.bmp)
What happens when air comes out of a balloon?
When the air comes out of the hole, it creates what's called a force. (You can think of a force as something that pushes. You can tell that this happens because if you let the air out of the balloon slowly and hold your hand in front of it, you can feel the air pushing on your hand.) Well,...
What causes a balloon to go in the opposite direction?
As air particles leave the balloon, they exert a force in the opposite direction. This causes the balloon to go in the direction of that force. The air that is flowing out of the balloon in one direction provides a force in the opposite direction.
How can you tell that air is pushing on a balloon?
You can tell that this happens because if you let the air out of the balloon slowly and hold your hand in front of it, you can feel the air pushing on your hand.) Well, one of the most important rules about the way the world works is that "for every force there is an equal and opposite force."
What happens when a balloon is inflated with rubber?
The rubber is under extreme tension, putting the air pressure inside the balloon ever so slightly greater than the pressure on the outside of the balloon. As the balloon constricts, some gas is slowly pushed out.
What happens when air is pushed one way?
The air gets pushed one way, so the balloon gets pushed the other way.
Why is it so hard to blow up a balloon?
Sometimes it can be pretty hard to blow up a balloon, because it doesn't really want to stretch. And if you don't tie it off right away, it will probably unstretch by pushing air out of the hole. When the air comes out of the hole, it creates what's called a force. (You can think of a force as something that pushes.
What is the pressure with which the membrane of the balloon would compress the helium inside?
Solving the equation, I got Δ p = 5.73 P a. That would be the pressure with which the membrane of the balloon would compress the helium inside. It can give me an estimate of the flow at this extreme conditions.
Does external pressure affect the pressure of a balloon?
I'm not sure this is correct, but I suppose it is, as it seems to me that the external pressure acts only as an offset to the state of the internal pressure, and the stress on the membrane of the balloon depends only on the strain caused by expansion of its diameter (which will be controlled by the external pressure but won't be affected in terms of value by it).
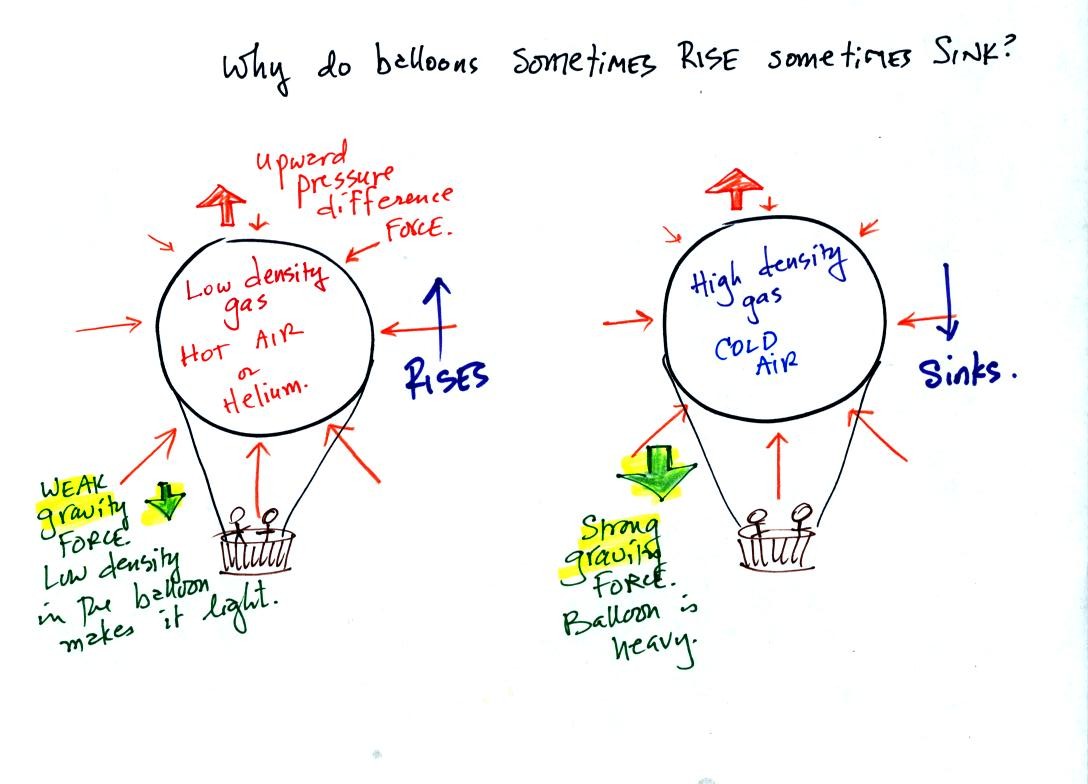
What is the physics behind a hot air balloon?
The physics behind a hot air balloon is buoyancy. When heated, the air inside the balloon becomes less dense than the surrounding atmosphere. Less dense things placed inside of more dense things float, and hence the hot air balloon rises, like an ice cube floating in a glass of water.
How does a floating balloon work?
To make this floating thing actually happen, there's of course a lot of cool microphysics going on. The air molecules constantly strike the outside of the balloon in all directions, while the molecules inside the balloon are doing the same thing. Almost magically, all these interactions and bombardments nearly cancel each other out , leaving a slight pushing force that resists gravity and raises the balloon.
