseudostratified epithelium?
respiratory airwaysPseudostratified columnar epithelia are most commonly found along the respiratory airways. These cells contain cilia on their apical surface. Cilia are motile, beating in a synchronous rhythm to move fluid in a constant direction.
What are goblet cells?
Goblet cells are modified epithelial cells that secrete mucus on the surface of mucous membranes of organs, particularly those of the lower digestive tract and airways .#N#Histologically, they are mucous merocrine exocrine glands. What does that mean?
What is the function of goblet cells?
Their main function here is to produce mucus which protects and lubricates the surface of the intestines. In the respiratory tract, besides protecting the epithelial surface, mucus traps harming particles inhaled with air to protect the airway.
Why do goblet cells decrease?
Going down the respiratory tree, the number of goblet cells decrease, while the number of club cells increase. This is due to terminal bronchiole needing different kinds of protection which club cells can bring them–breaking down of inhaled toxins that couldn’t be stopped by the mucus of goblet cells.
Which organelle is polarized?
Besides containing the nucleus and mitochondria, the cytoplasm is especially rich in rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and Golgi complexes. Mucins are produced by mucinogen granules in RER and packed into vesicles in Golgi complexes. To make the entire process of synthesis more efficient, goblet cells are polarized, meaning that the organelles have a specific layout within the cytoplasm: the nucleus, mitochondria, RER, and Golgi apparatus are found in the basal portion of the cell; while the vesicles with mucins are located apically, in order to be close to the apical membrane through which their exocytosis occurs.
What are epithelial cells?
Epithelial tissue is made up of epithelial cells. The cells can be different shapes and can be arranged in a single layer or multiple layers depending on where they are in your body and what kind of functions they have.
What is the epithelium?
The epithelium is a type of body tissue that forms the covering on all internal and external surfaces of your body, lines body cavities and hollow organs and is the major tissue in glands . Epithelial tissue has a variety of functions depending on where it’s located in your body, including protection, secretion and absorption.
What are the different kinds of epithelial cell tests?
Since epithelial cells exist in several important parts of your body, several types of tests examine epithelial cells to check for certain medical conditions. In medicine, pathology is the laboratory examination of cells in samples of body tissue or fluids for diagnostic purposes. A scientist called a pathologist examines the cells.
What is the difference between epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium?
Epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium are three types of epithelial cell layers that line your internal organs, body cavities and form the outer layer of your skin.
What are the different types of goblet cells?
Different types of goblet cells can be identified based on location and function. [1] . Colonic and small intestinal crypt goblet cells secrete upon stimulation. Examples of stimulation include responses to endocytosis or acetylcholine. Surface colonic goblet cells constantly secrete to maintain the inner mucus layer.
What is the function of goblet cells?
The primary function of goblet cells is to secrete mucin and create a protective mucus layer. Goblet cells are also thought to be involved with immunoregulation. Samples of goblet cells can be preserved through cryopreservation and analyzed with light microscopy.
How do goblet cells help maintain homeostasis?
Goblet cells help maintain homeostasis through their function of providing bicarbonate for proper mucin unfolding in the small intestine. Goblet cells can also form a line of defense at the intestinal mucosa and have a common secretory role.
How do goblet cells get their name?
Formed by mucin granules, goblet cells derive their name from their goblet, cup-like appearance .[1] . At the base of the intestinal crypt, pluripotent stem cells secrete many substances such as trefoil peptide and mucin. Goblet cells originate from these pluripotent stem cells and form the intestinal mucus layer used to protect epithelial ...
Why do goblet cells deplete?
Chronic infections can cause goblet cell depletion and thus cause immunologic implications; this is because goblet cell secretion of mucus encourage path ogen elimination and additionally safeguards the protective mucus layers.
What is goblet cell metaplasia?
A hallmark of chronic lung disease, goblet cell metaplasia lacks curative treatment. In this disease, mucin-secreting goblet cells accumulate in the airway and thus, invoke mucus hypersecretion. This blockage affects epithelial cells, immune cells, and other types in the airways.
How to see goblet cells?
Goblet cells are visible through laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM).[8] Some tissues for light microscopy are dehydrated in graded ethanols and embedded in plastic or resin. Methods for staining tissues are the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), mucicarmine stains, and iron hematoxylin.[9] In one study, researchers used nine different locations and three different depths to scan goblet cells. Using laser scanning confocal microscopy can determine the size, shape, reflectivity of goblet cells, and cell counting. Due to their balloon-like appearance and size, goblet cells were reportedly easily differentiated from their surrounding cells. Through a non-invasive manner, LSCM remains a promising method for the quantification of goblet cells.[8] A different study examined goblet cell carcinoids through light microscopy on paraffin sections. These sections were then mounted with Entellan and not counterstained to better visualize the product. Light microscopy was able to identify goblet cells in the submucous and muscle layer of the appendix. [10]