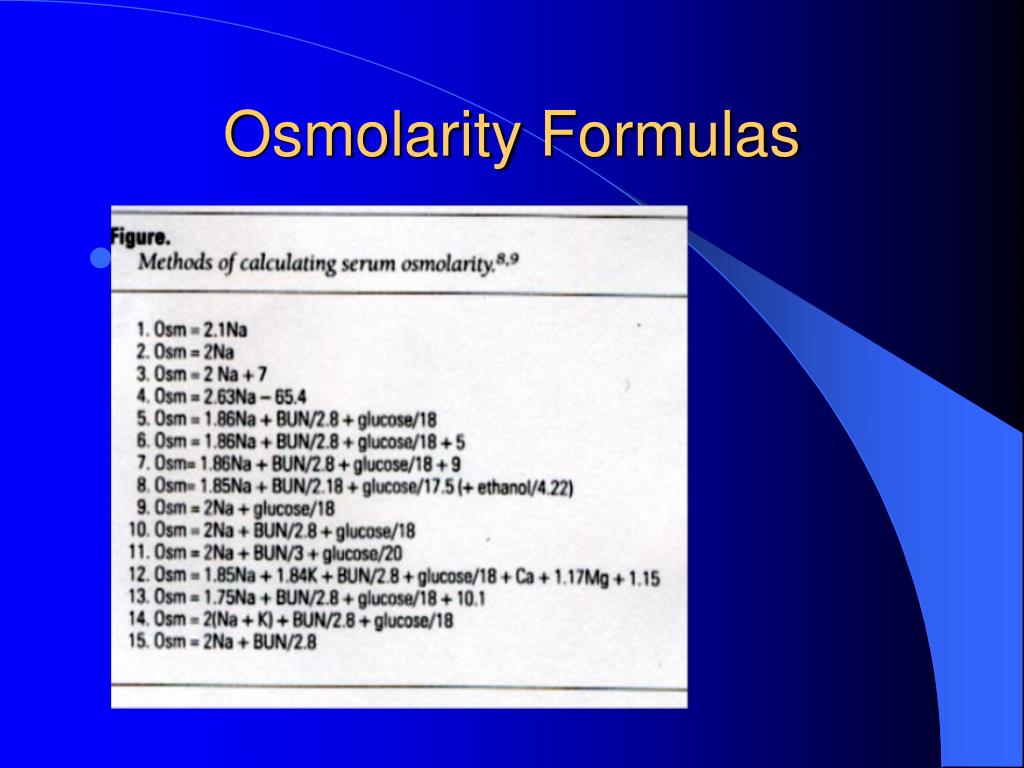
What is osmolite Cal?
OSMOLITE 1.0 CAL is therapeutic nutrition that provides complete, balanced nutrition for long- or short-term tube-feeding for patients with caloric requirements of less than 2000 calories per day or for patients with increased protein requirements. For tube feeding. For supplemental or sole-source nutrition.
What is osmolite tube feed?
Osmolite is a 1.0kcal/ml, isotonic tube feed for people with caloric requirements of less than 2000 Cal per day or for patients with increased protein requirements. Osmolite is available in 1000ml Ready to Hang bottles, which attach directly to Abbott Nutrition giving sets. Suitable for lactose intolerance* without fibre.
What is the difference between osmolite and vital HN?
Osmolite contains approximately 29% of calories from lipid and 54% of calories from hydrolyzable carbohydrate (mostly sugars), and Vital HN provides about 10% of calories from lipids and 74% from carbohydrates.
Does osmolite need to be refrigerated?
Osmolite is suitable as a sole or supplemental source of nutrition to be used under medical supervision. Ready to hang. Shake well. Open immediately prior to use. Once opened, cover and place in refrigeration, discarding any unused feed after 24 hours. Store unopened at room temperature avoiding prolonged exposure to light.
How long does osmolite last?
Where does tube feeding start?
Is osmolite a tube feed?
What kind of formula is Osmolite?
A high-protein, low-residue formula, Osmolite 1.2 Cal is for tube-fed patients who may benefit from increased protein and calories. Concentrated calories (1.2 Cal/mL) and high in protein (18.5% of Cal) to help patients gain and maintain healthy weight. Protein is needed for lean body tissue maintenance and repair.
Is Osmolite isotonic?
Osmolite is a 1.0kcal/ml, isotonic tube feed for people with caloric requirements of less than 2000 Cal per day or for patients with increased protein requirements.
Is Osmolite milk based?
Contains milk and soy ingredients.
What is Osmolite made of?
Water, Corn Maltodextrin, Corn Syrup Solids, Sodium Caseinate, Soy Protein Isolate, Canola Oil, Corn Oil, Medium Chain Triglycerides, Calcium Caseinate.
What is an isotonic tube feeding formula?
Isotonic Formulas If the enteral formula has an osmolality near that of the body fluid it is considered an isotonic formula. Isotonic formulas are generally well tolerated by patients.
What type of formula is Jevity?
Product Overview. JEVITY 1 CAL is a fiber-fortified tube-feeding formula. For tube feeding; For supplemental or sole-source nutrition; May be used for oral feeding of patients with altered taste perception; Not for parenteral use.
What is peptide-based formula?
Peptide-based formulas contain proteins that have been hydrolyzed to produce peptides of varying lengths and are also referred to as “elemental” diets as well as “partially” or “semi-” elemental.
What formula is used for tube feeding?
STANDARD FORMULAS Examples include Isosource® HN, Isosource® 1.5 Cal, Fibersource® HN, Nutren® 1.0, Nutren® 1.0 Fiber, Nutren® 1.5, Nutren® 2.0, Replete® and Replete® Fiber, Nutren® Junior, Nutren® Junior Fiber.
What is the best tube feeding formula?
Jevity 1.5 CAL High-Protein Nutrition with Fiber. $2.48 - $137.03. ... Jevity 1.2 CAL High Protein Nutrition with Fiber. $2.06 - $127.00. ... Most Popular. ... NUTREN® 1.5. ... Osmolite 1.5 Cal High Protein & High Calorie Nutrition Drink. ... PediaSure 1.5 Cal Balanced Nutrition - Vanilla. ... Most Popular. ... PediaSure 1.0 Cal with Fiber.More items...
Is Osmolite good for you?
The Osmolite 1.5 Cal has a healthy blend of nutritious fat of high-oleic safflower, canola, and MCT oils. These oils have a very high content of omega-6 fatty acids, which support brain development, strengthen the immune system, and regulate blood pressure.
Can you drink Osmolite?
These drinks (Jevity, Osmolite) can be consumed orally but aren't designed to taste good and are often used in feeding tubes. Your doctor will have to supervise use of these.
Do tube feeds provide hydration?
A feeding tube is a treatment to give food and fluids by tubes if you can't eat. Artificial hydration is the process of taking in water and fluids through a tube or an IV.
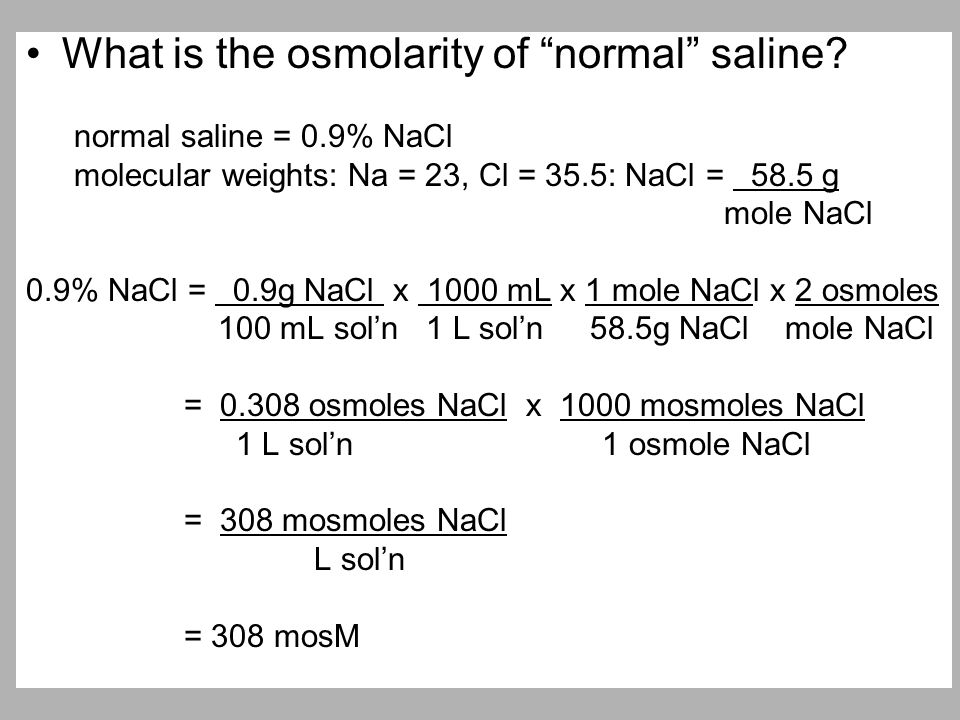
What is the example of isotonic solution?
Common examples of isotonic solutions are 0.9% normal saline and lactated ringers. These fluids are useful when the patient has lost fluid volume from blood loss, trauma, or dehydration due to excessive nausea/vomiting or diarrhea.
Is Jevity isotonic?
Jevity is a 1.0kcal/ml nutritionally complete and balanced isotonic liquid feed enriched with fibre to help maintain normal bowel function. Fibre has an important role in the diet by helping to support gastrointestinal function1,2,3.
What are isotonic & hypertonic solutions?
Isotonic solutions are most commonly used for regular maintenance of clean, healthy sinuses – a soothing wash to remove excess mucus, dust, and allergens – and for helping address such things as post-nasal drip. A hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of salt than your body's fluids.
Do tube feeds provide hydration?
A feeding tube is a treatment to give food and fluids by tubes if you can't eat. Artificial hydration is the process of taking in water and fluids through a tube or an IV.
What is the Z-1-HETCA-CoA isomer?
The ( Z )-1-HETCA-CoA isomers would chemically racemize at C-4 and thus reduction of only the erythro isomer would produce HTCA or its CoA derivative with the correct stereochemistry at C-4 and C-5. Retaining the CoA portion of the molecule as indicated in Figure 4 would produce an activated carboxylic acid that could be used for the incorporation of HTCA into the final methanofuran. The biosynthetic intermediates, erythro -HPTCA, threo -HPTCA, erythro -PTCA, and threo -PTCA were each identified in cell extracts of Methanococcus vannielii, M. thermophilia strain TM-1, and M. thermoautotrophicus, indicating the widespread occurrence of this pathway in the methanogens.
How many calories are in osmolite?
Osmolite contains approximately 29% of calories from lipid and 54% of calories from hydrolyzable carbohydrate (mostly sugars), and Vital HN provides about 10% of calories from lipids and 74% from carbohydrates.
How to feed a horse with a pellet feed tube?
Pelleted feeds should be soaked in warm water to soften before mixing in a blender (ratio of 1 kg pelleted feed to 6 L of water). A fresh batch of diet should be made before each feeding. A tube with a ½-inch (12-mm) inner diameter is suitable for most enteral diets that contain fiber. The end of the tube should be open ended, rather than fenestrated, to prevent the tube from becoming clogged. Intermittent nasogastric intubation or placement of an indwelling nasogastric tube can be used to facilitate feeding. In hospitalized horses feeding tubes can be left in place for up to 8 days, although nasopharyngeal irritation and mucoid nasal discharge are expected outcomes (when longer term AEF is anticipated, placement of the tube through cervical esophagostomy is recommended). Softer silicon tubes are less irritating compared with tubes made of polyvinylchloride, do not tend to harden when left in place, and are generally recommended for horses requiring AEF for a number of days. Before placing the tube, the clinician should establish that the diet solution flows adequately through the tube. It may be necessary to add more water or to mix the feed in a blender a second time. The tube should be positioned in the stomach rather than the distal esophagus to minimize risk of reflux of feed around the tube. The tube should be secured to the halter; between feedings application of a muzzle may be necessary to prevent the horse from dislodging the tube. A marine bilge pump is recommended for infusion of fiber-containing diets. After administration of the diet, the tube should be flushed with approximately 1 L of water followed by a small volume of air to ensure that no feed material remains in the tube. The end of the tube should be capped with a syringe case between feedings.
What is the function of NAA?
One role is to serve as a substrate for NAAG, an excitatory neuromodulator. Another is that NAA itself appears to be an excitatory neuromodulator. Intraventricular injection of NAA produced epileptiform discharges. Hippocampal slice preparations perfused with NAA brain produces repetitive firing of hippocampal CA3 neurons. Genomic deletion within a region in which the aspartoacylase gene is located result in the tremor rat with absence-like seizures and spongiform degeneration. NAA has been proposed as a neuron–glia signaling system, perhaps critical for the formationof nodes of Ranvier.
What is the role of aldehyde reductase in neuropathy?
Aldehyde reductase is thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and cataracts in diabetes Das and Srivastava (1985). Considerable evidence supports the hypothesis that enhanced metabolism of glucose through the polyol pathway results in the production of significant quantities of sorbitol: It accumulates in cells because of (1) poor penetration across cellular membranes and (2) slow metabolism by sorbitol dehydrogenase, resulting in hyperosmotic stress and eventual loss of cellular integrity.
How is sorbitol metabolized?
In a further enzymatic step, sorbitol can be metabolized to fructose by the NAD-specific sorbitol dehydrogenase. The conversion of glucose to fructose by this means constitutes the polyol pathway of glucose metabolism, which plays a minor role in glucose metabolism in most tissues.
What enzyme catalyzes the reduction of an aldose to the corresponding sugar alcohol?
Aldehyde reductase, also known as aldose reductase, is an NAD (P)H-dependant enzyme that catalyses the reduction of an aldose to the corresponding sugar alcohol, in particular, D-glucose to sorbitol. Under normal conditions, the production of sorbitol constitutes in some tissues a significant fraction of the cellular osmolite.
Feeding Jejunostomy – Laparoscopic
undefined Elsevier Inc undefined, in Essential Surgical Procedures, 2016
Cofactors
Laura L. Grochowski, Robert H. White, in Comprehensive Natural Products II, 2010
Feeding Jejunostomy – Open
undefined Elsevier Inc undefined, in Essential Surgical Procedures, 2016
Aldehyde Reductase
Aldehyde reductase, also known as aldose reductase, is an NAD (P)H-dependant enzyme that catalyses the reduction of an aldose to the corresponding sugar alcohol, in particular, D-glucose to sorbitol. Under normal conditions, the production of sorbitol constitutes in some tissues a significant fraction of the cellular osmolite.
Nutrition Support
Joseph E. Parrillo MD, in Critical Care Medicine: Principles of Diagnosis and Management in the Adult, 2019
Nutrition
Jocelyn M. Logan-Collins MD, in The Mont Reid Surgical Handbook (Sixth Edition), 2008
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Hoby Hetherington, ... Mark R. Wellard, in Magnetic Resonance in Epilepsy (Second Edition), 2005
What is osmolite 1.5 cal?
Osmolite 1.5 Cal nutrition drink is a low-residue enteral feeding formula for patients needing increased calories and protein. This formula is high in calories to help patients gain and maintain weight and is ideal for those with limited volume tolerance. Osmolite 1.5 Cal High-Protein, High-Calorie Nutrition also offers complete, balanced nutrition with 24 essential vitamins and minerals. The formula is fortified with ultratrace minerals and conditionally essential nutrients to support good health which is particularly beneficial for patients requiring tube feeding. Patients with malabsorption also benefit from the formulation containing MCT oil has medium-chain triglycerides shown to absorb better.
Is osmolite high in protein?
Osmolite 1.5 Cal High-Protein, High-Calorie Nutrition also offers complete, balanced nutrition with 24 essential vitamins and minerals. The formula is fortified with ultratrace minerals and conditionally essential nutrients to support good health which is particularly beneficial for patients requiring tube feeding.
How long does osmolite last?
Ready to hang. Shake well. Open immediately prior to use. Once opened, cover and place in refrigeration, discarding any unused feed after 24 hours.
Where does tube feeding start?
Tube feeding usually starts in hospital and involves delivering a nutritionally complete liquid feed directly into the stomach or small bowel via a narrow tube. Your healthcare professional will be able to advise you on which tube feed is right for you or your child. * Not for people with galactosemia. SELECT FLAVOR N/A.
Is osmolite a tube feed?
Suitable for lactose intolerance* without fibre. Tube feeds are designed for people who cannot take in all of the calories and nutrients they need by mouth .
