
What is dialysis tubing?
What is Dialysis Tubing? Dialysis tubing is a semi-permeable membrane, usually made of cellulose acetate. It is used in dialysis, a process which involves the removal of very small molecular weight solutes from a solution, along with equilibrating the solution in a new buffer.
What type of membrane is dialysis membrane?
A dialysis membrane is a semi-permeable film (usually a sheet of regenerated cellulose) containing various sized pores. Molecules larger than the pores cannot pass through the membrane but small molecules can do so freely. What type of membrane does dialysis tubing represent?
What is the pore size of dialysis membrane?
History, properties and composition. Thus, a dialysis membrane with a 10K MWCO will generally retain >90% of a protein having a molecular mass of at least 10 kDa. Pore sizes typically range from ~10-100 Angstroms for 1K to 50K MWCO membranes.
What is biotech grade dialysis tubing made of?
Biotech Grade Dialysis Tubing is available in 2 cellulosic polymer types: Cellulose Ester (CE) and Regenerated Cellulose (RC) OMW! With XCell
What type of membrane is used in dialysis?
There are three types of membranes currently used to manufacture dialyzers: cellulose, substituted cellulose, and synthetic noncellulose. Cellulose — Cellulose, primarily manufactured as cuprophan (or cuprophane), is a polysaccharide-based membrane obtained from pressed cotton.
Are the membranes in dialysis machines permeable or impermeable?
Inside the dialysis device, the blood flows through small tubes. These are made of semipermeable membranes and are surrounded by dialysis fluid. The dialysis fluid flows in the opposite direction to the blood.
How is dialysis tubing like a cell membrane?
Like the plasma membrane, dialysis tubing is a type of selectively permeable membrane. Microscopic holes, or pores, in the dialysis tubing allow substances to be separated on the basis of their size. Molecules smaller than the pores pass freely across the tubing while larger molecules are trapped inside (or outside).
Why the dialysis tubing membrane is a selectively permeable membrane?
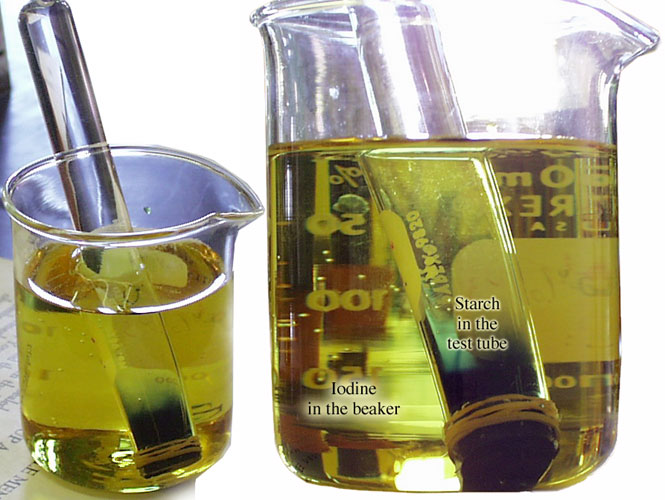
The dialysis tubing is selectively permeable because substances such as water, glucose, and iodine were able to pass through the tubing but the starch molecule was too large to pass.
Is dialysis tubing semi-permeable?
The dialysis tubing is a semipermeable membrane. Water molecules can pass through the membrane. The salt ions can not pass through the membrane.
Does dialysis use diffusion or osmosis?
Small waste products in your blood flow through the membrane/filter and into the dialysate. The three principles that make dialysis work are diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration.
Why is dialysis tubing not a true cell membrane?
A biological membrane is composed of phospholipid bilayer, while the dialysis tubing is composed of cellulose.
How is dialysis tubing functionally different from a cellular membrane?
How is the dialysis tubing functionally different from a cellular membrane? The tubing only allows passive transport while a cellular membrane uses active transport as well.
Is a semipermeable membrane?
A semipermeable membrane is a barrier that will only allow some molecules to pass through while blocking the passage of other molecules. A semipermeable barrier essentially acts as a filter. Different types of semipermeable membranes can block out different sized molecules.
What is selective permeability of cell membrane?
Selective permeability of the cell membrane refers to its ability to differentiate between different types of molecules, only allowing some molecules through while blocking others.
What do you mean by a selectively permeable membrane?
Selectively permeable membrane is the one which allows entry of certain substances, exit of some substances but prevents the passage of other substances, through it.
What is special about the dialysis tube?
Dialysis tubing is a semi-permeable membrane, usually made of cellulose acetate. It is used in dialysis, a process which involves the removal of very small molecular weight solutes from a solution, along with equilibrating the solution in a new buffer. This can also be useful for concentrating a dilute solution.
Are artificial membranes in dialysis permeable?
So, semipermeable membranes are used as the filter in dialysis treatments. Waste passes through semipermeable membranes in the dialyzer and gets removed from the blood.
What can pass through a dialysis membrane?
The dialysis membrane is one of the critical components that determine dialysis performance. These membranes allow only low-molecular-weight molecules, such as sodium, potassium, urea, and creatinine, to pass through while blocking proteins, such as albumin, and other larger molecules.
How does a dialysis membrane work?
How dialysis membranes work. A dialysis membrane is a semi-permeable film (usually a sheet of regenerated cellulose) containing various sized pores. Molecules larger than the pores cannot pass through the membrane but small molecules can do so freely.
What is the most biocompatible dialyzer membrane?
Unmodified cellulose membranes, such as cuprophan, are relatively inexpensive but also the most bioincompatible. The modified cellulose membranes (such as those made of cellulose acetate or hemophan) have some or all of the hydroxyl groups esterified to make them more biocompatible.
What is dialysis tubing made of?
Dialysis tubing for laboratory use is typically made of a film of regenerated cellulose or cellulose ester. However; dialysis membranes made of polysulfone, polyethersulfone (PES), etched polycarbonate, or collagen are also extensively used for specific medical, food, or water treatment applications.
What is the MWCO of a dialysis tubing?
Different dialysis tubing or flat membranes are produced and characterized as differing molecular-weight cutoffs (MWCO) ranging from 1–1,000,000 kDa. The MWCO determination is the result of the number and average size of the pores created during the production of the dialysis membrane. The MWCO typically refers to the smallest average molecular mass of a standard molecule that will not effectively diffuse across the membrane upon extended dialysis. Thus, a dialysis membrane with a 10K MWCO will generally retain >90% of a protein having a molecular mass of at least 10 kDa. Pore sizes typically range from ~10–100 Angstroms for 1K to 50K MWCO membranes.
What is dialysis used for?
For information on the use of dialysis as a treatment for kidney or liver failure see, dialysis or liver dialysis. For information on dialysis or reverse osmosis usage in water treatment see, reverse osmosis. For additional information on laboratory dialysis see Dialysis (biochemistry).
When was dialysis first used?
The term dialysis was first routinely used for scientific or medical purposes in the late 1800s and early 1900s , pioneered by the work of Thomas Graham.
How are cellulose membranes made?
Membranes, composed of either regenerated cellulose or cellulose esters, are manufactured through distinct processes of modifying and cross-linking cellulose fibers (derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers) to form films with differing properties and pore sizes. Variations in the manufacturing process significantly change the properties and pore sizes of the films; depending on the cross-linkages introduced in cellulose, the size of pores can be modulated. While similar in composition, most of the cellulose-based membranes currently manufactured are not necessarily useful for dialysis. Cellulose-based membranes are also widely used for applications ranging from food wrapping, film stock, or “plastic” wrap.
