Common Causes
There are no FDA-approved drugs that restore hearing loss. Another emerging area of research is gene therapy for hearing loss, though it could be many years before human testing begins. These and other developments towards restoring hearing in the scientific community are exciting but still preliminary.
Related Conditions
When a cause can be identified, the most common ones are: 2
- Infectious diseases like viruses (e.g., Lyme disease, bacterial meningitis)
- Trauma, particularly a head injury
- Autoimmune diseases, such as Cogan’s syndrome
Can You restore your lost hearing?
Hearing loss is a common problem caused by noise, aging, disease, and heredity. People with hearing loss may find it hard to have conversations with friends and family. They may also have trouble understanding a doctor’s advice, responding to warnings, and hearing doorbells and alarms. Approximately one in three people between the ages of 65 ...
Why do people lose their hearing?
- Difficulty hearing on the phone
- Finding it hard to keep up with a conversation
- Feeling tired or stressed from having to concentrate while listening
What are the problems with hearing loss?
What are the reasons for hearing loss?

Is presbycusis mixed hearing loss?
Presbycusis is the third most common chronic health condition among the elderly and it usually affects both ears equally. While men develop a high-frequency hearing loss, women mostly show a low-frequency hearing loss.
What type of hearing loss is sensorineural?
Sensorineural Hearing Loss This type of hearing loss occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes damaged. This loss generally occurs when some of the hair cells within the cochlea are damaged. Sensorineural loss is the most common type of hearing loss.
What are the 4 types of hearing loss?
The four types of hearing loss are sensorineural, conductive, mixed (sensorineural and conductive) and auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD).
What are the 3 types of hearing losses?
There are three basic types of hearing loss: Conductive hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss. Mixed hearing loss.
How do you know if hearing loss is sensorineural or conductive?
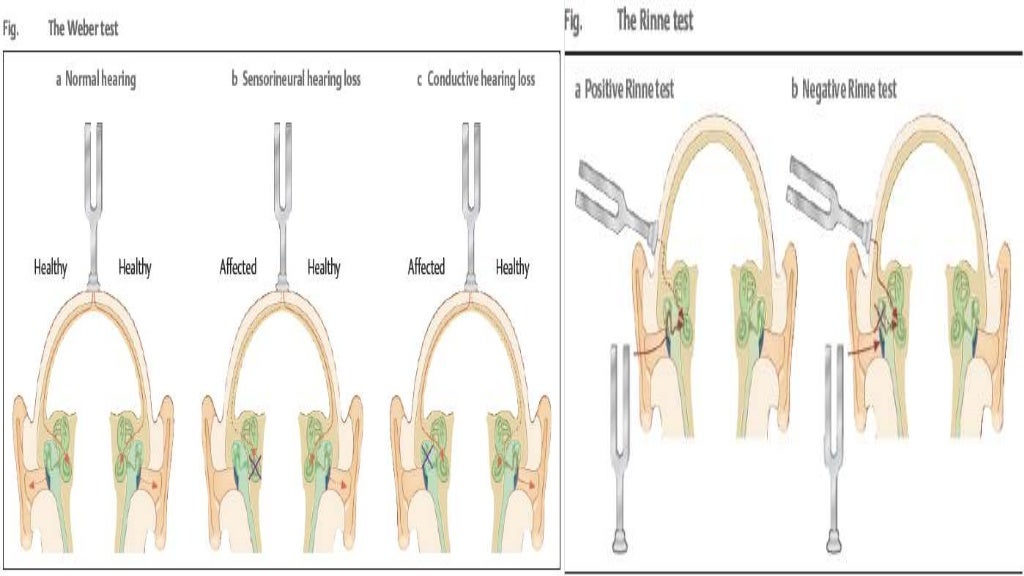
If the hearing loss is conductive, the sound will be heard best in the affected ear. If the loss is sensorineural, the sound will be heard best in the normal ear. The sound remains midline in patients with normal hearing. The Rinne test compares air conduction with bone conduction.
What are 3 causes of sensorineural hearing loss?
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Illnesses. Drugs that are toxic to hearing. Hearing loss that runs in the family. Aging.
What are the 5 levels of hearing loss?
There are 5 different levels of hearing loss: mild, moderate, moderately-severe, severe and profound. Mild Hearing Loss (26 dB- 40dB): this type of hearing loss is often associated with the inability to hear soft sounds. These sounds often include rustling leaves, bird chirping, or the refrigerator humming.
How do you classify types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss can be classified according to the severity or degree of the disease. Hearing losses between 26 and 40 dB are considered mild, 41 and 55 dB moderate, 56 and 70 dB moderately severe, 71 and 90 dB severe, and greater than 91 dB profound (Table 1) [5, 6].
What is the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss?
Rothholtz says that the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss in adults is aging. This form of hearing loss occurs in the inner ear when tiny hair cells become damaged. The cells do not regrow, so the damage is permanent.
What is the most common type of hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss The most common type of hearing loss is sensorineural. It is a permanent hearing loss that occurs when there is damage to either the tiny hair-like cells of the inner ear, known as stereocilia, or the auditory nerve itself, which prevents or weakens the transfer of nerve signals to the brain.
Is sensorineural hearing loss progressive?
Progressive sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is defined as hearing loss of unknown etiology with fairly high-speed progression. Its diagnostic criteria consist of the following: that it is 1) progressive, 2) with bilateral involvement, and 3) of unknown etiology.
What is a functional hearing loss?
FUNCTIONAL hearing loss is a term applied to all nonorganic deafness. It is a condition in which the patient does not fully utilize his residual hearing as determined by numerous available tests for detecting organic loss in auditory acuity.
What is the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss?
Rothholtz says that the most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss in adults is aging. This form of hearing loss occurs in the inner ear when tiny hair cells become damaged. The cells do not regrow, so the damage is permanent.
What is the meaning of sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural deafness is a type of hearing loss. It occurs from damage to the inner ear, the nerve that runs from the ear to the brain (auditory nerve), or the brain.
What is sensorineural hearing loss on audiogram?
Sensorineural hearing losses (SNHL) SNHL are characterized by a reduction in hearing ability due to disorders involving the cochlea and/or the auditory nervous system. This type of hearing loss is usually irreversible. Sensorineural hearing losses can be further divided into sensory and neural losses.
What is the definition of sensorineural?
Definition of sensorineural : of, relating to, or involving the aspects of sense perception mediated by nerves sensorineural hearing loss.
What is age-related hearing loss?
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) is the loss of hearing that gradually occurs in most of us as we grow older. It is one of the most common conditions affecting older and elderly adults.
How to help someone with hearing loss?
You and your family can work together to make living with hearing loss easier. Here are some things you can do: 1 Tell your friends and family about your hearing loss. The more friends and family you tell, the more people there will be to help you cope with your hearing loss. 2 Ask your friends and family to face you when they talk so that you can see their faces. If you watch their faces move and see their expressions, it may help you to understand them better. 3 Ask people to speak louder, but not shout. Tell them they do not have to talk slowly, just more clearly. 4 Turn off the TV or the radio when you aren't actively listening to it. 5 Be aware of noise around you that can make hearing more difficult. When you go to a restaurant, for example, don't sit near the kitchen or near a band playing music. Background noise makes it hard to hear people talk.
Why do we lose our hearing as we get older?
It can be difficult to distinguish age-related hearing loss from hearing loss that can occur for other reasons, such as long-term exposure to noise.
What should I do if I have trouble hearing?
Hearing problems can be serious. The most important thing you can do if you think you have a hearing problem is to seek advice from a health care provider. There are several types of professionals who can help you. You might want to start with your primary care physician, an otolaryngologist, an audiologist, or a hearing aid specialist. Each has a different type of training and expertise. Each can be an important part of your hearing health care.
Where can I find additional information about age-related hearing loss?
The NIDCD maintains a directory of organizations that provide information on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, taste, smell, voice, speech, and language.
How many people have difficulty hearing?
Approximately one in three people in the United States between the ages of 65 and 74 has hearing loss, and nearly half of those older than 75 have difficulty hearing. Having trouble hearing can make it hard to understand and follow a doctor's advice, respond to warnings, and hear phones, doorbells, and smoke alarms. Hearing loss can also make it hard to enjoy talking with family and friends, leading to feelings of isolation.
Can high blood pressure cause hearing loss?
Conditions that are more common in older people, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, can contribute to hearing loss. Medications that are toxic to the sensory cells in your ears (for example, some chemotherapy drugs) can also cause hearing loss. Rarely, age-related hearing loss can be caused by abnormalities of the outer ear or middle ear.
What is presbycusis hearing loss?
Presbycusis definition can be complicated but simply put it is a slowly progressing sensorineural hearing loss. It always affects both ears to the same degree, and usually starts at the age of 50. One characteristic of presbycusis is that sounds within the high-frequency range are significantly impacted (more so at the start of the illness) more than deeper sounds.
What happens if you have presbycusis and you have audiometry?
If speech audiometry is performed on a patient with presbycusis, the examination will reveal impaired speech comprehension.
How to diagnose presbycusis?
Among other things, this includes the examination of the ear using a specialist microscope (ear microscopy). In patients suffering from presbycusis, the ENT specialist will usually find a normally structured eardrum (i.e. no tear or hole in the eardrum). A pure-tone and speech audiogram are also performed to ultimately confirm the diagnosis. If all other causes can be excluded, the ENT specialist will usually recommend the provision of a hearing aid. Modern hearing aids can treat presbycusis efficiently and restore near-perfect comprehension of speech, tones and sounds.
What age does presbycusis start?
It always affects both ears to the same degree, and usually starts at the age of 50. One characteristic of presbycusis is that sounds within the high-frequency range are significantly impacted (more so at the start of the illness) ...
What does a speech audiometry test reveal?
Once the test is complete, the information collected from the exam will help doctor determine if there is a deficit in speech comprehension . If speech audiometry is performed on a patient with presbycusis, the examination will reveal impaired speech comprehension.
What is the purpose of audiometry test?
Once the test is complete, the information collected from the exam will help doctor determine if there is a deficit in speech comprehension.
What to do if you have presbycusis?
Once you have been diagnosed with presbycusis it is important to get it treated or following it up with the audiologist. For e.g. if you were having other medical concerns or were suffering with your sight, you would look for a treatment, get glasses etc. Similarily, it is important to get a treatment for this.
What is presbycusis hearing loss?
Presbycusis refers to bilateral age-related hearing loss . In literal terms, presbycusis means "old hearing" or "elder hearing."[1] It becomes noticeable around age 60 and progresses slowly; however, there is evidence that certain stressors can speed the rate of deterioration. The diagnosis can be confirmed with audiometry.[2] The hallmark of presbycusis is the impaired ability to understand high-frequency components of speech (voiceless consonants, such as p, k, f, s, and ch).[3] There is no cure; however, hearing aids that amplify sounds can be used to mitigate symptoms. Anatomically, presbycusis involves multiple components of the auditory system. It is primarily due to age-related changes in hair cells, the stria vascularis, and afferent spiral ganglion neurons.[4]
How many categories of presbycusis are there?
[6][8][9] Presently, there are thought to be six categories of presbycusis: sensory, neural, strial, mechanical, mixed, and indeterminate. [4][10]
What are the factors that contribute to presbycusis?
In addition to age-related degeneration leading to physiologic and anatomic changes, other contributing factors include genetic factors, hormones, exposure to loud noises or ototoxic agents, history of ear infection, and the presence of certain systemic diseases. [6][7]
How many people will have presbycusis by 2025?
Presbycusis affects more than half of older adults by age 75 and nearly all adults over age 90.[28] The World Health Organization estimates that by 2025, among those aged 60 and above, greater than 500 million will have significant age-related hearing loss. [29]
What is the most common cause of hearing loss?
Presbycusis is the most common cause of hearing loss worldwide and is estimated to affect approximately two-thirds of Americans aged 70 or older.[24] It is difficult to determine the exact prevalence because the criteria used to define hearing loss differs among investigators. There have been multiple attempts to assess the frequency of hearing loss among large cohort populations, including participants from studies such as the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES), and the health aging and body composition (ABC) study.[25] According to data from NHANES, which represents a cross-section of non-institutionalized Americans, the prevalence of hearing loss approximately doubles with each subsequent decade from age 12 to age 79.[26] Among participants in the Health ABC study, hearing loss was most prevalent in white men, followed by white women, black men, and black women. [27]
What is stria presbycusis?
Strial presbycusis: degeneration of stria vascularis cells. These cells are essential for maintaining the appropriate ion composition of endolymph to generate the endocochlear potential for signal transduction.[11] Sometimes referred to as metabolic presbycusis.
What are the genetic factors of presbycusis?
Genetic factors, specifically, differences in mitochondrial DNA expression genes related to oxidative stress, have been found in patients with presbycusis when compared to controls. [12][13][14]
What are the different types of hearing loss?
The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss. Here is what patients should know about each type.
Where does hearing loss occur?
This type of hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle ear where sound waves are not able to carry all the way through to the inner ear. Sound may be blocked by earwax or a foreign object located in the ear canal; the middle ear space may be impacted with fluid, infection or a bone abnormality; or the eardrum may have been injured.
Why do we need hearing tests?
Hearing testing is critical for discovering exactly what type of hearing loss you have, and will help determine the hearing care solution that is right for you. Hearing aids are available in many sizes, styles and technologies; there are also many alternatives to hearing aids.
How many people have hearing loss?
One in five Americans is affected by hearing loss, but there are many different causes -- and many different treatment options.
Can hearing loss discriminate?
Hearing problems don’t discriminate and can affect people at any stage of life. Don’t suffer in silence with hearing loss. Our center’s physicians are among the finest and most highly skilled otologists and neurotologists (ear, nose and throat doctors) in the world.
Can hearing aids help with hearing loss?
It can be a result of aging, exposure to loud noise, injury, disease, certain drugs or an inherited condition. This type of hearing loss is typically not medically or surgically treatable; however, many people with this type of loss find that hearing aids can be beneficial.
Can hearing loss be reversed?
In some people, conductive hearing loss may be reversed through medical or surgical intervention. Conductive hearing loss is most common in children who may have recurrent ear infections or who insert foreign objects into their ear canal.
What are the three types of hearing loss?
Hearing loss is defined as one of three types: Conductive (involves outer or middle ear) Sensorineural (involves inner ear) Mixed (combination of the two) Aging and chronic exposure to loud noises both contribute to hearing loss.
Why does hearing loss cause isolation?
Because hearing loss can make conversation difficult, some people experience feelings of isolation. Hearing loss is also associated with cognitive impairment and decline. The mechanism of interaction between hearing loss, cognitive impairment, depression and isolation is being actively studied.
What are the three tubes in the inner ear called?
The other fluid-filled chambers of the inner ear include three tubes called the semicircular canals (vestibular labyrinth). Hair cells in the semicircular canals detect the motion of the fluid when you move in any direction. They convert the motion into electrical signals that are transmitted along the vestibular nerve to the brain. This sensory information enables you to maintain your sense of balance.
What is the middle ear?
The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that holds a chain of three bones: the hammer (malleus), the anvil (incus) and the stirrup (stapes). These bones are separated from the outer ear by the eardrum (tympanic membrane), which vibrates when struck by a sound wave.
What part of the brain processes and interprets sound?
The auditory cortices sort, process, interpret and file information about the sound. The comparison and analysis of all the signals that reach the brain enable you to detect certain sounds and suppress other sounds as background noise.
Can hearing loss happen when your ears are plugged with wax?
Vivien Williams: Dr. Matthew Carlson says temporary hearing loss can happen when your ears are plugged with wax or fluid behind the ear drum, for example. Nerve-related hearing loss is usually permanent.
Can loud noises damage your ear?
Loud noise. Exposure to loud sounds can damage the cells of your inner ear. Damage can occur with long-term exposure to loud noises, or from a short blast of noise, such as from a gunshot.
What is the loss of hearing in presbycusis?
Individuals with sensory presbycusis show a major and sudden loss of hearing in the high-frequency range (4 kHz), indicating a selective deficit in transduction mechanisms of high-frequency sounds (Fig. 8B). Speech discrimination is normal. Although the hearing deficit is observed from middle age, the histopatho-logical problems believed to be mainly associated with the cochlear hair cells may start much earlier. Cochleas of humans with sensory presbycusis typically show loss of outer hair cells and less often of the inner hair cells of the organ of Corti (Fig. 8A) (123,130). The loss is diffuse or patchy and is mainly limited to the first quadrant of the cochlea's lower basal turn. This part of the cochlea is specialized for detection of high-frequency sounds. The affected sensory hair cells and other supporting cells (Hensen's and Claudius' cells) show accumulation of the aging pigment lipofuscin, the amount of which corresponds with the degree of sensory deficits.
What are the different types of presbycusis?
Based on the source of damage, four types of presbycusis are recognized: sensory, neural, metabolic (or strial ), and cochlear conductive (123,130). The onset of presbycusis may be any time from the third to sixth decade of life, depending on type.
What part of the cochlea is affected by sensory presbycusis?
8A) (123,130). The loss is diffuse or patchy and is mainly limited to the first quadrant of the cochlea's lower basal turn. This part of the cochlea is specialized for detection ...
When does presbycusis start?
The onset of presbycusis may be any time from the third to sixth decade of life, depending on type. Individuals suffering from these disturbances show distinct and differing audiograms (Fig. 8), which are clinically used to diagnose types of impairment.
How does speech discrimination affect the auditory system?
As a result, speech discrimination is reduced to 60% of the normal level. In the aging auditory system, the first-order sensory neurons are adversely affected. This damage ranges from synaptic structures between the hair cells and the dendrites of the auditory nerve fibers, accumulation of lipofuscin, to signs of degeneration in the cell bodies ...
