- Errors in Meiosis Meiosis is an orderly phenomenon, which guarantees every stage with a suitable finish, but sometimes, at any point the result may be unexpected, causing abnormalities. ...
- Patau syndrome ...
- Edwards syndrome ...
- Klinefelter’s Syndrome ...
- Turner’s Syndrome ...
- Jacobs syndrome ...
Does crossing over always occur in meiosis?
Crossing over (recombination) only occurs during Prophase 1 of Meiosis because at this point homologous chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell. …. However, after meiosis 1, the newly formed cells consist of single chromosomes, instead of homologous chromosomes. Therefore, crossing over cannot occur after meiosis 1.
What is the end result in meiosis?
What is the end result of meiosis? The end result of meiosis is four haploid cells that are genetically different from their parent cells. These cells are called gametes.
How can error in meiosis can cause abnormalities?
Errors during meiosis can alter the number of chromosomes in cells and lead to genetic disorders. People are always pointing out differences between cultures, ethnicities and nationalities. But we all belong to the same species. DNA evidence shows that all humans are more than 99% genetically identical.
What is the correct sequence of meiosis?
Correct Answer - B The correct sequence of events of meiosis are synapsis (in zygotene) `to`crossing over (in pachytene)`to`terminalisation of chiasmata (in diplotene)`to`disappearance of nucleolus (in diakinesis).

What are 2 errors that can occur during meiosis?
Nondisjunctions, Duplications, and Deletions Of all the chromosomal disorders, abnormalities in chromosome number are the most easily identifiable from a karyogram. Disorders of chromosome number include the duplication or loss of entire chromosomes, as well as changes in the number of complete sets of chromosomes.
What is the most common error in meiosis?
non-disjunctionOne of the most common errors during meiosis is non-disjunction. Non-disjunction occurs when the chromosomes fail to separate properly as the cell divides.
What can cause errors in meiosis?
They are caused by nondisjunction, which occurs when pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis. The risk of nondisjunction increases with the age of the parents.
What type of error in meiosis causes Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is caused by a random error in cell division that results in the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. The type of error is called nondisjunction (pronounced non-dis-JUHNGK-shuhn).
What can go wrong during meiosis quizlet?
What can go wrong during meiosis? A gamete can get the wrong number of chromosomes. Portions of a chromosome may be lost. Part of a chromosome can get inverted.
What errors can occur during mitosis?
Sources of mitotic errorsSpindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) defects. The objective of mitosis is to faithfully segregate the replicated chromosomes into two new daughter cells. ... Cohesion defects. ... Merotelic attachments. ... K–MT stability. ... Centrosome amplification. ... Timing of centrosome separation. ... Tetraploidy.
What sorts of mistakes or errors are sometimes made during meiosis I and meiosis II?
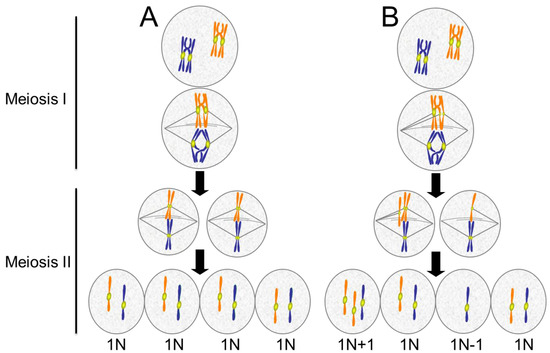
Figure 2 Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis, resulting in an abnormal chromosome number. Nondisjunction may occur during meiosis I or meiosis II.
What are the 4 chromosomal abnormalities?
Chromosomal aberrations, or abnormalities, are changes to the structure or number of chromosomes, which are strands of condensed genetic material. ... The four main types of structural chromosomal aberrations are deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation.More items...
How do errors during meiosis contribute to evolution by natural selection?
If a mutation occurs in cells that will make gametes by meiosis or during meiosis itself, it can be passed on to offspring and contribute to genetic variability of the population. Mutations are the sole source of genetic variability that can occur in asexual reproduction.
Does Down syndrome occur in meiosis?
Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome (DS) is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities. The majority of full trisomy 21 is caused by chromosomal nondisjunction occurring during maternal meiotic division (∼90%). Errors occur more frequently in the first maternal meiotic division than the second (73% vs.
What will happen if something goes wrong with meiosis?
When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the union leads to a baby with 46 chromosomes. But if meiosis doesn't happen normally, a baby may have an extra chromosome (trisomy), or have a missing chromosome (monosomy). These problems can cause pregnancy loss. Or they can cause health problems in a child.
What stage of meiosis causes Turner syndrome?
These findings suggest that most problems related to loss of a sex chromosome in Turner syndrome occur during the pairing of the X and Y chromosomes during paternal meiosis.
What sorts of mistakes or errors are sometimes made during meiosis I and meiosis II?
Figure 2 Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis, resulting in an abnormal chromosome number. Nondisjunction may occur during meiosis I or meiosis II.
Which effect is most likely caused by nondisjunction during meiosis?
Nondisjunction during meiosis is the most common cause of the aneuploidies, which can also occasionally result from a chromosomal rearrangement (e.g., Robertsonian translocation or a balanced sex chromosome translocation) [26].
What is nondisjunction in meiosis?
The phenomenon of unequal separation in meiosis is called nondisjunction. If nondisjunction causes a missing chromosome in a haploid gamete, the diploid zygote it forms with another gamete will contain only one copy of that chromosome from the other parent, a condition known as monosomy.
What type of error in meiosis causes aneuploidy quizlet?
Nondisjunction is a situation where a pair of homologous chromosomes fails to separate during meiosis I or meiosis II. Failure to separate causes aneuploidy which is a condition where a zygote will have an abnormal amount of chromosome.
What is the primary method of detecting chromosome abnormalities in humans?
The isolation and microscopic observation of chromosomes forms the basis of cytogenetics and is the primary method by which clinicians detect chromosomal abnormalities in humans. A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes, including their length, banding pattern, and centromere position.
What are the two categories of chromosome disorders?
Chromosome disorders can be divided into two categories: abnormalities in chromosome number and chromosome structural rearrangements. Because even small segments of chromosomes can span many genes, chromosomal disorders are characteristically dramatic and often fatal.
What is the term for a segment of genetic material that breaks from one chromosome and reattache?
Finally, the karyotype can pinpoint translocations , which occur when a segment of genetic material breaks from one chromosome and reattaches to another chromosome or to a different part of the same chromosome. Translocations are implicated in certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia.
How to identify chromosomes?
The geneticist then stains chromosomes with one of several dyes to better visualize the distinct and reproducible banding patterns of each chromosome pair. Following staining, chromosomes are viewed using bright-field microscopy. An experienced cytogeneticist can identify each band. In addition to the banding patterns, chromosomes are further identified on the basis of size and centromere location. To obtain the classic depiction of the karyotype in which homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned in numerical order from longest to shortest, the geneticist obtains a digital image, identifies each chromosome, and manually arranges the chromosomes into this pattern (Figure 1).
How many copies of each chromosome are in each gamete?
Figure 2: Following meiosis, each gamete has one copy of each chromosome. Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes (meiosis I) or sister chromatids (meiosis II) fail to separate during meiosis.
Why do humans have deleterious effects?
In part, this occurs because of a process called X inactivation.
When did the chromosome 18 inversion occur?
The chromosome 18 inversion is believed to have occurred in early humans following their divergence from a common ancestor with chimpanzees approximately five million years ago . Researchers have suggested that a long stretch of DNA was duplicated on chromosome 18 of an ancestor to humans, but that during the duplication it was inverted (inserted into the chromosome in reverse orientation.
What is the primary method of detecting chromosome abnormalities in humans?
Disorders in Chromosome Number. The isolation and microscopic observation of chromosomes forms the basis of cytogenetics and is the primary method by which clinicians detect chromosomal abnormalities in humans. A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes, including their length, banding pattern, and centromere position.
How to identify chromosome inversions?
Chromosome inversions and translocations can be identified by observing cells during meiosis because homologous chromosomes with a rearrangement in one of the pair must contort to maintain appropriate gene alignment and pair effectively during prophase I.
What is the karyotype of a chromosome?
A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes, including their length, banding pattern , and centromere position. To obtain a view of an individual’s karyotype, cytologists photograph the chromosomes and then cut and paste each chromosome into a chart, or karyogram ( Figure 1 ).
What are the two categories of chromosome disorders?
Chromosome disorders can be divided into two categories: abnormalities in chromosome number and chromosome structural rearrangements. Because even small segments of chromosomes can span many genes, chromosomal disorders are characteristically dramatic and often fatal.
How many pairs of chromosomes are there in a human?
In humans, an individual with the typical number of chromosomes has 22 pairs of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) and one pair of sex chromosomes (X and Y; such as is seen in the karyotype in Figure 1). An individual with an error in chromosome number is described as aneuploid, a term that includes monosomy (loss of one chromosome) ...
When does nondisjunction occur?
Figure 2 Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis, resulting in an abnormal chromosome number. Nondisjunction may occur during meiosis I or meiosis II. Photo credit Tweety207; Wikimedia.
How to determine karyotype?
To observe an individual’s karyotype, a person’s cells (like white blood cells) are first collected from a blood sample or other tissue. In the laboratory, the isolated cells are stimulated to begin actively dividing. A chemical called colchicine is then applied to cells to arrest condensed chromosomes in metaphase.
What is the primary method of detecting chromosome abnormalities in humans?
The isolation and microscopic observation of chromosomes forms the basis of cytogenetics and is the primary method by which clinicians detect chromosomal abnormalities in humans. A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes, including their length, banding pattern, and centromere position.
What are the two categories of chromosome disorders?
Chromosome disorders can be divided into two categories: abnormalities in chromosome number and chromosome structural rearrangements. Because even small segments of chromosomes can span many genes, chromosomal disorders are characteristically dramatic and often fatal.
What is the term for a segment of genetic material that breaks from one chromosome and reattache?
Finally, the karyotype can pinpoint translocations , which occur when a segment of genetic material breaks from one chromosome and reattaches to another chromosome or to a different part of the same chromosome. Translocations are implicated in certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia.
How to identify chromosomes?
An experienced cytogeneticist can identify each band. In addition to the banding patterns, chromosomes are further identified on the basis of size and centromere location. To obtain the classic depiction of the karyotype in which homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned in numerical order from longest to shortest, the geneticist obtains a digital image, identifies each chromosome , and manually arranges the chromosomes into this pattern.
How many copies of each chromosome are in each gamete?
Figure 7.8 Following meiosis, each gamete has one copy of each chromosome. Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes (meiosis I) or sister chromatids (meiosis II) fail to separate during meiosis.
Why do humans have deleterious effects?
In part, this occurs because of a process called X inactivation.
When did the chromosome 18 inversion occur?
The chromosome 18 inversion is believed to have occurred in early humans following their divergence from a common ancestor with chimpanzees approximately five million years ago . Researchers have suggested that a long stretch of DNA was duplicated on chromosome 18 of an ancestor to humans, but that during the duplication it was inverted (inserted into the chromosome in reverse orientation.
Where does meiosis occur?
Meiosis is a two-step process that occurs in the reproductive organs. The steps are called meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes line up in pairs at the centre of a cell. Then, they are pulled apart into two new cells.
What does the letter N mean in meiosis?
Diagram showing normal meiosis as well as nondisjunction errors that can occur in meiosis I and II. The letter “n” stands for the number of chromosomes (© 2019 Let’s Talk Science based on an image by Bioninja ).
What happens if you have too many chromosomes?
Sarah Gordy is a British actress who has Down syndrome. In 2018, she became the first woman with Down syndrome to receive the prestigious Most Excellent Order of the British Empire.
What problems do extra X and Y chromosomes cause?
In a female fetus, an extra X chromosome causes Triple X syndrome. It is associated with learning disabilities and organ abnormalities.
How many chromosomes are there in the human body?
The human body has 23 different chromosomes. Each cell has two copies of each chromosome, one from your mother and the other from your father. This makes for a grand total of 46 chromosomes. Almost every single cell in your body contains the exact same chromosomes. The human karyotype has 23 sets of chromosomes.
Can meiosis cause genetic disorders?
Share on: Errors during meiosis can alter the number of chromosomes in cells and lead to genetic disorders. People are always pointing out differences between cultures, ethnicities and nationalities. But we all belong to the same species. DNA evidence shows that all humans are more than 99% genetically identical.
