What is fumaric acid?
A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit -like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. [3] The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C 4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.
What is the difference between maleic acid and fumaric acid?
Maleic acid, the cis isomer (I), has a melting point of 130°C and a boiling point of 160°C; fumaric acid, the trans isomer (II), has a melting point of 286°C and a boiling point of 290°C. Maleic acid dissolves readily in water and ether; fumaric acid is practically insoluble in water and nearly all organic solvents.
How do you synthesize fumaric acid?
A traditional synthesis involves oxidation of furfural (from the processing of maize) using chlorate in the presence of a vanadium-based catalyst. Currently, industrial synthesis of fumaric acid is mostly based on catalytic isomerisation of maleic acid in aqueous solutions at low pH.
Is fumaric acid toxic to dogs?
The European Commission Scientific Committee on Animal Nutrition, part of DG Health, found in 2014 that fumaric acid is "practically non-toxic" but high doses are probably nephrotoxic after long-term use. [11]

Which type of isomerism is possible for fumaric acid?
Maleic acid and fumaric acid exhibits geometric isomerism.
What is the structure of fumaric acid?
C4H4O4Fumaric acid / Formula
Is malic acid cis-isomer?
Maleic acid or cis-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the cis-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans-isomer....Maleic acid.NamesHazard statementsH302 , H315 , H317 , H319 , H33545 more rows
What is the functional group of fumaric acid?
Fumaric Acid or trans-butenedioic acid is the chemical compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. This white crystalline compound is one of two isomeric unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, the other being maleic acid. In fumaric acid the carboxylic acid groups are trans (E) and in maleic acid they are cis (Z).
Does maleic acid show geometrical isomerism?
Maleic acid & fumaric acid show geometrical isomerism. Was this answer helpful?
Is fumaric acid polar or nonpolar?
In maleic acid, both -COOH groups are present on the same side of the double bond. In contrast, two -COOH groups in fumaric acid are present on the opposite sides of the double bond. So, maleic acid is a polar molecule, whereas fumaric acid is a nonpolar molecule due to the absence of dipole moment.
Is maleic acid Monoprotic?
A 0.010M solution of maleic acid, a monoprotic organic acid is 14% ionised.
Which is more stable fumaric or maleic?
Note: The maleic acid or the cis-form of butenedioic acid is less stable than the Fumaric acid or the trans form of butenedioic acid. Maleic acid is soluble in water but Fumaric acid is not soluble in water.
Is fumaric acid optically active?
Constructed in Museum. Maleic and fumaric acids, examples of geometrical isomerism, have identical chemical compositions and a very similar general structure. In 1874, can't Hoff explained the stereoisomerism of the two acids, which are not optically active since the molecules are symmetrical.
Is citric acid a structure?
Citric acid is odorless, sour in taste, and appears as a white crystalline solid....Citric Acid.Chemical Formula of Citric acidC6H8O7Extended Formula of citric acidHOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2Molar Mass / Molecular Weight192.124gmol–1Density of Citric acid1.665gcm–3Boiling Point of Citric acid310°C2 more rows•Mar 14, 2022
What is the Iupac name of fumaric acid?
(E)-Butenedioic acidFumaric acid / IUPAC ID
What is the chemical structure of malonic acid?
C3H4O4Malonic acid / Formula
What is fumaric acid?
Fumaric acid is an acidulant that possesses a fruitlike flavor. It occurs naturally, albeit in limited amounts, in such fruits as papayas, pears, and plums. Fumaric acid has FDA GRAS status in the United States, but its application is not permitted in Europe. In the United States, fumaric acid is used principally in fruit juices, gelatin desserts, tortillas, and pie fillings. It is relatively cheap, but it has the great disadvantage of a stronger taste than citric acid and is difficult to dissolve in water. The solubility of fumaric acid, in fact, is only ∼6 g l −1 (i.e., 0.6%), which is further complicated by the extended times necessary for solubility concentrations to go into solution. For this reason, solubility often is hastened by heating the solvent, which frequently precludes its use for many food industry applications.
How is fumaric acid produced?
Currently, fumaric acid is mainly produced by petroleum-based chemical synthesis. Limited petroleum resources, rising oil prices, and heightened environmental concern of chemical synthesis have prompted interest in the development of bio-based fumaric acid from renewable resources. Filamentous fungal fermentation with Rhizopus spp. can produce fumaric acid from glucose via a reductive tricarboxylic acid (TCA) pathway and was once used in the industry before the rising of the petrochemical industry. However, conventional fumaric acid fermentation is expensive because of its low product yield and productivity. Filamentous fungal fermentation is also difficult to operate because of its morphology. Methods to control cell growth in the pellet form and to immobilize the mycelia in biofilm have been developed to improve fermentation performance. In this article, we provide detailed discussions on fumaric acid producing microorganisms (mainly Rhizopus oryzae ); the metabolic pathway; key enzymes involved in fumaric acid overproduction; fermentation process conditions including substrates, nutrients, and methods to control cell morphology, fermentation pH, and dissolved oxygen; and separation methods for fumaric acid recovery from the fermentation broth. We conclude that future research aiming at understanding the metabolic pathway and regulatory network associated with fumaric acid biosynthesis should pave the way leading to the development of novel strains for the economical production of fumaric acid from biomass.
What is fumarate in the TCA cycle?
Fumarate is the product of succinate oxidation in the TCA cycle, but is also produced through tyrosine breakdown and urea cycle. Like succinate, fumarate inhibits 2OGDD. Fumarate also is involved in a PTM named succination, which is the irreversible formation of S-2-succino-cysteine, resulting from the nonenzymatic reaction of fumarate with cysteine residues. 83 Because it modifies cysteins, succination often targets redox reactive proteins. Succination induced the aberrant activation of Keap1/Nrf2 antioxidant response pathway. Increased succination of many skeletal muscles and adipocyte proteins has been observed in diabetes mice models. 84 Recent works suggest that the succination of ER chaperones could be the link between mitochondrial and ER-stress observed in diabetes. 85
Why was the production of fumaric acid terminated?
The biological production of fumaric acid was terminated when the chemical synthesis became economically more attractive. Fumaric acid is a symmetrical molecule having no isomers and, therefore, the biological process offers no specific advantage over the chemical process.
What is the purpose of DMF?
Fumaric acid esters (FAEs), mixtures of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) and other FAE salts, have been used as oral treatments of psoriasis for decades.31 Administration of FAEs to psoriasis patients with concomitant MS showed relief of the MS symptoms. 32 More recently, DMF, with an enteric coated formulation intended to reduce gastrointestinal side effects, was evaluated as a single compound for the treatment of MS, for which it received marketing approval. 33 In vivo, one of the esters of DMF is hydrolyzed rapidly to give monomethyl fumarate (MMF), which serves as the likely bioactive species. Although not completely understood, the mechanism by which DMF (or MMF as the active moiety) exerts its beneficial effects is thought to involve upregulation of the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) pathway. 34
Where does fumaric acid come from?
Fumaric acid (2-butenedioic acid trans, C 4 H 4 O 4) ( Figure 14) derives its name from the fact that the acid is found in plants that belong to the genus Fumaria, a common European herb. Fumaric acid is the trans -isomer of symmetric, unsaturated dicarboxylic acid; the cis -isomer is maleic acid. It is produced as a colorless, crystalline powder with a fruit-like taste (a fruit acid), and it is a weak acid which forms diesters, has low solubility in water, and it undergoes additions across the double bond.
Does rhizopus have fumarate?
The cytosolic fumarate hydratase (FumR) activity which is present in Rhizopus spp. also increases during the production stage of the fumarate fermentation ( Peleg et al., 1989b ). The role of the latter is, however, still unclear: its overexpression in R. delemar and other fungi resulted in the accumulation of more L-malate than fumarate ( de Jongh and Nielsen, 2008; Xu et al., 2012; Zhang and Yang, 2012 ), which is consistent with the fact that the equilibrium of FumR lies on the side of L-malate ( Meussen et al., 2012 ). It is likely that R. delemar has a specific fumarate transporter which removes fumarate from this equilibrium, but this has not been investigated so far. Interestingly, a transcriptomic and proteomic analysis has recently led to the hypothesis that during nitrogen starvation a substantial part of accumulated fumarate accumulates from the urea cycle due to amino acid catabolism ( Odoni et al., 2017a ). The responsible enzyme – argininosuccinate lyase – is located in the cytosol, and the resulting fumarate therefore needs no further transport step to mix with the rTCA fumarate pool. This offers new strategies for the improvement of fumarate production.
What is fumaric acid?
Fumaric acid (E297 or INS297) is a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid (Fig. 1, Table 2) and used as acidity regulator in food ( Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization, 2017 ). Its low cost and non-toxicity are at the basis of its popularity as a food additive since 1946. Fumaric acid is claimed to be 1.5 times more acid than citric acid. Microbial inactivation studies have shown that fumaric acid can inactivate food-borne pathogens and extend the shelf life of products such as fresh beef ( Tango et al., 2014 ). It is often used as a beverage ingredient, but also finds application in bakery products, powdery dessert mixes and confectionary ( Santini et al., 2012 ). Next to food applications, fumaric acid is used in feed as antibacterial agent and is a well-known chemical that is used in the production of polymers and as intermediate in the production of L-malic and L-aspartic acid. Fumaric acid is predominantly produced by petroleum-based chemical synthesis, but research focusing on microbial fumaric acid production ( e.g. using Rhizopus oryzae) from starchy materials is in the process of optimizing and commercializing this ‘green’ technique ( Xu et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2011; Alonso et al., 2014 ).
Where is fumaric acid found?
Fumaric acid (2-butenedioic acid trans, C 4 H 4 O 4) ( Figure 14) derives its name from the fact that the acid is found in plants that belong to the genus Fumaria, a common European herb . Fumaric acid is the trans -isomer of symmetric, unsaturated dicarboxylic acid; the cis -isomer is maleic acid. It is produced as a colorless, crystalline powder with a fruit-like taste (a fruit acid), and it is a weak acid which forms diesters, has low solubility in water, and it undergoes additions across the double bond.
How is fumaric acid produced?
Currently, fumaric acid is mainly produced by petroleum-based chemical synthesis. Limited petroleum resources, rising oil prices, and heightened environmental concern of chemical synthesis have prompted interest in the development of bio-based fumaric acid from renewable resources. Filamentous fungal fermentation with Rhizopus spp. can produce fumaric acid from glucose via a reductive tricarboxylic acid (TCA) pathway and was once used in the industry before the rising of the petrochemical industry. However, conventional fumaric acid fermentation is expensive because of its low product yield and productivity. Filamentous fungal fermentation is also difficult to operate because of its morphology. Methods to control cell growth in the pellet form and to immobilize the mycelia in biofilm have been developed to improve fermentation performance. In this article, we provide detailed discussions on fumaric acid producing microorganisms (mainly Rhizopus oryzae ); the metabolic pathway; key enzymes involved in fumaric acid overproduction; fermentation process conditions including substrates, nutrients, and methods to control cell morphology, fermentation pH, and dissolved oxygen; and separation methods for fumaric acid recovery from the fermentation broth. We conclude that future research aiming at understanding the metabolic pathway and regulatory network associated with fumaric acid biosynthesis should pave the way leading to the development of novel strains for the economical production of fumaric acid from biomass.
What is the effect of fumaric acid on gelatines?
Fumaric acid increases the gel strength of gelatines and acts as a calcium ion liberator when incorporated in alginate preparations.
What is the purpose of fumaric acid?
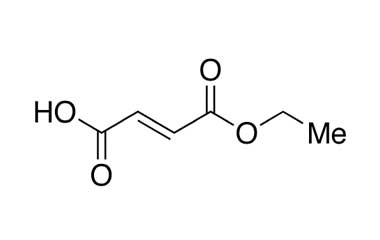
Fumaric acid is used by the pharmaceutical industry to produce alexipharmic sodium dimercaptosuccinate and ferrous fumarate, as an optical bleaching agent, in formulations for alternative medicine or as fumaric acid esters monoethylfumarate and dimethylfumarate to treat psoriasis.
What is the name of the acid that is found in papayas?
Fumaric Acid. Fumaric acid is an acidulant that possesses a fruitlike flavor. It occurs naturally, albeit in limited amounts, in such fruits as papayas, pears, and plums. Fumaric acid has FDA GRAS status in the United States, but its application is not permitted in Europe.
Why was the production of fumaric acid terminated?
The biological production of fumaric acid was terminated when the chemical synthesis became economically more attractive. Fumaric acid is a symmetrical molecule having no isomers and, therefore, the biological process offers no specific advantage over the chemical process.
What is Maleic Acid?
Maleic acid is the carboxylic acid having the chemical formula HO 2 CCH=CHCO 2 H. It is a dicarboxylic acid because it has two carboxylic groups per molecule. It is an isomer of fumaric acid. The molar mass of maleic acid is 116.072 g/mol. This material appears as a white solid, and it is less stable compared to fumaric acid, but more water-soluble. Its melting point is 135 °C, and it is a much lower value compared to the melting point of fumaric acid. Above this temperature, the compound decomposes. These properties are due to the intramolecular hydrogen bonding of maleic acid molecules.
How is maleic acid produced?
In the industrial scale, we produce maleic acid via hydrolysis of maleic anhydride. We can also produce it using the oxidation of benzene or butane.
What is the difference between maleic acid and fumaric acid?
The key difference between maleic acid and fumaric acid is that maleic acid is the cis-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans-isomer. Maleic acid and fumaric acid are carboxylic acids. They are cis-trans isomers of each other. Both these compounds have two carboxylic acid groups per molecule.
What is the melting point of fumaric acid?
The melting point is 287 °C, and upon further heating, the compound decomposes. Besides, we can produce fumaric acid via catalytic isomerization of maleic acid at low pH. Also, this is done in an aqueous solution.
What is Madhu's degree?
Madhu is a graduate in Biological Sciences with BSc (Honours) Degree and currently persuing a Masters Degree in Industrial and Environmental Chemistry. With a mind rooted firmly to basic principals of chemistry and passion for ever evolving field of industrial chemistry, she is keenly interested to be a true companion for those who seek knowledge in the subject of chemistry.
Is maleic acid a carboxylic acid?
Both maleic acid and fumaric acid are carboxylic acids. Moreover, they are cis-trans isomers of each other. The key difference between maleic acid and fumaric acid is that maleic acid is the cis-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans-isomer.
Is maleic acid stronger than fumaric acid?
Moreover, maleic acid forms weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds and has a much lower melting point than fumaric acid. It is because the intramolecular hydrogen bonds in fumaric acid are much stronger due to the trans geometry. Below infographic provides more details on the difference between maleic acid and fumaric acid.
What type of isomerism is observed in but-2-ene?
The presence of a double or triple bond restricts the bond rotation within a molecule, which can lead to cis-trans iso merism. This type of isomerism can be observed in the organic compound but-2-ene.
Which complexes have cis-trans isomerism?
Many diazenes and diphosphenes are known to have cis-trans isomers. Coordination complexes having square planar or octahedral geometries also display cis-trans isomerism based on the position of the ligands. The isomers of the coordination compound Pt (NH 3) 2 Cl 2 are illustrated below.
What is the difference between cis and trans isomers?
Cis-trans isomers exhibit a type of stereoisomerism where the atoms have different spatial arrangements in three-dimensional space. In the field of organic chemistry, cis isomers contain functional groups on the same side of the carbon chain whereas the functional groups are on opposite sides in trans isomers.
Where are similar ligands positioned in the cis isomer?
It can be observed that similar ligands are positioned near each other in the cis isomer, but they are positioned on opposite sides in the corresponding trans isomer. To learn about cis-trans isomers and other types of isomerism, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
Is butenedioic acid a trans isomer?
The cis and trans isomers of butenedioic acid display very different reactivities, which can be attributed to the difference in their properties. Maleic acid is the cis isomer and fumaric acid is the trans isomer. Elaidic acid and oleic acid are cis-trans isomers.
Is oleic acid a solid?
Elaidic acid and oleic acid are cis-trans isomers. The former is solid at room temperature (melting point = 43 o C) and the latter is found to be liquid, with a melting point of 13.4 o
Do trans isomers have lower solubility?
They also tend to have lower solubility in solvents that are inert in nature. It has been suggested that the densities of trans isomers tend to be lower than that of cis isomers. Generally, it can be observed that the individual bond dipole moments in trans isomers cancel each other out since they are on opposite sides.
