What happens when two disaccharides are linked together?
Disaccharides. So when this happens individual monosaccharides link together to make an acetal. This linkage is known as glycosidic linkage. This linkage is an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. When two monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic linkage the resulting product is a disaccharide.
What is a disaccharide made of?
Disaccharides (C 12 H 22 O 11) are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the OH group of a second monosaccharide.
What are the key points of a disaccharide?
Key Points. A disaccharide is a sugar (a type of carbohydrate) made by linking together two monosaccharides. A dehydration reaction forms a disaccharide. One molecule of water is removed for each linkage formed between the monosaccharide subunits.
What type of linkage is present in sucrose?
The sucrose molecule is unique among the common disaccharides in having an α-1,β-2-glycosidic (head-to-head) linkage. Because this glycosidic linkage is formed by the OH group on the anomeric carbon of α-D-glucose and the OH group on the anomeric carbon of β-D-fructose, it ties up the anomeric carbons of both glucose and fructose.

What is the linkage of a disaccharide?
Disaccharides (C12H22O11) are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage.
What type of bond is formed between two sugars in a disaccharide?
What type of bond is formed between two sugars in a disaccharide? Glycosidic linkage.
What type of linkage is sucrose?
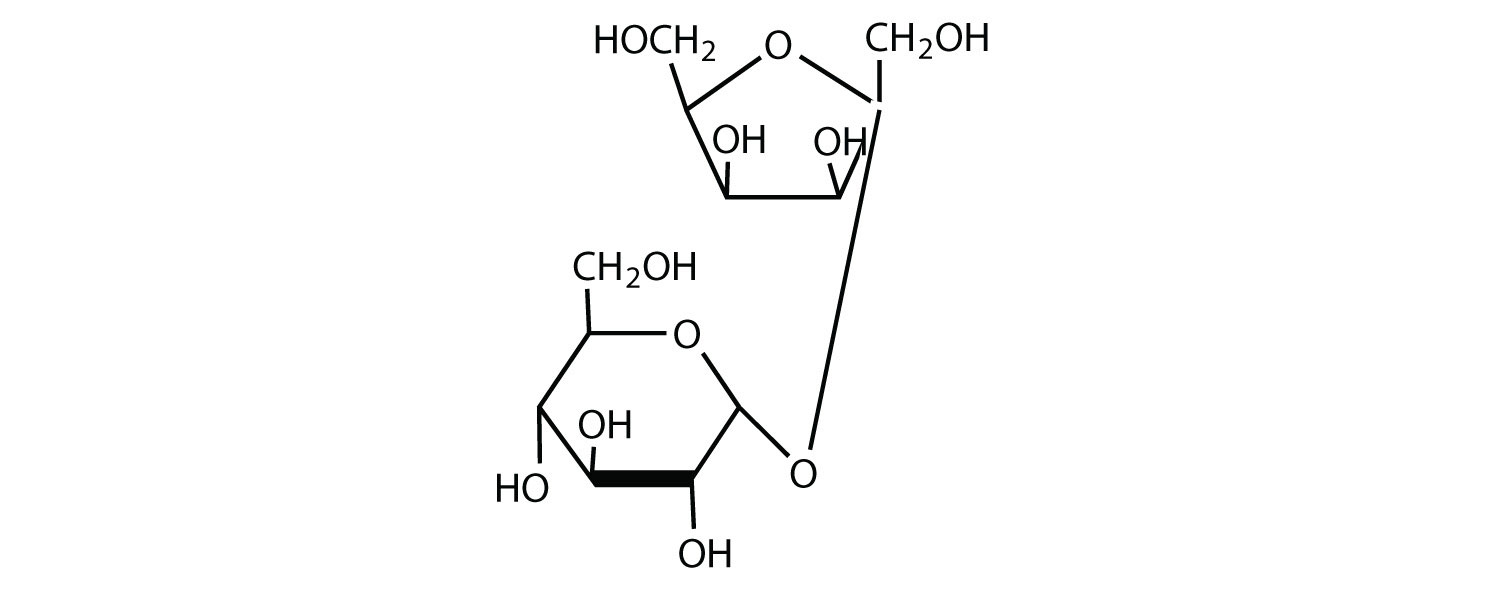
Sucrose is composed of a molecule of glucose joined to a molecule of fructose by an α-1,β-2-glycosidic linkage. It is a nonreducing sugar that is found in sugar cane and sugar beets.
Which disaccharide has an alpha linkage?
sucrose moleculeThe sucrose molecule is unique among the common disaccharides in having an α-1,β-2-glycosidic (head-to-head) linkage.
What are disaccharides made of?
two monosaccharide unitsDisaccharides. Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units, linked together with glycosidic bonds in the α or β orientation. The most important of them are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
What is N glycosidic linkage?
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Where are glycosidic linkages found?
Glycosidic linkage is a structure found in tea, sugar, mushrooms, plants, DNA, and other living organisms. Only sugars with the cyclic forms have an anomeric carbon and are capable of forming a glycosidic link. An anomeric carbon can be identified as the carbonyl carbon in the open-chain form of sugar.
What are disaccharides?
A disaccharide, also called a double sugar, is a molecule formed by two monosaccharides, or simple sugars. Three common disaccharides are sucrose, maltose, and lactose.
How is a disaccharide formed?
Disaccharides are formed by joining pairs of various monosaccharides via α- or β-glycosidic bonds. A hemiacetal hydroxyl group formed from the oxygen of the carbonyl group (−C=O) always participates in the formation of these bonds. In certain cases, all the carbonyl groups in the molecule are used.
What is α and β glycosidic bond?
An α-glycosidic bond for a D-sugar emanates below the plane of the sugar while the hydroxyl (or other substituent group) on the other carbon points above the plane (opposite configuration), while a β-glycosidic bond emanates above that plane (the same configuration).
What is alpha linkage and beta linkage?
There are are two types of glycosidic bonds - 1,4 alpha and 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds. 1,4 alpha glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring; while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
What is an alpha linkage?
1:412:34What is a Glycosidic bond? Difference between alpha and beta ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIn short in alpha 1-4 glycosidic linkage. The Oh H group in the first anomeric carbon is below theMoreIn short in alpha 1-4 glycosidic linkage. The Oh H group in the first anomeric carbon is below the plane whereas in beta 1-4 glycosidic linkage.
What are the types of glycosidic bonds?
There are are two types of glycosidic bonds - 1,4 alpha and 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds. 1,4 alpha glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring; while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
What type of glycosidic bond is found in the disaccharide Sophorose?
sophorose (CHEBI:1230) A glycosylglucose that is D-glucopyranose attached to a β-D-glucopyranosyl unit at position 2 via a glycosidic linkage.
What type of bond holds two monosaccharides together?
Carbohydrates are made up of monosaccharides linked together into polysaccharide chains by a type of covalent bond known as a glycosidic bond. These glycosidic bonds are formed in a dehydration synthesis reaction.
How a disaccharide is formed?
Disaccharides are formed by joining pairs of various monosaccharides via α- or β-glycosidic bonds. A hemiacetal hydroxyl group formed from the oxygen of the carbonyl group (−C=O) always participates in the formation of these bonds. In certain cases, all the carbonyl groups in the molecule are used.
What is the General Formula of Carbohydrates?
The general formula for carbohydrates is Cx(H2O)y. Carbohydrates (or sugars) were originally believed to be “hydrates of carbon,” because they hav...
What is the molecular formula of the most common disaccharide?
Disaccharides are the carbohydrates that on hydrolysis gives two same or different carbohydrates. Their general formula is C12H22O11.
What Is Maltose?
Maltose which is also known as a disaccharide made up of two alpha D glucose unit. The two-unit of glucose are linked with an alpha 1,4 glycosidic...
Is maltose a monosaccharide or disaccharide?
Maltose is a disaccharide.
Does maltose give Fehling’s test?
Yes, maltose gives a positive Fehling’s test.
What are Disaccharides?
Disaccharides are those carbohydrates that on hydrolysis with acids or enzymes give two molecules of monosaccharides which can either be the same or different.
What is the structure of a disaccharide?
Structure of Disaccharides (Sucrose) The most common disaccharide is sucrose which gives D - (+)- glucose and D- (-)- fructose on hydrolysis. Both the monosaccharides i.e. glucose and fructose are connected through the glycosidic linkage between alpha glucose and second carbon beta fructose. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar as both ...
What are some examples of disaccharides?
Examples of Disaccharides. 1. Sucrose. Sucrose being dextrorotatory in nature gives dextrorotatory glucose as well as laevorotatory fructose on hydrolysis. The overall mixture is laevorotatory and this is because the laevorotation of fructose (-92.4) is more than the dextrorotation of glucose (+52.5). 2.
What is the name of the sugar that is produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution?
In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows reducing properties. 3. Lactose. Commonly it is called milk sugar as this disaccharide is found in milk.
Which disaccharide has two -D-glucose units?
Maltose. Maltose is also one of the disaccharides which have two α -D-glucose units which are connected by the first carbon of the glucose and also linked to the fourth carbon of another glucose unit. In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows ...
Where is glucosamine found?
It comprises two glucosamine molecules which are linked. It is seen in some bacteria, exoskeletons of insects and is also found in fish, octopus, and squid.
What is the name of the linkage between monosaccharides?
So when this happens individual monosaccharides link together to make an acetal. This linkage is known as glycosidic linkage . This linkage is an oxide linkage formed by the loss of a water molecule. When two monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic linkage the resulting product is a disaccharide.
What are the two molecules that form a disaccharide?
Disaccharides. Disaccharides are sugars ( carbohydrate molecules) that form when two simple sugars i.e. monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide. Learn about Monosaccharides in more detail here. Cyclic monosaccharides react with alcohols to form acetals and ketals. Sometimes this alcohol is actually a carbohydrate since they function very ...
What is the chemical formula of sucrose?
Let us take a look at some chemical properties of sucrose. The molecular formula of sucrose is C12H22O11. If sucrose goes through acid catalysed hydrolysis it will give one mole of D-Glucose and one mole of D-Fructose. The chemical structure of sucrose comprises of α form of glucose and β form of fructose. The glycosidic linkage is α linkage ...
How to prove the structural formula of sucrose?
We can prove the structural formula of sucrose by hydrolysing it with α-glycosidase enzymes which only hydrolyses α glucose. This test is positive for sucrose.
Is maltose a monosaccharide?
Maltose is another disaccharide commonly found. It has two monosaccharide glucose molecules bound together, The link is between the first carbon atom of glucose and the fourth carbon of another glucose molecule. This, as you know, is the one-four glycosidic linkage. Let us look at a few of its properties
Is lactose a sugar?
Also from the structure, we can notice that lactose is a reacting sugar since it has one free hemiacetal hydroxide. So when we react Lactose with bromine water it will give monocarboxylic acid.
Is maltose a glycosidic linkage?
This, as you know, is the one-four glycosidic linkage. Let us look at a few of its properties. On acid catalysed hydrolysis one mole of maltose gives two moles of D-glucose. Maltose has a free hemiacetal hydroxide, hence it undergoes mutarotation. It exists as both α-Maltose and also β-Maltose.
What is a disaccharide?
A disaccharide is a sugar (a type of carbohydrate) made by linking together two monosaccharides. A dehydration reaction forms a disaccharide. One molecule of water is removed for each linkage formed between the monosaccharide subunits. Both natural and artificial disaccharides are known. Examples of common disaccharides include sucrose, maltose, ...
What are the different types of disaccharides?
Here is a list of some disaccharides, including the monosaccharides they are made from and foods containing them. Sucrose, maltose, and lactose are the most familiar disaccharides, but there are others.
What is glucose and glucose#N#Trehalose?
glucose + glucose#N#Trehalose is also known as tremalose or mycose. It is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide with extremely high water retention properties. In nature, it helps plants and animals reduce long periods without water.
What is the name of the hydrolysis product of cellulose?
glucose + glucose. Cellobiose is a hydrolysis product of cellulose or cellulose-rich materials, such as paper or cotton. It is formed by linking two beta-glucose molecules by a β (1→4) bond.
Why is lactose intolerant?
As humans age, lactose becomes less-tolerated. This is because lactose digestion requires the enyzme lactase. People who are lactose intolerant can take a lactase supplement to reduce bloating, cramping, nausea, and diarrhea. 3
What type of bond is formed between hydroxyl groups?
A glycosidic bond can form between any hydroxyl group on the monosaccharide, so even if the two subunits are the same sugar, there are many different combinations of bonds and stereochemistry, producing disaccharides with unique properties. Depending on the component sugars, disaccharides may be sweet, sticky, water-soluble, or crystalline.
Is sucrose a carbohydrate?
In the human body and in other animals, sucrose is digested and broken into its component simple sugars for quick energy. Excess sucrose can be converted from a carbohydrate into a lipid for storage as fat. Sucrose has a sweet flavor.
What are the three common disaccharides?
There are three common disaccharides: maltose, lactose, and sucrose. All three are white crystalline solids at room temperature and are soluble in water. We’ll consider each sugar in more detail.
What is the link between the C1 of one sugar and one of the hydroxyl groups of a second sugar?
identify disaccharides as compounds consisting of two monosaccharide units joined by a glycoside link between the C1 of one sugar and one of the hydroxyl groups of a second sugar.
How is maltose linked to aldehyde?
Maltose is a reducing sugar. Thus, its two glucose molecules must be linked in such a way as to leave one anomeric carbon that can open to form an aldehyde group. The glucose units in maltose are joined in a head-to-tail fashion through an α-linkage from the first carbon atom of one glucose molecule to the fourth carbon atom of the second glucose molecule (that is, an α-1,4-glycosidic linkage; see Figure 1). The bond from the anomeric carbon of the first monosaccharide unit is directed downward, which is why this is known as an α-glycosidic linkage. The OH group on the anomeric carbon of the second glucose can be in either the α or the β position, as shown in Figure 1.
How do monosaccharides form a cyclic structure?
Previously, you learned that monosaccharides can form cyclic structures by the reaction of the carbonyl group with an OH group , resulting in an cyclic hemiacetal (or hemiketal for ketoses). In the same way that hemiacetals and ketals can react with an additional alcohol forming acetals and ketals, these cyclic monosaccahrides can in turn react with another alcohol molecule. In the case of disaccharides, one monosaccharide acts a the hemiacetal while the other monosaccharides acts as the alcohol. The formation of an acetal (or ketal) bond between two monosaccharides is called a glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage . Therefore, disaccharides are sugars composed of two monosaccharide units that are joined by a carbon–oxygen-carbon linkage known as a glycosidic linkage. This linkage is formed from the reaction of the anomeric carbon of one cyclic monosaccharide with the OH group of a second monosaccharide.
How does lactose intolerance affect the colon?
In people with lactose intolerance, some of the unhydrolyzed lactose passes into the colon, where it tends to draw water from the interstitial fluid into the intestinal lumen by osmosis. At the same time, intestinal bacteria may act on the lactose to produce organic acids and gases. The buildup of water and bacterial decay products leads to abdominal distention, cramps, and diarrhea, which are symptoms of the condition.
Why is lactose sugar called milk sugar?
Lactose is known as milk sugar because it occurs in the milk of humans, cows, and other mammals. In fact, the natural synthesis of lactose occurs only in mammary tissue, whereas most other carbohydrates are plant products. Human milk contains about 7.5% lactose, and cow’s milk contains about 4.5%. This sugar is one of the lowest ranking in terms of sweetness, being about one-sixth as sweet as sucrose. Lactose is produced commercially from whey, a by-product in the manufacture of cheese. It is important as an infant food and in the production of penicillin.
Why is milk sour?
A more serious problem is the genetic disease galactosemia, which results from the absence of an enzyme needed to convert galactose to glucose. Certain bacteria can metabolize lactose, forming lactic acid as one of the products. This reaction is responsible for the “souring” of milk.