How do you classify epithelium?
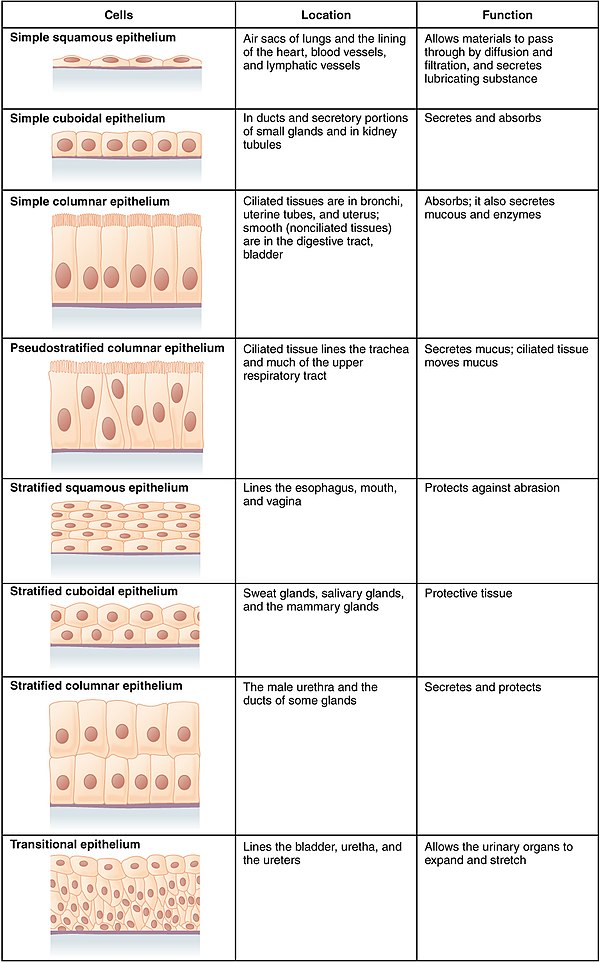
Epithelia are classified by: 1. the number of cell layers 2. the cell shaoe at the surface Simple squamous epithelium - Consists of a single layer of flattened cells - When viewed looking onto the surface, the irregularly shaped cells display a spherical to oval nucleus, & the cells are tightly bound together.
What are the characteristics of simple squamous epithelium?
1. the number of cell layers 2. the cell shaoe at the surface Simple squamous epithelium - Consists of a single layer of flattened cells - When viewed looking onto the surface, the irregularly shaped cells display a spherical to oval nucleus, & the cells are tightly bound together.
What are the different types of epithelial cells?
Different types of epithelial cells based on shape include: Squamous epithelium: Squamous epithelial cells are flat and sheet-like in appearance. Cuboidal epithelium: Cuboidal epithelial cells are cube-like in appearance, meaning they have equal width, height and depth.
What is epithelial tissue made of?
Epithelial tissue is made up of epithelial cells. The cells can be different shapes and can be arranged in a single layer or multiple layers depending on where they are in your body and what kind of functions they have. In biology, a cell is the smallest unit that can live on its own. Cells make up all living organisms and the tissues of your body.

Which epithelium has flat cells?
Simple squamous epitheliumSimple squamous epithelium cells are flat in shape and arranged in a single layer. This single layer is thin enough to form a membrane that compounds can move through via passive diffusion.
What type of epithelium is composed of flat cells quizlet?
The most correct classification of an epithelial tissue consisting of a single layer of thin, flat cells is: simple columnar epithelium.
What tissue has a single layer of flat cells?
Simple EpitheliumSimple Epithelium The endothelium is the epithelial tissue that lines vessels of the lymphatic and cardiovascular system, and it is made up of a single layer of squamous cells.
Why are squamous cells flat?
Squamous epithelial cells are flat and are usually found lining surfaces that require a smooth flow of fluid, such as your blood vessels. They also line areas that require a very thin surface for molecules to pass through, such as the air sacs in your lungs.
What is a stratified squamous epithelium?
Stratified squamous epithelium: This type of epithelium usually has protective functions, including protection against microorganisms from invading underlying tissue and/or protection against water loss. The outer layer of your skin (the epidermis) is made of stratified squamous epithelial cells.
What is stratified columnar epithelium?
Stratified columnar epithelium is a rare type of epithelial tissue composed of column-shaped cells arranged in multiple layers. It is found in the conjunctiva, pharynx, anus, and male urethra. It also occurs in embryo.
Where is stratified squamous epithelium found?
Stratified squamous epithelia are found in nearly every organ system where the body comes into close contact with the outside environment – from the skin to the respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive systems.
What are the types of stratified epithelium?
Stratified epitheliumSquamous. - nonkeratinized (covers the mucosa) - keratinized (skin)Cuboidal (lines excretory ducts of glands)Columnar (conjunctiva of the eyelids)Transitional (urinary tract)
What type of epithelium contains thin flat cells stacked upon each other?
Simple squamous epithelium – a single layer of thin flattened cells. This type of epithelium forms thin delicate sheets of cells through which molecules can easily pass (diffusion, filtration).
What epithelial cells are flat and slightly irregular in shape?
Squamous epithelial cells are generally round, flat, and have a small, centrally located nucleus. The cell outline is slightly irregular, and cells fit together to form a covering or lining.
Where can simple squamous epithelial tissue be found?
Simple squamous epithelia are found lining the cavities of the body including the pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities, or in areas where passive diffusion occurs, such as glomeruli in the kidney and alveoli in the respiratory tract.
How many layers does transitional epithelium have?
Transitional epithelium is made up of three types of cell layers: basal, intermediate, and superficial.
What are the superficial layers of the epithelium made of?
the superficial layers are composed of cells that are dead. These cells lack nucli & all organells, & instead are filled w/ the protein keratin <- w/ is a tough, protective protien that strengthens the tissue. New cells produced in the basal region of the epithelium migrate toward the apical surface of the tissue.
Which epithelium is thicker?
Contains 2 or more layers of cells, and the superficial cells tend to be cuboidal shape. Stratified cuboidal epithelium, like simple epithelium forms tubes & coverings. Stratified epithelium is thicker & functions in protection and secretion. This tissue forms the walls of the ducts of most exocrine glands, such as the ducts of the sweat glands in the skin, the lining of some parts of the male urethra, & the periphery of ovarian follicles
What are basal cells?
In a relaxed state, the basal cells appear cuboidal or polyhedral , & the apical cells are large & rounded. Glands. : r individual cells or multicellular organs composed predominantly of epithelial tissue. They secret substances either for use elsewhere in the body or for elimination from the body.
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Physical protection: epithelial tissues protect both external & internal surfaces from dehydration, abrasion, & destruction by physical, chemical, or biological agents. Selective permeability: the epithelial cells in the epithelium act as "gatekeepers". Secretions: some epithelial cells are specialized to produce & release secretions.
What is the name of the unicellular glands that are found in the microvilli?
often contains microvilli & a scattering of unicellular glands called goblet cells. Individual microvilli collectively appear as a bright, fuzzy structure known as a brush border.
What is the first type of connective tissue to emerge in the developing embryo?
1st type of connective tissue to emerge in the developing embryo. It has a star-shaped (stell ate).
Which epithelial layer contains 2 or more layers of epithelial cells?
Stratified epithelium. contains 2 or more layers of epithelial cells. Only the cell in the deepest (basal) layer r in direct contact w/ the basement membrane. Provides either more structural support or better protection for underlying tissue.
What are the different types of epithelial cells?
The common types are simple squamous cells, simple cuboidal cells, simple columnar, stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar and pseudostratified columnar.
Which side of the epithelial cell faces the underlying tissue?
First, these cells are polarized. The top or apical side is the one that faces the cell surface, while the bottom or basal side faces the underlying tissue.
What Is the Role of Epithelial Tissue?
In addition, they are in glands. Epithelial cells have many roles in an organism, such as playing a part in secretion, absorption, sensation, protection and transport.
How do epithelial cells help you stay cool?
This keeps out environmental problems like dirt, bacteria and viruses. Additionally, epithelial cells can help you stay cool by allowing you to sweat in hot conditions. Their ability to stretch allows your skin to move and stay flexible.
What are the cells that line the body?
It consists of epithelial cells, which line the surfaces of the body. Epithelial cells are tightly packed in various organ systems, such as your skin. You can also find these cells lining the airways and respiratory system, blood vessels, urinary tract, digestive tract and kidneys.
Why are epithelial cells important?
Epithelial cells have important roles in secretion and absorption. They help multicellular organisms maintain a stable internal environment.
What is the function of basal lamina?
The function of the basal lamina varies based on its location. For example, the basement membrane in a kidney works like a filter. Sometimes, epithelial cells become cancerous and go through the basal lamina to grow into other tissues.
